Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
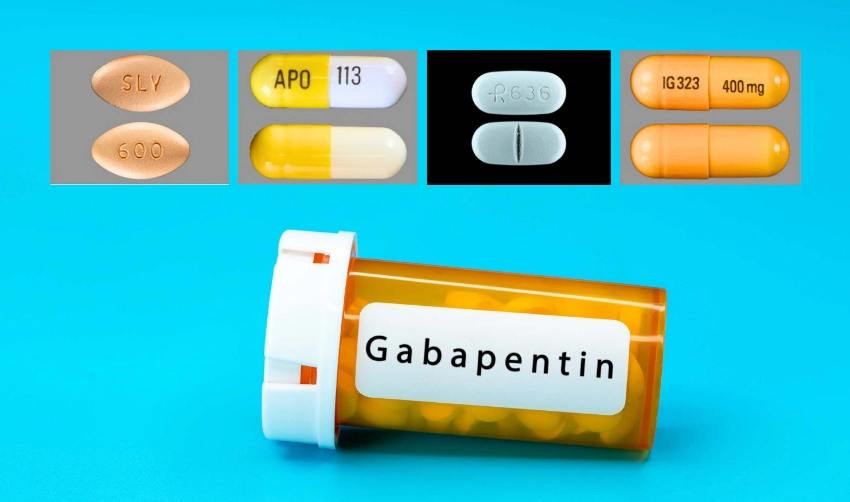
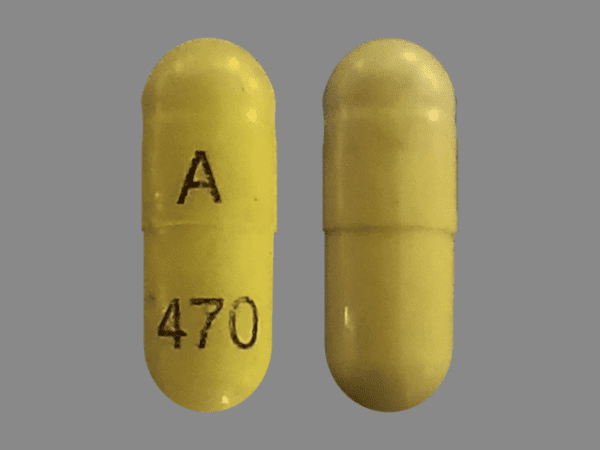
Sleep Aid and Gabapentin: Combining Medications Safely is a crucial topic to discuss with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment. Withdrawal symptoms and tapering off gabapentin are important considerations for those who have been using the medication long-term. There is also a potential for drug interactions when taking sleep aids and gabapentin together. Sleep aids can interact with gabapentin and increase the level of gabapentin in your blood. This can increase your risk of experiencing side effects from gabapentin, such as dizziness, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat insomnia. Studies show it can increase the amount of deep sleep you get at night and improve your sleep quality. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is prescribed for epilepsy and nerve pain, but some people may take gabapentin for sleep. Learn about whether off-label gabapentin works for sleep disorders. Gabapentin, initially developed for seizure management, has found its niche in the realm of sleep aids. Its influence on neuropathic pain and anxiety suggests a potential benefit for those struggling with sleep issues as well. Types of Sleep Disorders Treated Gabapentin has been used to treat a variety of sleep disorders. The dosage of Gabapentin prescribed by doctors to treat the sleep disorder insomnia and improve overall sleep quality is generally between 100-400 mg. Have you used Gabapentin for sleep or insomnia? If you’ve used gabapentin to treat a sleep disorder such as insomnia or to enhance sleep, be sure to share your experience in the comments section below. Navigating the twilight zone between wakefulness and slumber, your brain’s nightly odyssey through REM sleep might be forever altered by a seemingly innocuous pill called gabapentin. This medication, originally developed to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain, has found its way into the realm of sleep medicine, raising questions about its impact on our most enigmatic sleep stage. As we delve Some research shows gabapentin may be effective for sleep. But it’s best to talk with a healthcare provider to see if it’s right for you. If gabapentin isn’t an option, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, over-the-counter sleep aids, or prescription sleeping pills. The aim of this study was to systematically review the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin in the treatment of sleep disturbance in patients with medical illness. PubMed was searched for randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trials that Known drug interactions between gabapentin and sleep aids are relatively few, but the cumulative effects of multiple CNS depressants can be significant. For instance, combining gabapentin with benzodiazepines or non-benzodiazepine sleep medications may increase the risk of respiratory depression, especially in elderly patients or those with Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin helps calm the nervous system, which is why it can affect sleep. While prescribed for insomnia, you may experience sleep disruptions when taking it. By weighing the benefits against the potential risks, individuals can make informed decisions about using gabapentin for sleep. This ensures that it is utilized safely and appropriately in their treatment plans, addressing their specific sleep concerns while minimizing any adverse effects on their overall health and well-being. Intro Gabapentin is a medication that has garnered attention for its potential role in sleep disorders. Initially developed to treat epilepsy, it has found varied applications, including pain management and anxiety relief. An increasing number of individuals are exploring its efficacy for sleep-related issues. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of gabapentin dosage Gabapentin is a prescription medication that may help you sleep. That may be why it has been prescribed for people with insomnia, even though it is not approved for that use. However, gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat a sleep disorder called restless legs syndrome (RLS). One of the most common side effects of gabapentin is The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved gabapentin specifically to treat insomnia. When it comes to taking gabapentin (Neurontin) for sleep, it is an “off-label” use, which means that it can be helpful for sleep issues, but not enough to be FDA-approved for it. While good sleep hygiene—like sticking to a bedtime routine or limiting screen time—can help, it’s not always enough. Some people need additional support to get the restful sleep their bodies crave. Gabapentin is a prescription medication primarily used for nerve pain and to treat certain types of seizures. Gabapentin isn't actually a "sleeping pill" but because it causes drowsiness, it is frequently prescribed to help people sleep who also have leg pains/discomfort. For me, it simply didn't work. I was told that it takes awhile for Gabapentin to work so I stayed on them for about two months.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |