Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
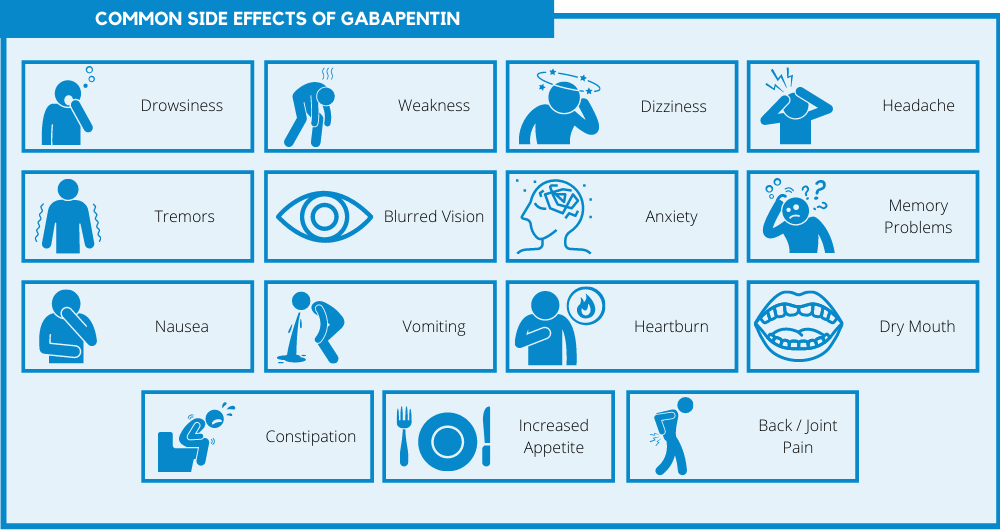
This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. More clinical trials with larger patient populations are needed to support gabapentin's off-label use in psychiatric disorders and substance use disorders. It is worth noting that numerous clinical studies that are discussed in this review are open-label trials, which are inherently less rigorously analyzed. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Objective: This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research: An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder Systematic reviews of gabapentin treatment in psychiatric and/or substance use disorders showed inconclusive evidence for efficacy in BD, but possible efficacy for some anxiety disorders [9, 10]. This article examines the role of gabapentin in antipsychotic treatment, discussing its effectiveness, potential side effects, and how it can be used in conjunction with other medications to manage symptoms of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. Objective: Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. More clinical trials with larger patient populations are needed to support gabapentin’s off-label use in psychiatric disorders and substance use disorders. It is worth noting that numerous clinical studies that are discussed in this review are open-label trials, which are inherently less rigorously analyzed. Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. But since it’s been available, gabapentin has also been used off-label in psychiatry to treat patients with treatment-resistant mood and anxiety disorders as well as alcohol-withdrawal and Objective: Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system de-pressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Gabapentin gained FDA approval in 1993 under the brand name Neurontin as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, and subsequently for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults in 2002. It became available as a generic in 2004. In this nationally representative sample, <1% of outpatient gabapentin use was for approved indications. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid This study examined off-label use of gabapentin for psychiatric indications and its concomitant use with CNS-D prescription drugs in a nationally representative sample of ambulatory care office visits.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |