Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
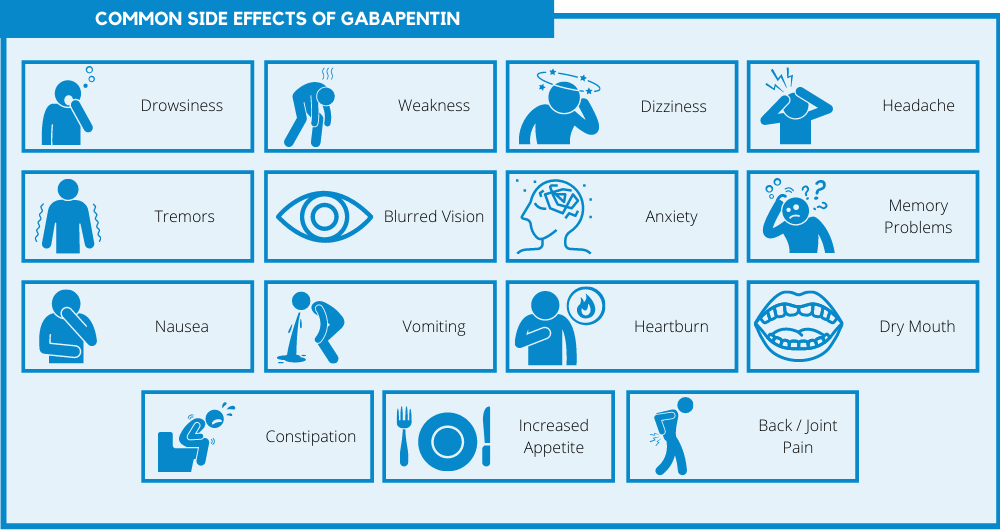
Effect of gabapentin on mechanical pain threshold in. Gabapentin is effective only in the phase of development of mechanical allodynia, but not in the phase of recovery, and its effect is observed in mice overexpressing mutated TA (hMT) (Friedman test = 13.67; p = 0.0005; Dunn’s multiple comparisons test: day 10 NT inactive dose vs. hMT Gabapentin acts primarily on the central nervous system. Therefore, we hypothesized that the direct epidural administration of gabapentin could have various advantages over its oral administration with respect to required dose, side effects, and efficacy. However, before administering gabapentin int Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain. While a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests a high risk for heart diseases in the patients taking GBP. In the present study, we used a preclinical model of rats to investigate (1) the acute cardiovascular responses Hello! Recently my vet prescribed gabapentin to one of my rats (50mg/ml suspension). She’s taking 0.04ml every 12 hours, and only started a few days ago. I’ve noticed that she has some urinary incontinence and is basically urinating clear liquid now. I’m concerned that she’s going to get The potential adverse effects of analgesics are also reviewed. While gaps still exist in our understanding of clinical pain management in rodents, effective pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic strategies are available that can and should be used to provide analgesia while minimizing adverse effects. Our study investigates the acute effects of gabapentin and pregabalin on rat brain GABA, glutamate and glutamine concentrations to further understand the mechanisms of these antiepileptic drugs. Vigabatrin serves as a positive control because it reliably increases cellular GABA levels in humans and rodents 15., 16.. (gabapentin) Brands Neurontin Availability Tablets: 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg Capsules: 600 mg and 800 mg Oral solution: 50 mg/mL *Note: Some human liquid oral formulations may contain xylitol, a sugar substitute. While this is toxic to dogs, it does not show the same response in rats at sub-acute levels. 1,2,3,4 Pharmacology Gabapentin is an analog of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). While Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate, firstly, the Background and aims The clinical management of neuropathic pain remains a challenge. We examined the interaction between gabapentin and NMDA receptor antagonists dextromethrophan and MK-801 in alleviating neuropathic pain-like behaviors in rats after spinal cord or sciatic nerve injury. Methods Fema The current work is targeted to review the risks of gabapentin misuse, its potential interactions with other drugs, side effects and use contraindications. This review consists of a total of 99 bio Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated Abstract Background & objectives: Several studies have shown the possible analgesic effects of gabapentin, widely used as an antiepileptic. Thus, clinical studies have been carried out especially for neuropathic syndroms. This study was undertaken to investigate experimentally whether gabapentin has analgesic effects in mice and rats. Methods: The mice were divided into 10 groups (n=7) with The current work is targeted to review the risks of gabapentin misuse, its potential interactions with other drugs, side effects and use contraindications. This review consists of a total of 99 biographical references (from the year 1983 to 2016). A Comparison of anti-nociceptive effect of the antiepileptic drug gabapentin to that of various dosage combinations of gabapentin with lamotrigine and topiramate in mice and rats. Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GB Abstract Postoperative pain management in laboratory animals relies heavily on a limited number of drug classes, such as opioids and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Here we evaluated the effects of saline, tramadol, tramadol with gabapentin, and buprenorphine (n = 6 per group) in a rat model of incisional pain by examining thermal hyperalgesia and weight-bearing daily for 6 d after ABSTRACT Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), which was first developed as an anticonvulsant agent, has recently gained great attention consider-ing its pain relieving and anti-inflammatory effects. The aim of the present study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of GBP on carrageenan (CAR)-induced paw edema and its gastric side effects by determining gastric mucus secretion in rats The gabapentenoids such as gabapentin (GP) and pregabalin are approved for the treatment of chronic pain, but their utility is limited by persistent side effects. These adverse effects result from GPs affecting many types of neurons and muscle cells, Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate Gabapentin modulated the central cardiovascular effect in the NTS We initially investigated the central cardiovascular effects of gabapentin in the SHR rats by microinjection into the NTS. Unilateral microinjection of increasing doses of gabapentin (3.03 to 33 nmol) into the NTS produced dose-dependent depressor and bradycardic effects (Figure 1A).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |