Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
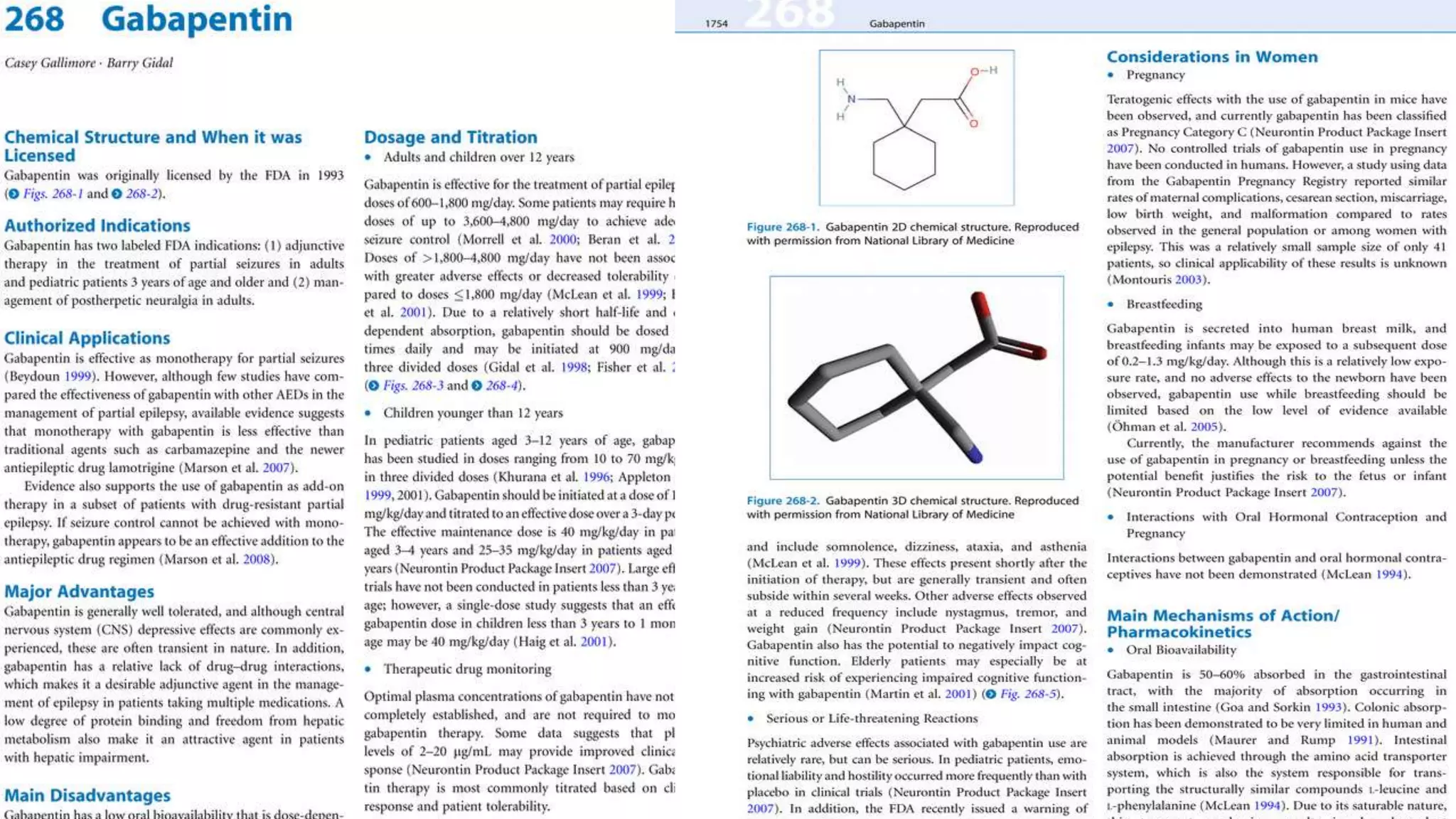
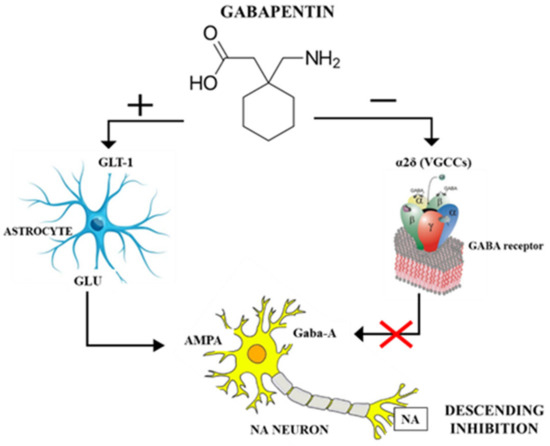
Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. Gabapentin Trade Name: Neurontin ® Drug Class: Antiepileptic & treatment of neuropathic pain 12.1 Mechanism of Action - The precise mechanisms by which gabapentin produces its analgesic and antiepileptic actions are unknown. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter General Description Gabapentin is an analgesic medication commonly used for neuropathic pain. It exerts its effects through various mechanisms of action, including the inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) and disruption of α2δ-1-NMDAR complexes. By reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and blocking synaptogenesis, gabapentin helps alleviate neuropathic pain. It Gabarone package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific bindin Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. The new antiepileptic medications are prescribed for the treatment of patients with seizure disorders since 17 years ago. Gabapentin (GBP) was approved on January 1994 as adjunctive treatment in patients 12 years or older with partial seizures, with Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. Find detailed information on Gabapentin including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half-life, administration, and more. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gaba Summary Although its exact mode of action is not known, gabapentin appears to have a unique effect on voltage-dependent calcium ion channels at the postsynaptic dorsal horns and may, therefore, inter Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral capsule. Gabapentin has also been shown to induce modulate other targets including transient receptor potential channels, NMDA receptors, protein kinase C and inflammatory cytokines. It may also act on supra-spinal region to stimulate noradrenaline mediated descending inhibition, which contributes to its anti-hypersensitivity action in neuropathic pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin) FDA-approved indications and off-label uses; gabapentin withdrawal and abuse potential; mechanism of action; how long it takes for gabapentin to start working. Gabapentin mechanism of action Researchers know that gabapentin operates on neurotransmitters and traverses the blood-brain barrier readily, but the specific mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unclear. A cyclohexyl group is attached to the molecular structure of the neurotransmitter GABA in gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse Learn how gabapentin works by binding calcium channel subunits. Full MOA, uses, MCQs, FAQs, and pharmacology inside.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |