Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
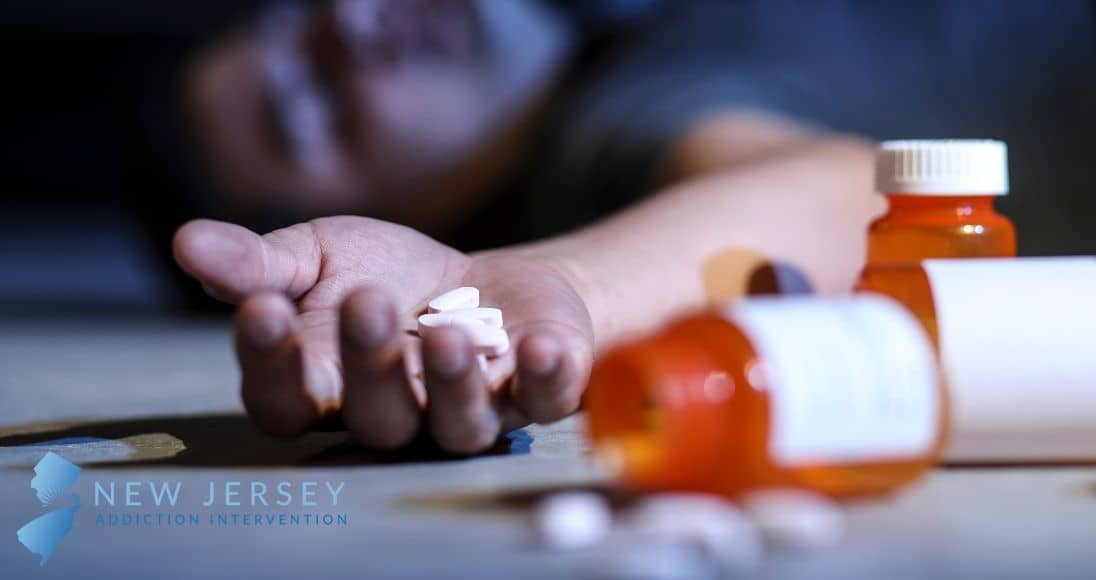
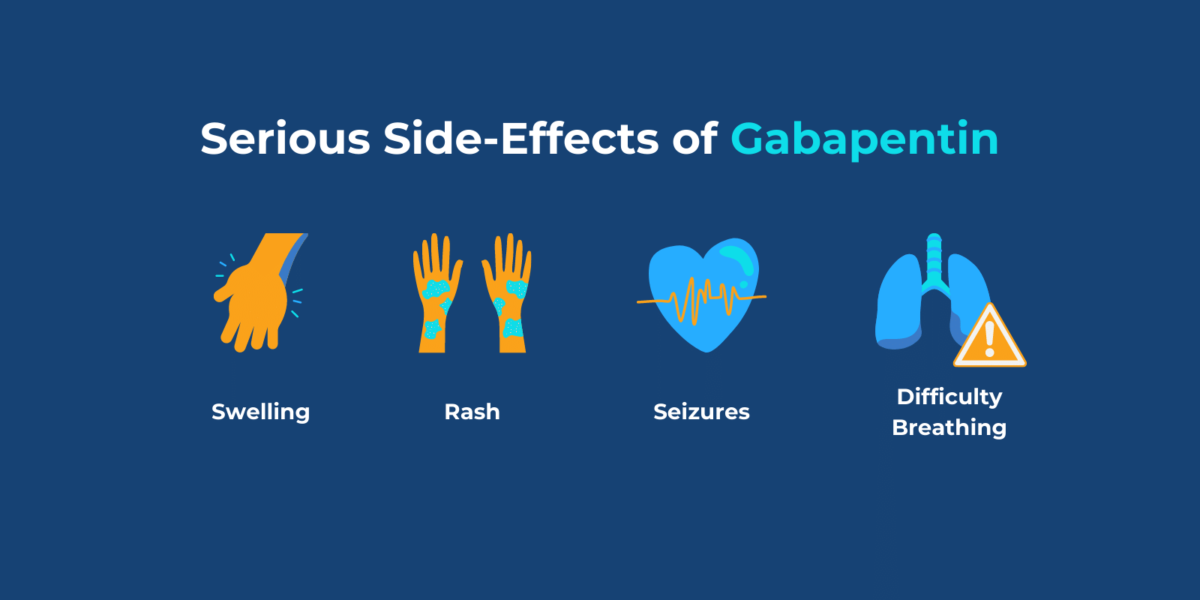
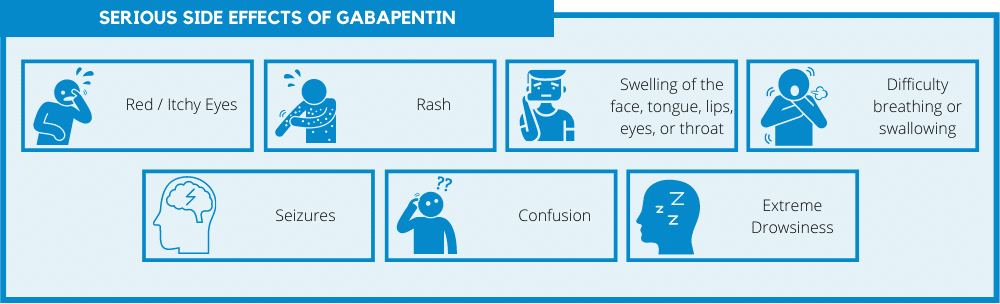
Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose are drowsiness, fast heartbeat, dizziness, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, lethargy, coma, and death may occur. If someone takes too much gabapentin or takes gabapentin by accident, get guidance from Poison Control immediately. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric If you or an elderly under your care take gabapentin and experiences fever, hives, a skin rash, swelling in the face or mouth, breathing problems, and swollen lymph nodes, it is important to stop using the drug and call your doctor immediately as it could be due to a hypersensitivity problem. Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. The goal of this study was to assess the association between gabapentin dosing and adverse outcomes by obtaining estimates of the 30-day risk of hospitalization with altered mental status and mortality in older adults (mean age 76 years) in Ontario, Canada It may be reasonable to start older adults on a low dose of gabapentin, which can be effective to treat pain while exposing patients to a lower risk of adverse mental status side effects of gabapentin (dizziness, drowsiness and confusion) [7]. Gabapentin can be a safe medication for older adults. Knowing what side effects to watch for, which drugs interact with it, and what health conditions influence the risk is the first step to take toward mitigating the risk of gabapentin side effects and interactions. Exposure: Higher-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin >300 mg/d or pregabalin >75 mg/d) versus lower-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin ≤300 mg/d or pregabalin ≤75 mg/d). Outcomes: The primary composite outcome was the 30-day risk of a hospital visit with encephalopathy, a fall, or a fracture or a hospitalization with respiratory depression. Learn about common and serious gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Understand risks, precautions, and when to seek medical help. Gabapentin’s side effects can range from mild to more disruptive, and elderly individuals are particularly vulnerable to some of them. One of the most reported physical side effects is dizziness. This can lead to a higher risk of falls, which is a serious concern for older adults. Gabapentin can cause significant side effects in elderly women, including dizziness, drowsiness, and altered mental status, with risks potentially increasing due to age-related changes in renal function. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Study Design: Population-based cohort study. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Our literature search found only 2 population-based studies examining the association between gabapentin use and risk of toxicity in patients with CKD (our search strategy is shown in Table S2 and the results in Table S3). 11,14 Only one study examined the risk of toxicity by initial gabapentin dose in new users, 14 and, in a subgroup analysis CONCLUSION: Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Conclusions Gabapentin prescription in adults with chronic low back pain is associated with increased risk of dementia and cognitive impairment, particularly in non-elderly adults. Physicians should monitor cognitive outcomes in patients prescribed gabapentin. Data may be obtained from a third party and are not publicly available. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin can cause memory problems, confusion, and difficulty concentrating in older adults, raising concerns about cognitive decline. Dizziness and impaired coordination are also common, increasing the risk of falls and injuries among elderly users. Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function, even after a single dose. We report a 57-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus and uraemia on regular
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |