Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |
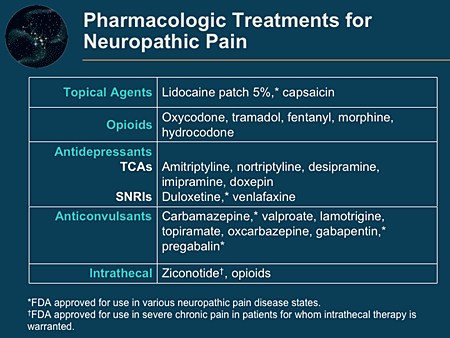
Discover why gabapentin isn't a cure-all for foot neuropathy. El Paso podiatrists can show you better options for nerve pain relief. Schedule your visit today! Abstract Background Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. Objectives To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Search methods For this update we searched CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Gabapentin is a medicine which may help improve your nerve pain, such as shooting, stabbing, or burning pain. Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. If the messages are reduced, then the pain will be reduced. Gabapentin is also used to treat epilepsy and anxiety, but you are taking it for pain. What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. That’s the situation for millions of people who suffer from idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. The term “idiopathic” means that no cause can be identified; “sensory” refers to the type of nerve, in this case those carrying nerve signals such as pain or temperature; “poly” means “many” and “neuropathy” means nerve disease. Gabapentin is primarily used to treat neuropathic pain caused by damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. This includes diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injuries. It is used for various types of nerve pain, such as trigeminal neuralgia or nerve pain associated with fibromyalgia, although its effectiveness for these conditions There are several treatment options for nerve pain, including antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids, and topicals. Learn about their uses and side effects. Gabapentin is a medication that has gained significant attention for its effectiveness in managing nerve pain. Originally developed as an anticonvulsant, it is now commonly prescribed for various conditions, including neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and even restless legs syndrome. Understanding the appropriate dosage, uses, and potential side effects of Gabapentin is essential for Neuropathy Can Gabapentin Make Nerve Pain Worse? September 25, 2024 (A Comprehensive Look at Peripheral Neuropathy and Nerve Pain Treatment) If you’re someone dealing with nerve pain or peripheral neuropathy, you may have been prescribed gabapentin as part of your treatment plan. Pain Drugs that relieve nerve pain When chronic pain comes from the nerves, these nerve pain medications can help when added to other pain relievers. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Learn more about how gabapentin is used in sciatica treatment. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that has been used for a number of off-label indications, including neuropathic pain. It is thought to act by binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, or by blocking new synapse formation. Neuropathic pain tends to be chronic, is complex, and can be difficult to treat effectively. Treatment often involves pharmacologic and physical Gabapentin is often used for this issue, typically at doses between 900mg and 3,600mg daily. Postherpetic neuralgia is nerve pain that sticks around after a shingles outbreak clears up. The pain can feel like burning, stabbing, or shooting sensations along affected nerve pathways. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Medical Indications In animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin Key Findings The findings from four systematic reviews and one RCT for gabapentin (GBP) compared to placebo or active comparators is limited by quantity and quality of evidence for studies on neuropathic pain associated with conditions including chronic lower back pain, fibromyalgia, mixed neuropathic pain, and nerve injury pain. While some studies reported little to no difference in pain, the Although gabapentin is typically known for its use as an anticonvulsant and treatment to manage seizure-related disorders, its use has successfully treated nerve pain in patients. Pain relievers. Medicines available without a prescription, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can improve mild symptoms. Anti-seizure medicines. Medicines such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, often improve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness. Topical treatments. Lidocaine cream that is
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |