Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
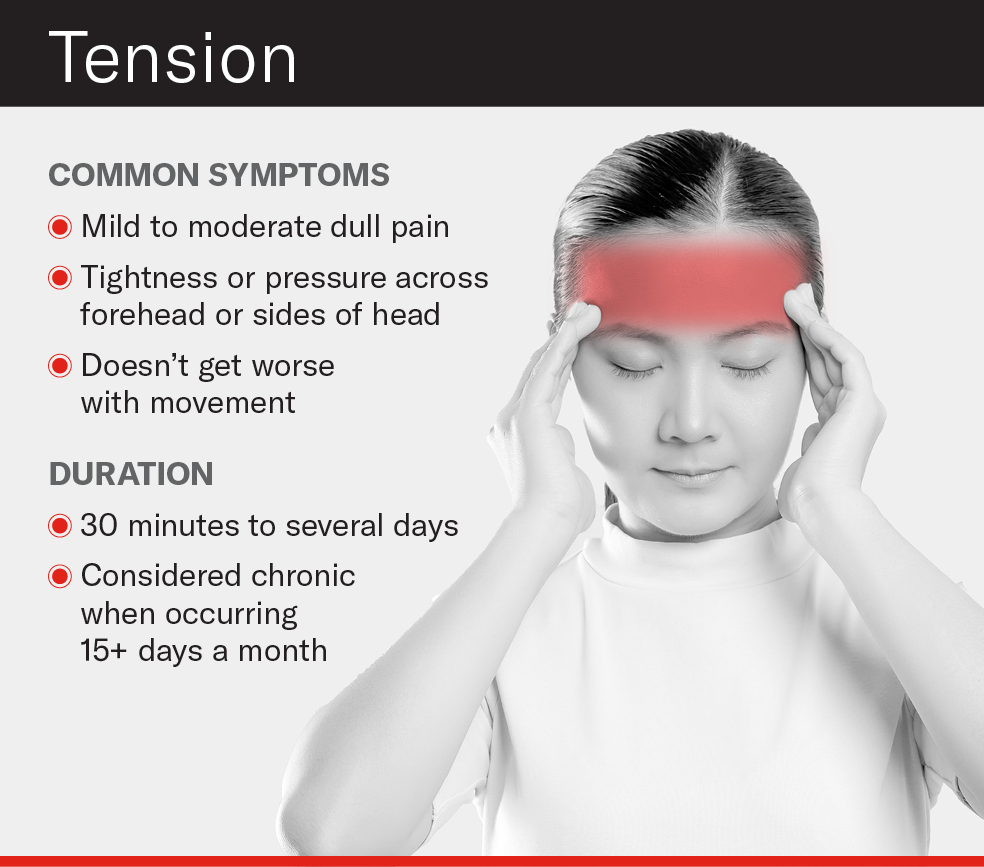
Gabapentin: A Detailed Review of Effectiveness, Side Effects, and Comparisons for Treating Tension Headache. Gabapentin is not a first-line option for tension headaches, with limited benefit reported by the community. While approved for nerve pain and seizures, its use for tension headaches is off-label. 71.0% of users reported no improvement, and 29.0% reported low improvement. Gabapentin A new review indicates that gabapentin may be an effective adjunct therapy for primary headache syndromes, but that there is not enough evidence to support its use as a primary treatment. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. The anti-seizure medicines gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin) and topiramate (Topamax, Qsymia, others) may help prevent headache pain. But more study is needed to understand how well they work to prevent tension-type headaches. The muscle relaxant tizanidine (Zanaflex) also can be used for prevention. We offer a panoramic view of nociception, from a central perspective, and discuss various pharmacological options available to treat headache and neck pain. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. Gabapentin is not typically known to cause migraines, but individual reactions can vary. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has gained attention for its potential side effects. While it's often prescribed for conditions like neuropathic pain and epilepsy, many individuals wonder about its impact on headaches and migraines. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Due to this ambiguity, a clinical evidence literature review was performed investigating GBP's efficacy in headache disorders. Gabapentin Role in Headache Management Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. However, recent studies have shown its potential in managing tension headaches. By modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, Gabapentin can help alleviate the underlying causes of headache pain. This makes it an attractive option for individuals seeking Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of migraine. 121 reviews submitted with a 7.8 average score. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic therapy. The anti-seizure medicines gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin) and topiramate (Topamax, Qsymia, others) may help prevent headache pain. But more study is needed to understand how well they work to prevent tension-type headaches. The muscle relaxant tizanidine (Zanaflex) also can be used for prevention. The recommendation to use amitriptyline for tension-type headache prevention will change my practice, and I have already started candesartan and telmisartan for migraine prevention. Comparison 1 Gabapentin versus placebo, Outcome 1 Headache frequency (change from baseline to post‐treatment, or post‐treatment alone). The sole trial of gabapentin enacarbil versus placebo (Silberstein 2013) did not report sufficient data for us to calculate MDs for this outcome. Responders (patients with ≥ 50% reduction in headache frequency) One trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 mg Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Off-label, gabapentin has been used in the treatment of migraine and other types of headache, including cluster and tension headaches. It shows potential as an option for those living with migraine and other headache disorders. Chronic daily headache is defined as the presence of a headache on 15 days or more per month for at least three months. The most common types of chronic daily headache are chronic migraines and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |