Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
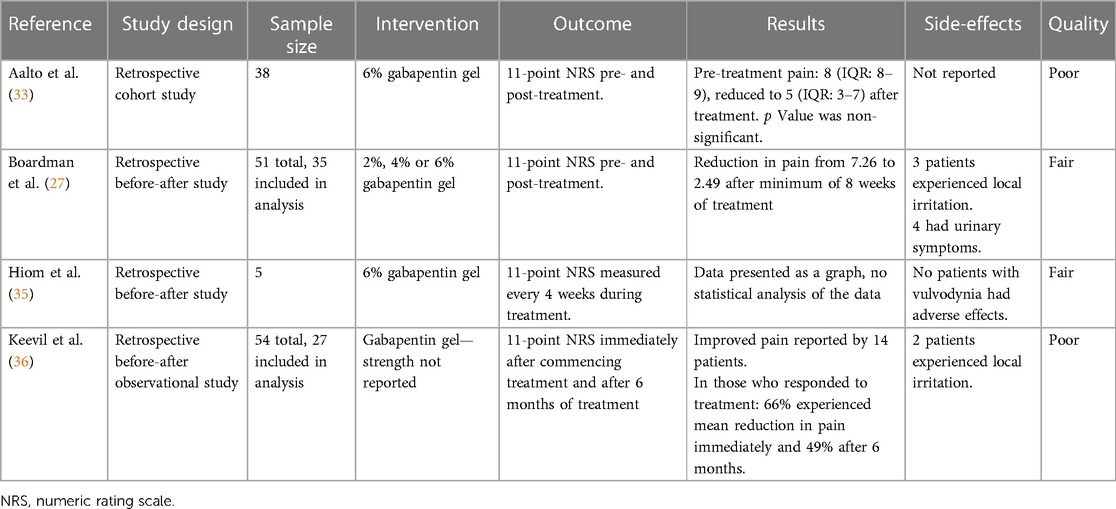 |  |
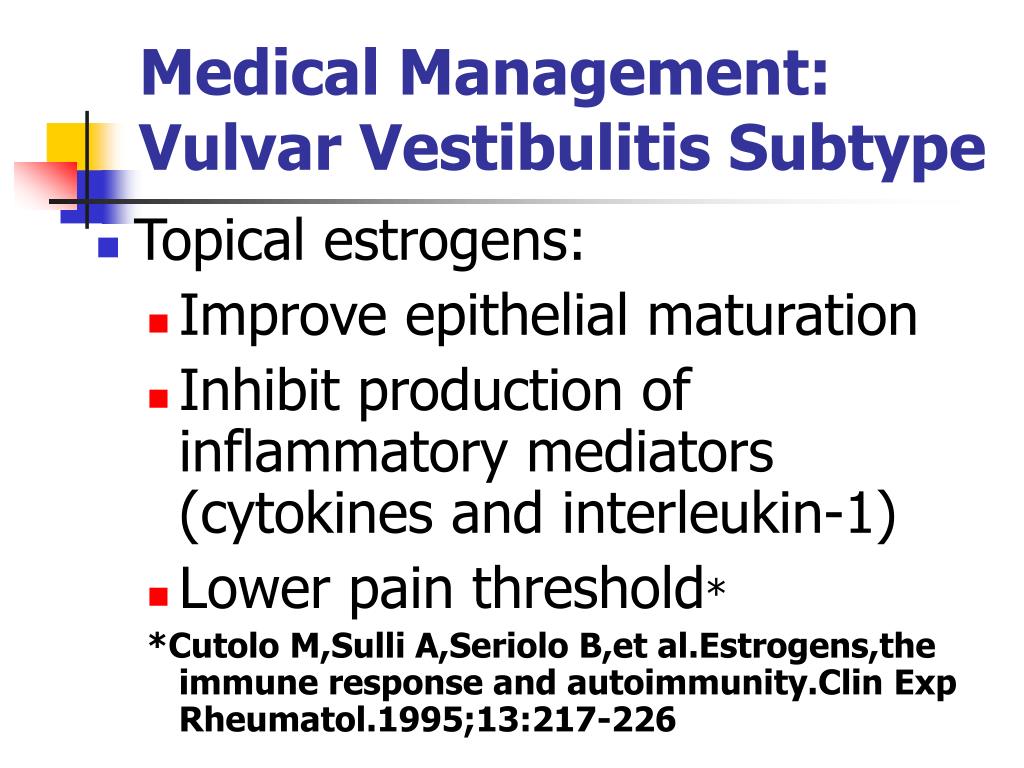
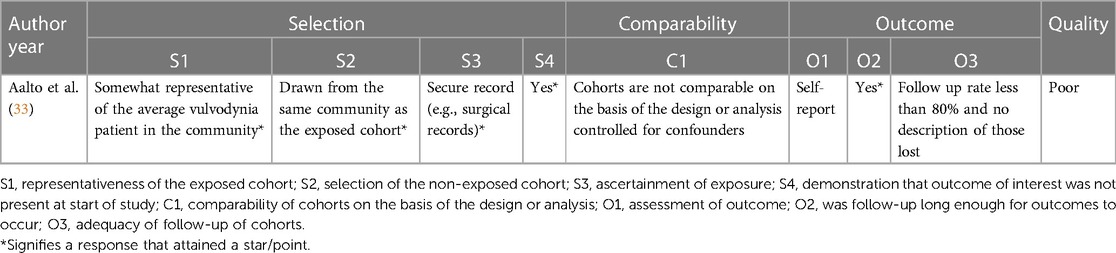
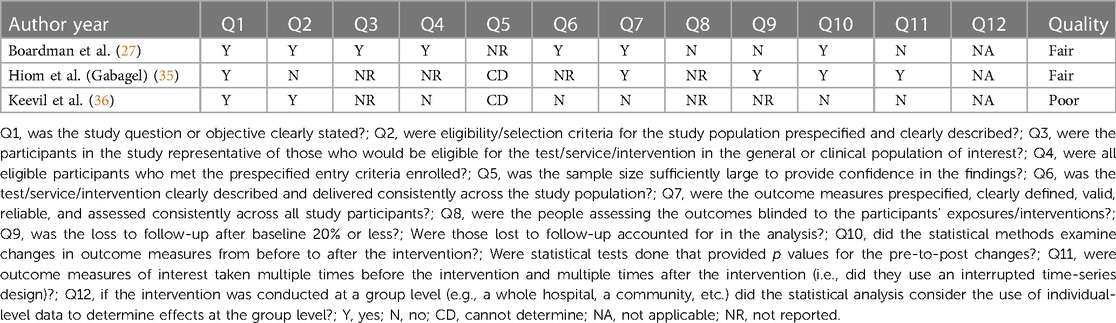
Application of topical gabapentin (10% gel) significantly reduced allodynia and vulvodynia in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic rat model (39). An analgesic effect was also observed in a rabbit model in which ocular pain was ameliorated following application of gabapentin eye drops (40). We begin by adding Neurontin and Elavil for sleep in those with Vulvodynia, but these sometimes cause unacceptable side effects. This new study showed that putting the Neurontin (Gabapentin) in a topical cream decreased pain by an average of 2/3, and decreased pain by over 50% in 80% of the women. Vulvodynia is a debilitating condition characterized by chronic vulvar pain, with a detrimental impact on the patient's overall quality of life. Its etiology is multifactorial, but still in the process of being clearly outlined. Objective: To evaluate the clinical efficacy and tolerability of topical gabapentin in the treatment of women with vulvodynia. Methods: A retrospective study was designed to ascertain clinical responses to topical gabapentin. Vulvodynia is a leading cause of dyspareunia in premenopausal women, causing considerable morbidity and sexual dysfunction. A multimodal approach is used to treat vulvodynia. Alongside psychosocial interventions and physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment such as oral gabapentin are used in the tre Since vulvodynia is a chronic condition, treatment usually needs to be continued indefinitely. Many women prefer a treatment with less systemic effects like a gabapentin topical cream. For menopausal women, an estrogen cream may also be an effective long-term treatment. Gabapentin for Treating Neuropathic Pain Application of topical gabapentin (10% gel) significantly reduced allodynia and vulvodynia in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic rat model (39). An analgesic effect was also observed in a rabbit model in which ocular pain was ameliorated following application of gabapentin eye drops (40). Topical gabapentin cream was well-tolerated and associated with significant pain relief and improved sexual function in women with vulvodynia. The newer consensus terminology notes that vulvar pain can be classified as vulvar pain caused by a specific disorder or vulvodynia. Vulvodynia is defined as vulvar pain of at least 3 month’s duration without identifiable cause and with potential associated factors 2 Box 1. Twenty-five trials explored the use of oral and topical medications in the treatment of vulvodynia. Data Synthesis: Vulvodynia is a poorly understood disease with an unknown etiology. Oral tricyclic antidepressants and gabapentin continue to be the most commonly used treatments for vulvodynia pain. Multiple treatments have been used for vulvodynia, in-cluding vulvar care measures; topical, oral, and injectable medications; biofeedback; physical therapy; low-oxalate diet and calcium citrate supplementation; and surgery (Figure 2). Newer treatments being used include acupunc-ture, hypnotherapy, nitroglycerin, and botulinum toxin. Topical creams Topical lidocaine with 2–5% gel or cream is often tried in women with vulvodynia to reduce nociceptive sensitivity of the skin and mucous membranes and for desensitization of vestibular nerves [47]. This page gives you information about the medication gabapentin which you have been prescribed to reduce the pain of vulvodynia. Vulvodynia is pain in the vulva (area around the outside of the vagina) that lasts at least 3 months and does not have a specific cause. Vulvar pain from a specific disorder often resolves with treatment or control of the condition, but in some cases, treatment of the pain is necessary in addition to treatment of the disorder. Currently there is no standardized treatment for vulvodynia, by definition pain of unknown cause. Although gabapentin is recommended and commonly prescribed for vulvodynia, its value in such cases is usually associated with complaints that have neuropathic components, such as dynamic allodynia. The diagnosis of vulvodynia is made after taking a careful history, ruling out infectious or dermatologic abnormalities, and eliciting pain in response to light pressure on the labia, introitus To evaluate whether extended-release gabapentin is more effective than placebo among women with vulvodynia. In a multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized crossover trial, gabapentin (1200 – 3000 mg/day) was compared to placebo. The Gabapentin inhibits voltage-gated calcium influx in neurons thereby preventing release of the nociceptive neurotransmitter glutamate. 38 Two nonrandomized studies and 1 case report investigated the use of topical gabapentin (Table 6). Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Lyrica have been used to treat chronic pain conditions, including vulvodynia Gabapentin tends to have fewer side effects than the tricyclic antidepressants. Physical therapy of the pelvic floor muscles is commonly employed in the treatment of vulvodynia, for both local and generalized pain. A topical version of Gabapentin for vulvodynia produces fewer side-effects because of its lower systematic absorption, which means your body absorbs less of it through the bloodstream.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |