Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
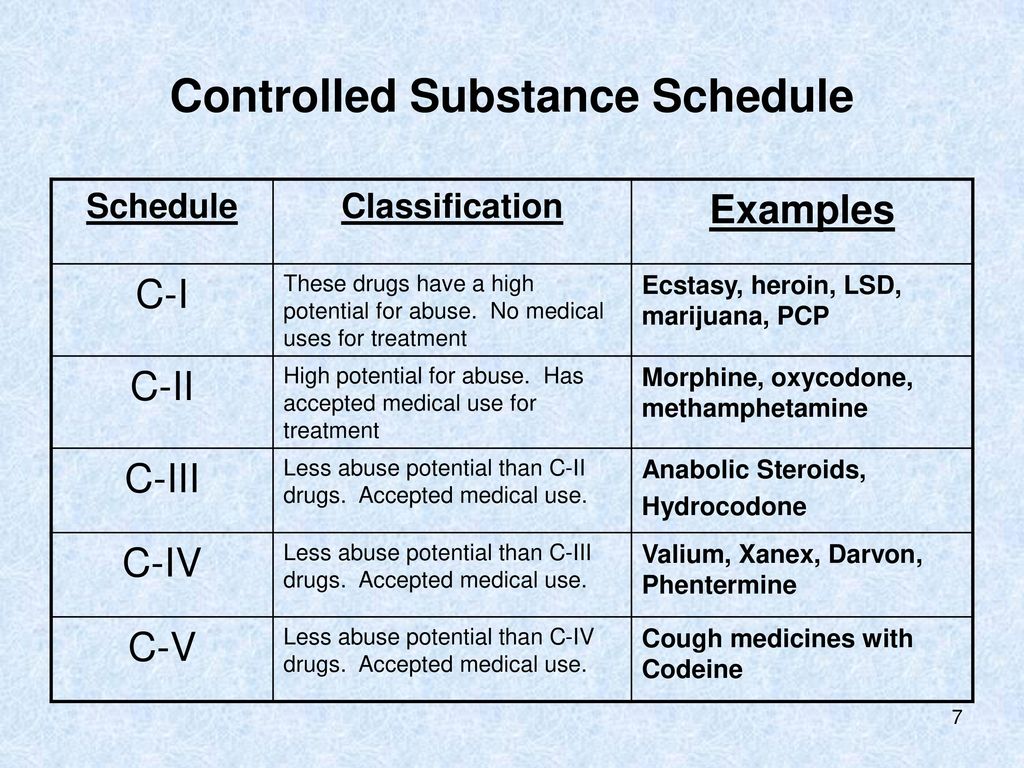
Pregabalin belongs to the same drug class as gabapentin, and its mechanism of action is similar to that of gabapentin. However, pregabalin has a greater affinity for the binding site at which these two drugs exert their effects, so it has greater potency than gabapentin. In veterinary medicine, is extra-label used in combination with other treatments to control seizures when other drugs are no longer effective or become toxic or for neuropathic pain treatment and anxiety. This review aimed to clarify gabapentin use and pharmacokinetic aspects to promote conscious use in dogs, cats, and horses. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed for dogs to help manage pain, seizures, and anxiety. This drug belongs to the class of medications known as anticonvulsants, which work by calming overactive brain activity. While gabapentin is primarily used in humans, it has gained popularity in veterinary medicine due to its effectiveness in treating various conditions in dogs. The use of What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anti-seizure (anticonvulsant) and pain medication that is prescribed to treat seizures and chronic pain (primarily nerve pain) in dogs. It is prescribed for cats to treat fear and anxiety associated with veterinary visits. It is often used in combination with other medications. Your veterinarian may prescribe Gabapentin under the brand names Neurontin What is gabapentin? Gabapentin (brand names: Neurontin®, Aclonium®, Equipax®, Gantin®, Gabarone®, Gralise®, Neurostil®, Progresse®) is an anti-seizure and pain medication that is used with other medications to treat seizures and chronic pain, primarily nerve pain, in dogs and cats. It has also been used in cats to treat fear and anxiety associated with veterinary visits. Its use in Gabapentin is used as an anticonvulsant, sedative, anxiolytic, and to treat chronic pain syndromes, including neuropathic pain. It is used to treat neuropathic pain that does not respond to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opiates. However, studies demonstrating efficacy for pain treatment in dogs and cats are currently lacking. Before prescribing drugs like gabapentin and xylazine to your patients, get an overview of the basic regulatory structure and impact on these drugs. This medication info sheet is meant to give you a good understanding of what gabapentin is used for, how it works, and potential side effects in cats and dogs. Always consult a veterinarian before giving your pet any medication. Gabapentin for Dogs and Cats What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a drug in the anticonvulsant class that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of seizures and certain neuropathic pain conditions in humans. It is commonly used off-label to treat seizures (not described in this article) and neuropathic pain in animals. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medicament used by both humans and animals. It belongs to the anticonvulsant drug class. It reduces abnormal brain signals, preventing seizures. The active ingredient in gabapentin is same for human and animal formulations. So, the effects and benefits should be similar. Veterinary use of gabapentin has also increased dramatically over the past several years, likely due to the desire to have an oral analgesic alternative to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). A recent survey of veterinarians found that 69% of respondents prescribe gabapentin daily or weekly, most commonly for acute and chronic pain.5 Despite this popularity, gabapentin has a Background Gabapentin is the most commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain in cats. Despite this common and chronic usage, clinically relevant pharmacokinetic In veterinary medicine, is extra-label used in combination with other treatments to control seizures when other drugs are no longer effective or become toxic or for neuropathic pain treatment and anxiety. This review aimed to clarify gabapentin use and pharmacokinetic aspects to promote conscious use in dogs, cats, and horses. Gabapentin can cause a false positive reading on urine dipstick tests for urinary protein. Interactions with Other Drugs For chronic pain relief, gabapentin is best started in combination with other pain relievers, but after a time, the other pain relievers can be discontinued, and gabapentin is effective as a sole agent. Gabapentin belongs to a class of drugs called anticonvulsants. A drug class is a group of drugs that act similarly, and such drugs are often used to treat similar conditions. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic medication that is frequently prescribed by veterinarians to treat seizures, pain, and anxiety in dogs. It is a human drug and is used off-label in veterinary medicine Gabapentin is most commonly used in veterinary medicine to relieve chronic pain and in some pets, to reduce fear and anxiety associated with veterinary appointments. Gabapentin may be used alone or in combination with other drugs. Gabapentin is available as capsules, tablets and as an oral solution. Conclusion The use of gabapentin in veterinary medicine has increased dramatically in the last several years. Despite its popularity, there is a narrow indication of its use in veterinary patients. There is also growing evidence that gabapentin is being diverted for recreational drug use, sometimes with fatal consequences. Gabapentin. There are no licensed veterinary products containing gabapentin. All use is off-licence and informed consent should be sought from owners. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug, which presents an established clinical efficacy in human patients for the management of refractory partial seizures, secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and for the control of chronic neuropathic pain. Gabapentin was synthesized as a structural analog Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |