Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
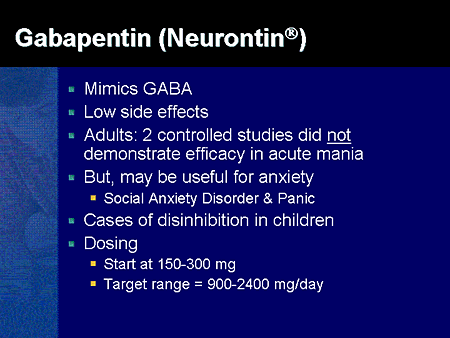
“Gabapentin helps neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells,” Dr. Teseschi says. She and her team just published a study in the journal Brain that showed that daily gabapentin treatment for six weeks after a stroke restored fine motor functions in the animals’ upper extremities. Gabapentin is a medication sometimes used post-stroke. Learn about its uses, side effects, and precautions to take for a safe recovery. Gabapentin increased neuroplasticity and corticospinal tract axonal sprouting, and improved fine motor function, in a rat model of stroke, according to a study published May 23 in the journal Brain. The findings point toward a potential clinical role in stroke rehabilitation for this widely used drug and expand the number of strategies for harnessing the nervous system's own regenerative Is there a link between gabapentin and stroke risk? Learn about the potential association, including the impact of dosage and duration of use, and the underlying mechanisms involved. Gabapentin's role in stroke recovery Gabapentin is a drug that has been approved for the treatment of seizures and nerve pain. It has been found to be effective in reducing pain and improving recovery after a stroke. Efficacy in pain reduction Central post-stroke pain (CPSP) is a type of neuropathic pain that occurs after a stroke, affecting 8-14% of patients. It is challenging to manage and Thalamic pain syndrome, a type of central post-stroke pain (CPSP), may develops after a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke and results in impairment of the thalamus. There is limited experience about gabapentin in treatment of central pains like CPSP. The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells, new research in mice suggests.The experiments mimicked ischemic stroke in humans, which occurs when a clot blocks bloo Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX national database of de-identified patient records from 2004 to 2024 Gabapentin is generally prescribed for nerve pain reduction and seizure control. Some pre-clinical studies found that it may help in functional recovery after a stroke. This study determines the effect of gabapentin on functional recovery measures such as mobility and GAIT abnormality among stroke survivors. Objective: This small clinical trial describes the efficacy of gabapentin therapy in patients with neuropathic pain syndromes after stroke. Background The problem of rehabilitation in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke remains one of the Gabapentin is often prescribed to stroke patients to alleviate post-stroke pain and improve recovery. Learn about its benefits, dosage guidelines, and potential side effects. Here, we report that daily administration of gabapentin, a clinically approved drug already used to treat various neurological disorders, promotes structural and functional plasticity of the corticospinal pathway after photothrombotic cortical stroke in adult mice. Gabapentin, a medication commonly prescribed to control seizure activity, may enhance stroke recovery and restore fine motor function, a new study reports. Gabapentin is already in use in humans for other neurological disorders, such as nerve pain and seizures, so its safety record and side effects are already known. The study found that administering gabapentin, an anticonvulsive medication, soon after a stroke helps the brain more effectively work around damaged areas. Gabapentinoid drugs (pregabalin and gabapentin) have been successfully used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and in focal seizure prevention. Recent research has demonstrated their potent activities in modulating neurotransmitter release in neuronal tissue, oxidative stress, and inflammation, which matches the mechanism of action via voltage-gated calcium channels. In this review, we Gabapentinoid drugs (pregabalin and gabapentin) have been successfully used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and in focal seizure prevention. Recent research has demonstrated their potent activities in modulating neurotransmitter release in neuronal tissue, oxidative stress, and inflammation, wh Current levetiracetam monotherapy showed a very high risk of ischaemic stroke [ (ORadj 5.1, CI95 % 3.7–6.9)]. Drugs used for other conditions than epilepsy (pregabalin, gabapentin) were the most used AED and both did not show a risk. Levetiracetam shows a risk for stroke even when assessed in current monotherapy. Gabapentinoid drugs (pregabalin and gabapentin) have been successfully used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and in focal seizure prevention. Recent research has demonstrated their potent activities in modulating neurotransmitter release in People with prior gabapentin use, dementia, epilepsy, stroke, or cancer were excluded from the study.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |