Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
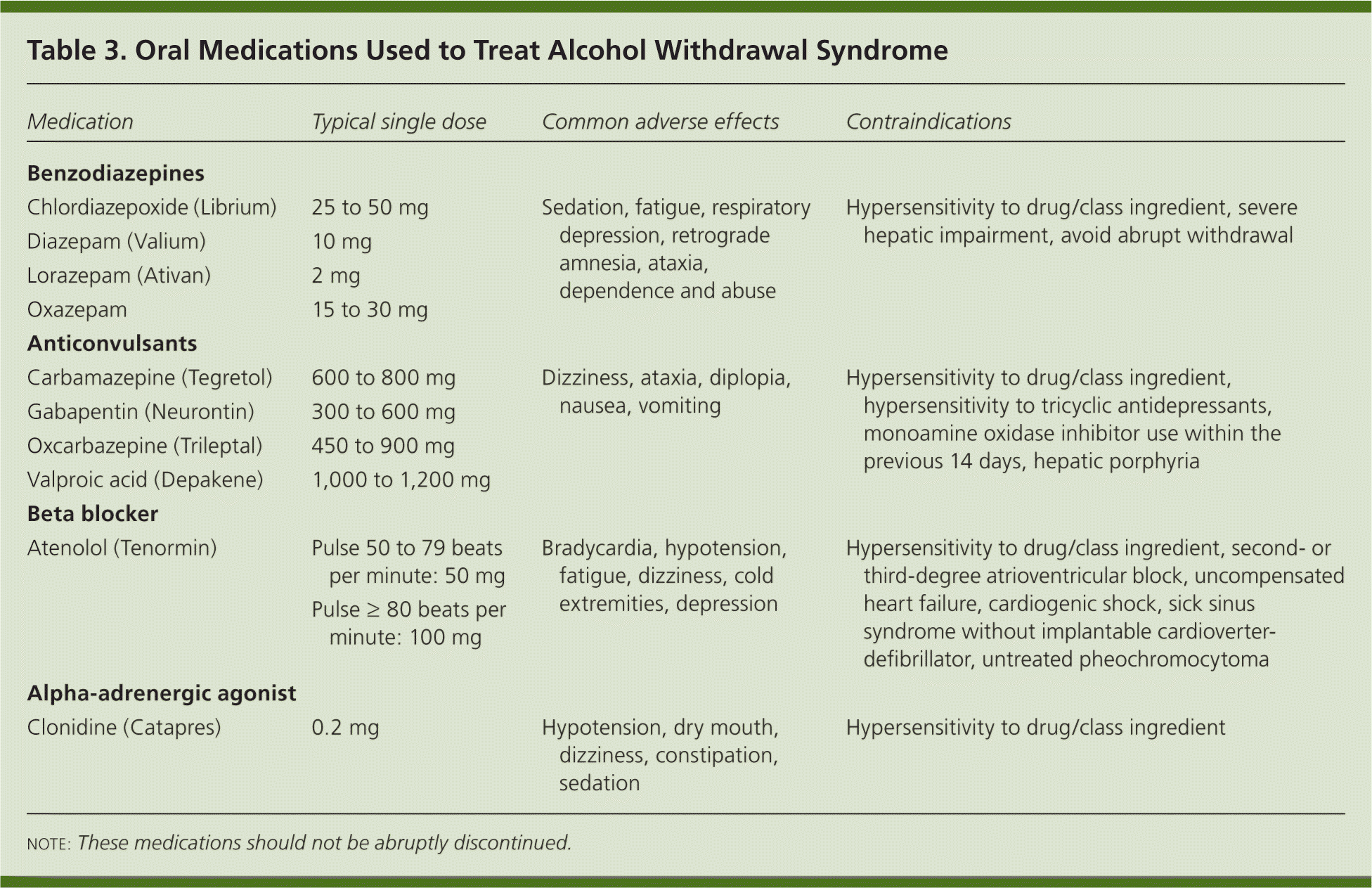
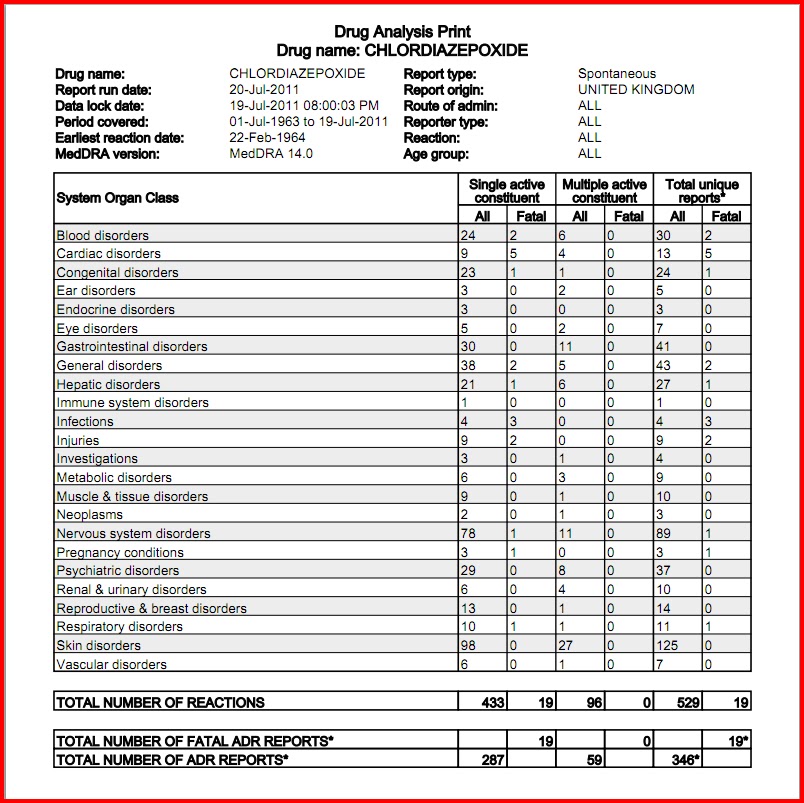
Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. We describe the effects of gabapentin on the central nervous system and how it may mitigate alcohol withdrawal and increase the likelihood of abstinence. In addition, we review clinical trials that evaluated potential roles of gabapentin in AUD, discuss the drug’s misuse potential, and suggest a framework for its appropriate use in AUD Abstract Gabapentin has been widely used to manage post-herpetic neuralgia, peripheral neuropathy, seizure disorders, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, and insomnia. Although usually well tolerated, gabapentin has been reported to cause severe physiologic dependence and withdrawal. Tapering gabapentin in this context poses a significant clinical challenge, with little published Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Gabapentin dependence and withdrawal requiring an 18-month taper in a patient with alcohol use disorder: a case report. Gabapentin has been widely used to manage post-herpetic neuralgia, peripheral neuropathy, seizure disorders, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, and insomnia. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Bottom line Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence Results are statistically significant unless indicated. Conclusion The evidence supporting topiramate for treatment of AUD is more promising than the evidence for gabapentin; however, most of the studies with topiramate reflect a comparison to placebo. Comparative evidence with topiramate or gabapentin with naltrexone or acamprosate are generally lacking. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to examine if gabapentin can effectively replace/reduce the use of benzodiazepines for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms in hospitalized patients. Time to alcohol withdrawal symptom resolution, amount of benzodiazepines administered, rate of resolution of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, serious withdrawal-related complications To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol for alcohol withdrawal in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively identified patients admitted to the hospital from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, for alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin 400 mg four times a day was compared to placebo in 61 alcohol-withdrawing patients and throughout the 7-day trial was found to have no advantage over placebo in reducing amount of clomethiazole required to decrease symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin was also noted to be safe, well-tolerated, and have a low side effect profile. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin’s anxiolytic and sedative properties along with its overall safety profile suggest that it may be a viable adjuvant to lorazepam in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal. While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. Gabapentin caused more dizziness, but this did not affect efficacy. Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |