Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
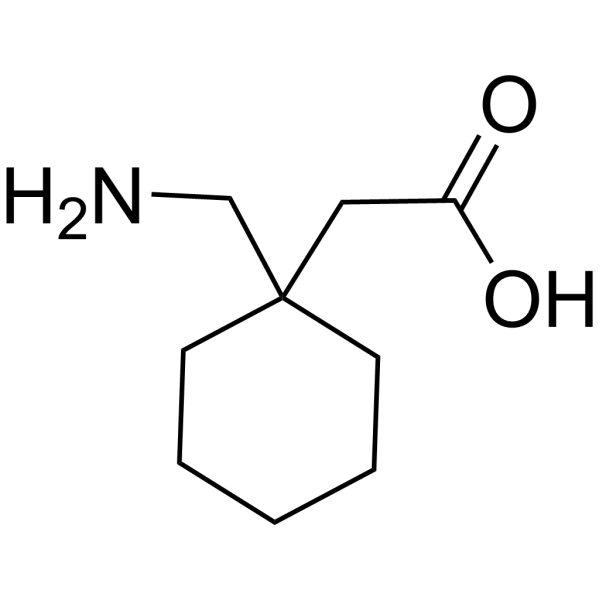 |  |
The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic prof Pharmacodynamics Mechanisms of action Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Pharmacology of Gabapentin Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication primarily used to prevent and control seizures and certain kinds of neuropathic pain, such as nerve pain after shingles and diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic Gabapentin is regarded as safe and tolerable with a promising pharmacokinetic profile and an extensive therapeutic index. 10 Also, gabapentin have been approved in Japan as adjunctive drug therapy for medically intractable seizures. 4 Gabapentin is a compound produced by addition of a cyclohexyl group to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (McLean 1995). From: Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 1998 Gabapentin has been clearly demonstrated to be effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain in diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. This evidence, combined with its favourable side-effect profile in various patient groups (including the elderly) and lack of drug interactions, makes it an attractive agent. The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles can have implications for clinical practice. This article has summarised these key differences. In addition to their use in managing ne Gabapentin is a structurally related to GABA that modulates the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. It is used for various indications, such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, restless legs syndrome, and postoperative pain. Learn how gabapentin works by binding calcium channel subunits. Full MOA, uses, MCQs, FAQs, and pharmacology inside. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration’s approved indications for prescription of gabapentinoids are refractory focal epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Use of gabapentinoids outside of the approved indications is common, but evidence for this Gabapentin is especially effective at relieving allodynia and hyperalgesia in animal models. It has been shown to be efficacious in numerous small clinical studies and case reports in a wide Several hypotheses of cellular mechanisms have been proposed to explain the pharmacology of gabapentin: 1. Gabapentin crosses several membrane barriers in the body via a specific amino acid transporter (system L) and competes with leucine, isoleucine, valine and phenylalanine for transport. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |