Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
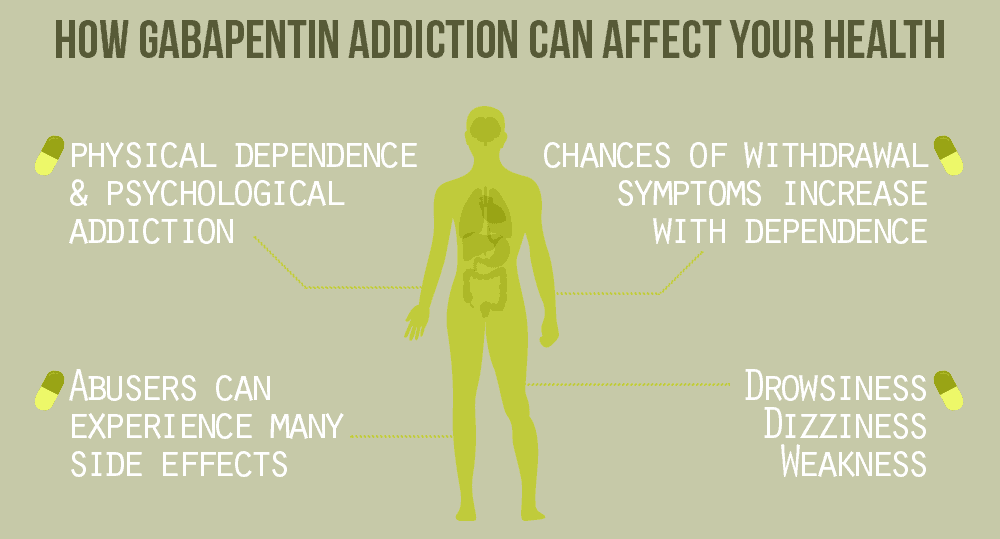
These side effects occur because gabapentin influences the way nerve signals are transmitted in the brain, which can temporarily impair cognitive functions. Does gabapentin cause memory loss? Gabapentin works by mimicking the effects of an inhibitory neurotransmitter called GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) in the brain. GABA is a chemical messenger that helps to reduce nerve activity in the central nervous system. Gabapentin binds to calcium channels within nerve cells, which improves their response to GABA and facilitates its release. While some patients may experience brain fog or slight confusion, studies have shown that gabapentin alone does not cause long-term memory loss. However, the potential for memory problems arises when gabapentin is combined with other drugs that have addictive effects on inhibiting excitatory neurotransmitters. Explore gabapentin memory loss, long-term side effects, and safety concerns for lasting brain and nerve health. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. It may be reasonable to start older adults on a low dose of gabapentin, which can be effective to treat pain while exposing patients to a lower risk of adverse mental status side effects of gabapentin (dizziness, drowsiness and confusion) [7]. The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects While gabapentin is generally considered safer than opioids, it’s crucial to use this medication responsibly. Misuse or abuse of gabapentin can lead to cognitive impairment and memory side effects. It should only be used as prescribed by a doctor to avoid potential adverse effects on mental function. Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Vertigo (dizziness) Feeling fatigued or sleepy Fluid retention Trouble balancing or controlling movement Diarrhea or constipation Nausea and vomiting Brain fog Headache Weight gain Dry mouth Blurry or double vision Unusual eye movements Sexual Background: Gabapentin is increasingly prescribed to older adults, which raises concerns about its potential to cause neurocognitive changes. Therefore, we aimed to examine the association of gabapentin use with neurocognitive changes (i.e., Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin has been associated with cognitive side effects in some individuals, including memory loss, although these effects are not universally experienced. The drug works by altering nerve activity in the brain, which can sometimes impact cognitive functions like memory, attention, and concentration. Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. What Is Gabapentin Used For? Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such [] Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. Fuzzy thinking is not an official FDA side effect of gabapentin or pregabalin. And yet we keep hearing from people who complain about this complication. Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. Can gabapentin cause brain fog? Yes, gabapentin can cause brain fog in some individuals. Cognitive issues, such as a decrease in alertness, may occur as side effects, often accompanied by dizziness and drowsiness, affecting about 10% of users. While gabapentin is used to manage conditions like nerve pain and menopause symptoms, its impact on cognitive function is a concern for some patients Explore gabapentin's effects on mental function, memory, and cognition. Learn about managing side effects and balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. A recent study has linked gabapentin, a popular painkiller for lower back pain, to increased risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in some adults.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |