Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
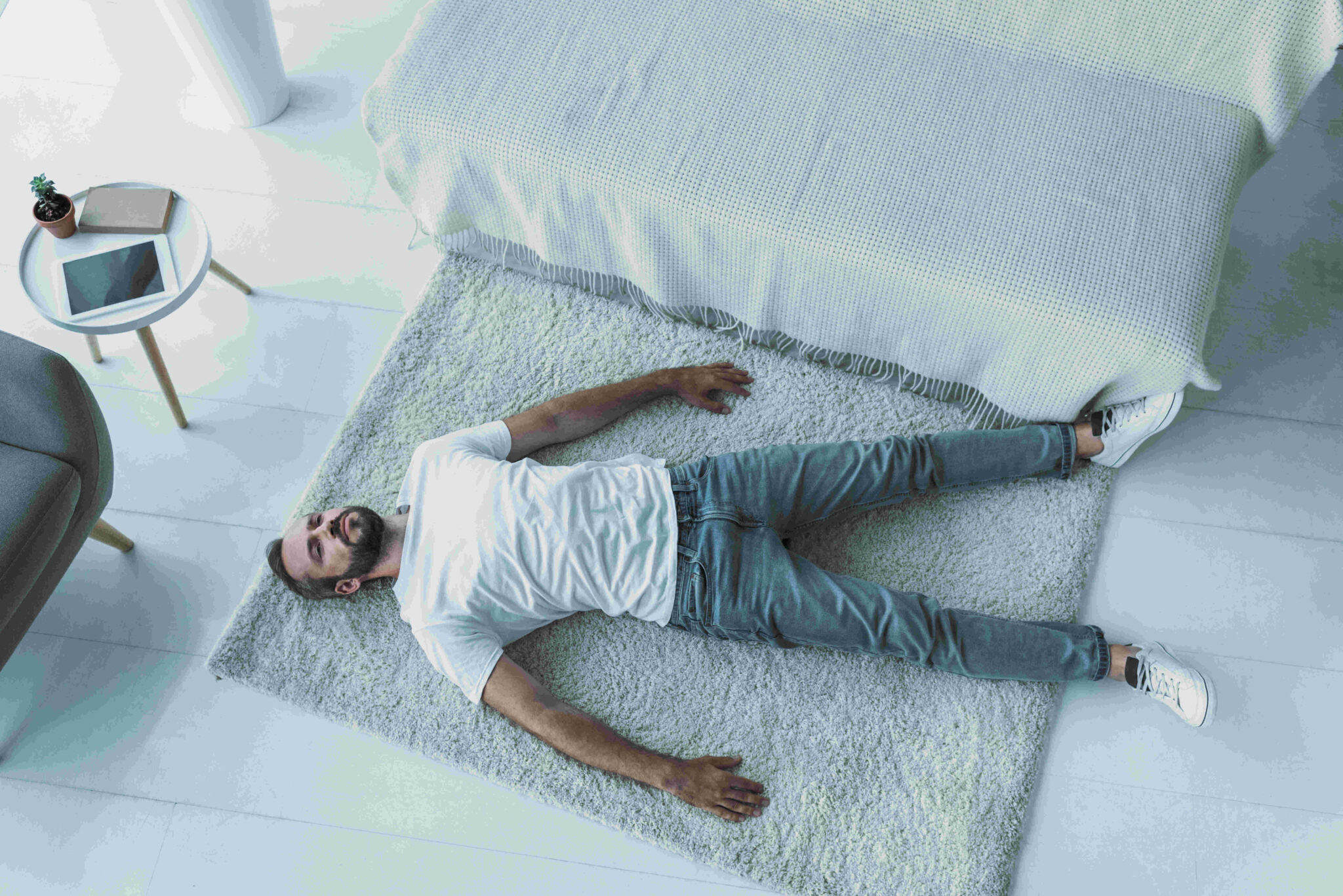
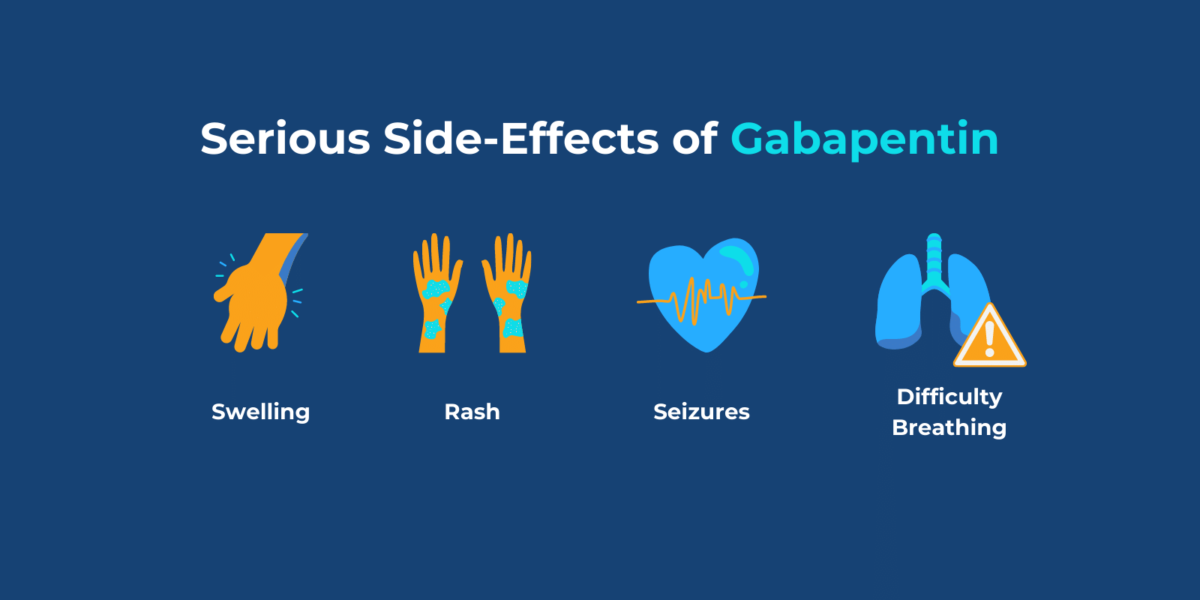
View lamotrigine information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding and important safety information. View apixaban information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, contra-indications and monitoring requirements. Though gabapentin may be safer than opioids, it’s not without risks of overdose, withdrawal, abuse, and addiction. Between 2019 and 2020, gabapentin has been implicated in about one in 10 overdose deaths – and ruled as the direct cause of death in over half of those cases. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose are drowsiness, fast heartbeat, dizziness, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, lethargy, coma, and death may occur. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin is a medication often prescribed for anxiety, nerve pain, and seizures. However, it can be addictive and lead to overdose. Learn more here. Pregabalin and Gabapentin Pregabalin is commonly used for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Overdose leads predominately to CNS effects. Management is supportive. Anyone who shows signs of an overdose or allergic reaction to gabapentin should contact emergency medical services immediately. Left untreated, these symptoms can turn fatal. View pregabalin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin overdoses can be dangerous, especially when it’s used alongside other substances. Learn how to avoid a gabapentin overdose and what to do about one. View duloxetine information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, important safety information and drug action. Explore Gabapentin (Neurontin): comprehensive information on uses, dosage guidelines, potential side effects, and overdose risks. Learn about pill forms, pricing, and generic alternatives for this medication. Gabapentin is licensed for treatment of partial seizures and for peripheral neuropathic pain. Whilst it is recognised that gabapentinoids can be useful medications, there is a significant risk of potential misuse and subsequent harm. View amitriptyline hydrochloride information, including dose, uses, side-effects, pregnancy, breast feeding and contra-indications. For years our patient tolerated 4,800mg daily, became critically ill after an overdose of approximately 24,000 mg, and finally was briefly encephalopathic after 7,500mg. Although further prescribing is banned by marking her EMR as “allergic”, we hope to alert others of the potential for serious GBP-induced toxicity. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. This treatment summary topic describes poisoning, emergency treatment
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |