Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
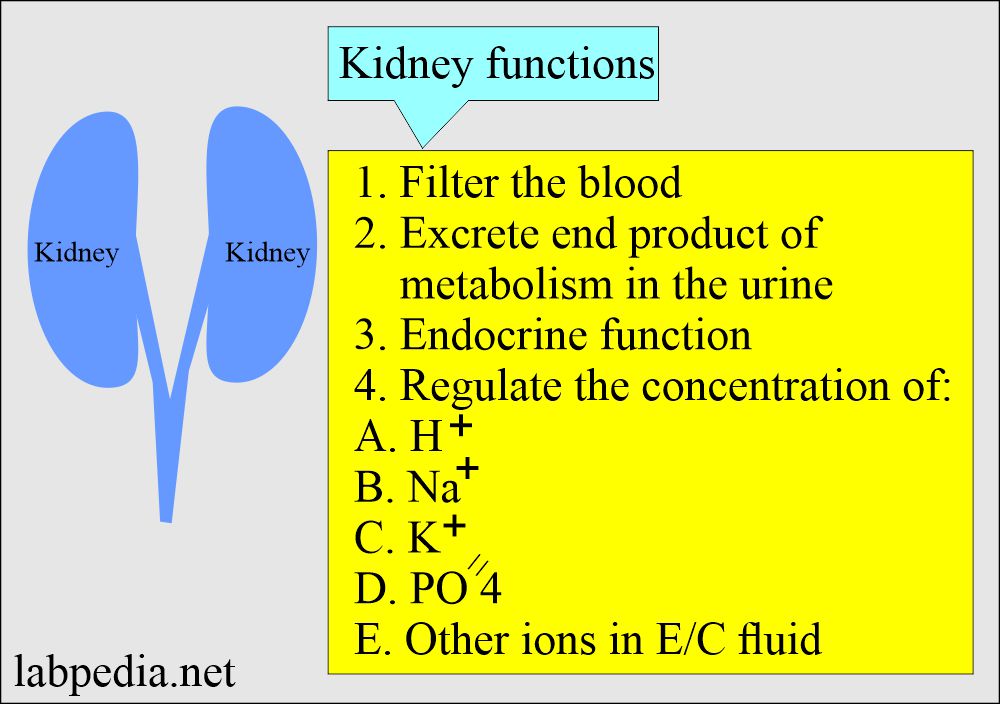 |  |
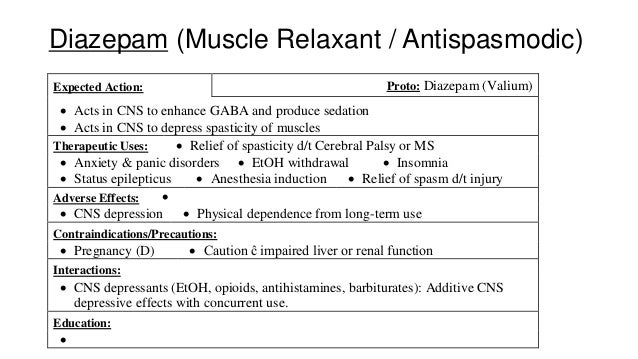
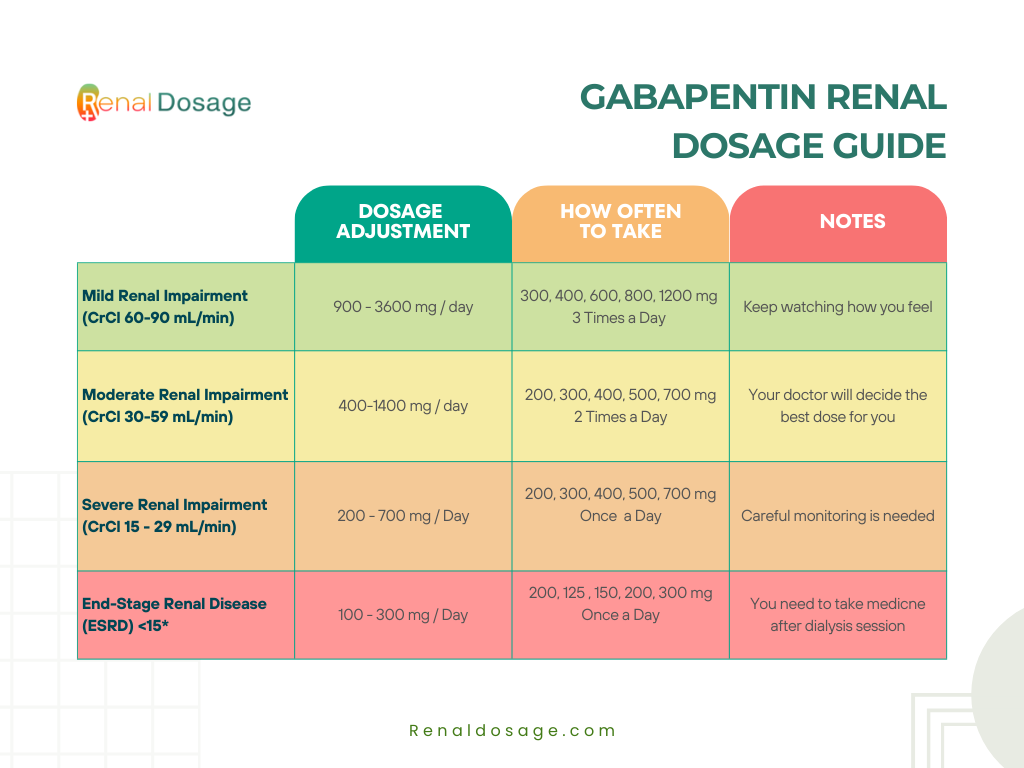
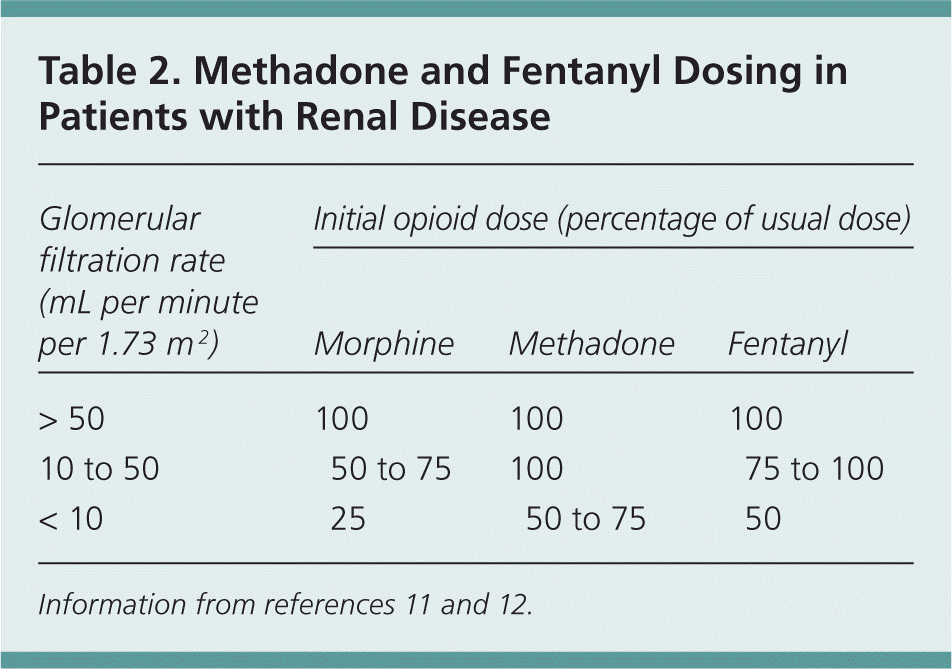
Gabapentin is a medication used to manage nerve pain (e.g., postherpetic neuralgia), restless leg syndrome, and seizures. Available as gabapentin capsules or extended-release tablets, it calms overactive nerves. Gabapentin Effects on Kidneys | Is Gabapentin Bad for Your Kidneys? In this video we talk about Gabapentin effects on kidneys. The question we’re getting a lot is, Is gabapentin bad for kidney disease? Now, gabapentin is a medication used for diabetic neuropathy or neuropathy or any type of nerve pain. It is also used for seizures, but it’s given to a lot in people that have diabetic Gabapentin can also be used in patients with renal function below 20 mg/dl (although a dosing adjustment is needed). A 2018 clinical review examined gabapentin and other drugs as anti-craving therapy in alcohol use disorder. Studies have shown that gabapentin toxicity can occur in patients with chronic kidney disease, particularly in those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities 4, 5. Dose Adjustment and Renal Function Dose adjustment of gabapentin is crucial in patients with decreased renal function to prevent toxicity 4, 5. Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis Gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body solely by the kidney, and pharmacokinetic studies show a stepwise prolongation in the elimination half-life of gabapentin and pregabalin as kidney function declines. 9,10 Gabapentinoids should therefore be started at lower doses in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD; guidelines are summarized Key takeaways Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia pain associated with shingles, restless leg syndrome, and diabetic neuropathy. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. Conclusion: Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Heightened awareness of such preventable risk, amid the chronic kidney disease epidemic Key Takeaways: Can Gabapentin Cause Kidney Problems? Gabapentin is primarily processed by the kidneys. Kidney function should be monitored during treatment. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for renal impairment. Some patients report mild kidney-related side effects. Consult a doctor if experiencing unusual symptoms. Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Background: Gabapentin and pregabalin are well-tolerated medications primarily cleared by the kidney. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited It is essential that a patient's renal function is taken into account when prescribing and reviewing medication. Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 what is DOSE Gabapentin IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT , what IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS Gabapentin,CLINICAL USE Gabapentin , for what can Gabapentin used for Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in patients with CKD primarily to treat neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome and given the high prevalence of diabetes in this population, the proportion who receive these drugs is very high. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/ min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption.1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |