Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 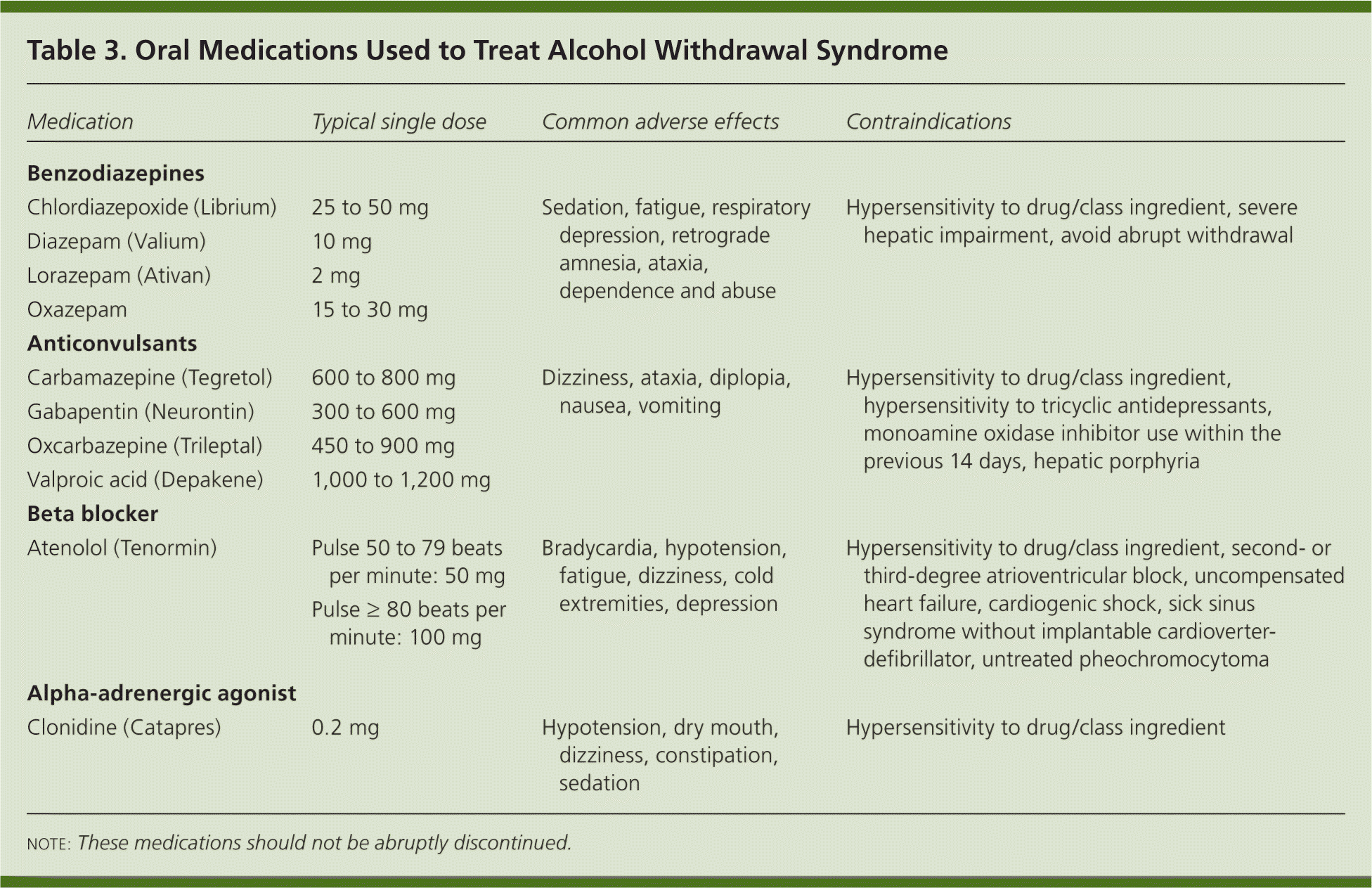 |
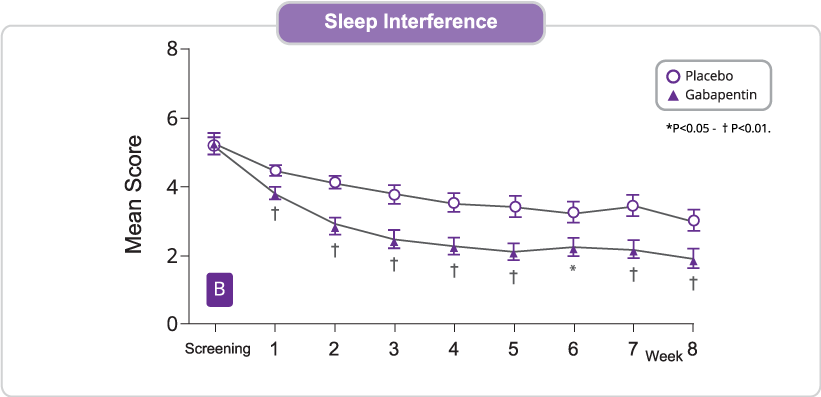
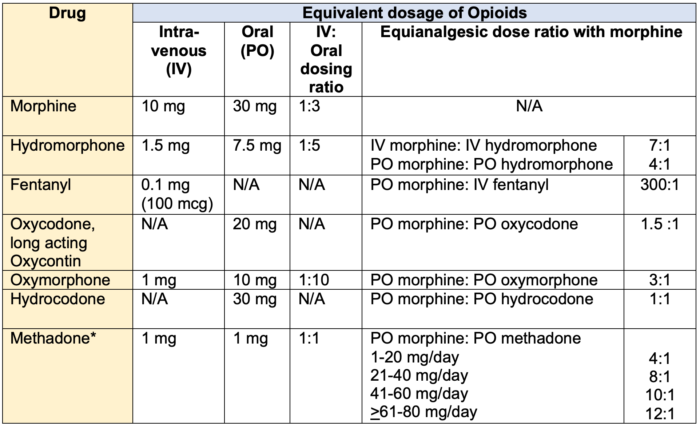
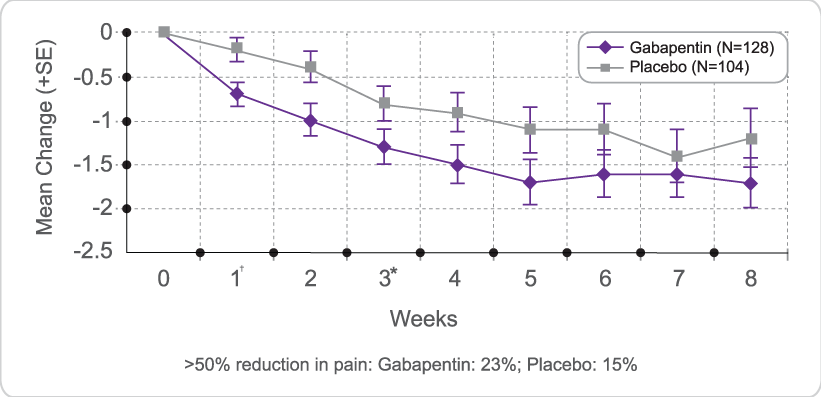
Detailed advice for the titration of gabapentin can be found in the Management of Neuropathic Pain guidance within the Central Nervous System Guidelines of the Tayside Area Formulary. A patient information leaflet for gabapentin is also available which details the usual and slower initiation regimen. Gabapentin should be started slowly according to the regimen below. In renal impairment, the elderly or drug sensitive patients, this titration may need to be done in 100mg increments. Advise patient on the medication, titration regime (see drug specific information below) and target dose. Document target dose on traffic light assessment tool sheet /PIL PROVIDE CLEAR DOSING AND TITRATION GUIDELINES Gabapentin has a short half-life and has to be dosed three to four times daily. To reduce troublesome adverse effects that can occur upon initiation (eg somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia), start with an evening dose,1 and then gradually up-titrate the dose as tolerated. It may take up to 4 weeks to achieve the optimal dose. a period of dose titration to response. If there has been no response to treatment within two-to four weeks, after titration to adequate dose, patients are u likely to develop a response thereafter. Integral to success is regular re-assessment of the patient and stopping me Co-prescribing of opioids and gabapentinoids should be avoided if possible, due to the increased risk of respiratory depression, accidental overdose, and death. The MHRA and manufacturers advise that when prescribing gabapentin in patients who require concomitant treatment with opioid medicines, patients should be carefully observed for signs of CNS depression, such as somnolence, sedation Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a]. However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is a safe and well-tolerated anticonvulsant with a wide therapeutic index, and it is used for neuropathic pain. The aim of this study was to compare previous dosing methods with the administration of four different doses of gabapentin Please note that if at any stage of the increasing dosage regimen you achieve satisfactory symptom control, then there is no need to further increase the dose. If you need to stop gabapentin, then follow the stepwise pattern in reverse to gradually decrease the dose each week or discuss with your doctor or spasticity team. *If *If patient patient is is unable unable to to reach reach maximum maximum effective effective dose dose of of Gabapentin Gabapentin despite despite titration titration consider consider pregabalin. pregabalin. Pregabalin Pregabalin works works on on the the same same pathway pathway as as gabapentin. gabapentin. Evaluate Evaluate people people carefully carefully for for a a history The dose can be increased further if necessary. Slow titration table for elderly patients or patients who are sensitive to Gabapentin Stay on this dose for a few days and if pain relief is adequate remain at this, but if pain is still a problem, try increasing the tablets as follows (see overleaf). Gabapentin is used to relieve pain from the nerves, from the spinal cord, or from the brain. Nerve pain may be associated with shingles (herpes zoster), diabetic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, sciatica, trigeminal neuralgia and other conditions. Gabapentin is also used in the management of certain types of seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. How do I take this medicine? 26. Patients should be made aware of the importance of dosage titration, the titration process and the requirement to take a stable regime for a few weeks (up to 8 weeks for gabapentin with at least 2 weeks at maximum dose, and 4 weeks for pregabalin) before assessing for improvement in pain.5 27. Note 4- Gabapentin has been associated with a rare risk of severe respiratory depression even without concomitant opioid medicines. Patients with compromised respiratory function, respiratory or neurological disease, renal impairment, concomitant use of CNS depressants, and elderly people might be at higher risk of experiencing severe View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. NEURONATIN (GABAPENTIN) TITRATION INSTRUCTIONS Day 1 and Day 2: Take one pill at night Gabapentin FAST UP-TITRATION DAY WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 1 to 2 300 mg daily^ 300 mg morning 600 mg three 300 mg midday times daily. 600 mg at night Continue on this 3 to 4 300 mg twice daily 300 mg morning dose. 600 mg midday 600 mg at night Lower doses of pregabalin are taken to achieve efficacy equivalent to gabapentin Titration of pregabalin may be faster than gabapentin Pregabalin is associated with a higher risk of misuse Start low and titrate dose to achieve maximum benefit or to reach the maximum tolerated dose. Gabapentin (standard dose increase) Patient Information The information in this leaflet is to guide your use of gabapentin safely. Further information is available inside the medication packaging. Some medicines used to treat pain symptoms are used for other health reasons. For example some medicines used to treat epilepsy can help to improve nerve pain. Your doctor, nurse or pharmacist will
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |