Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
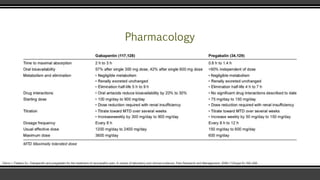
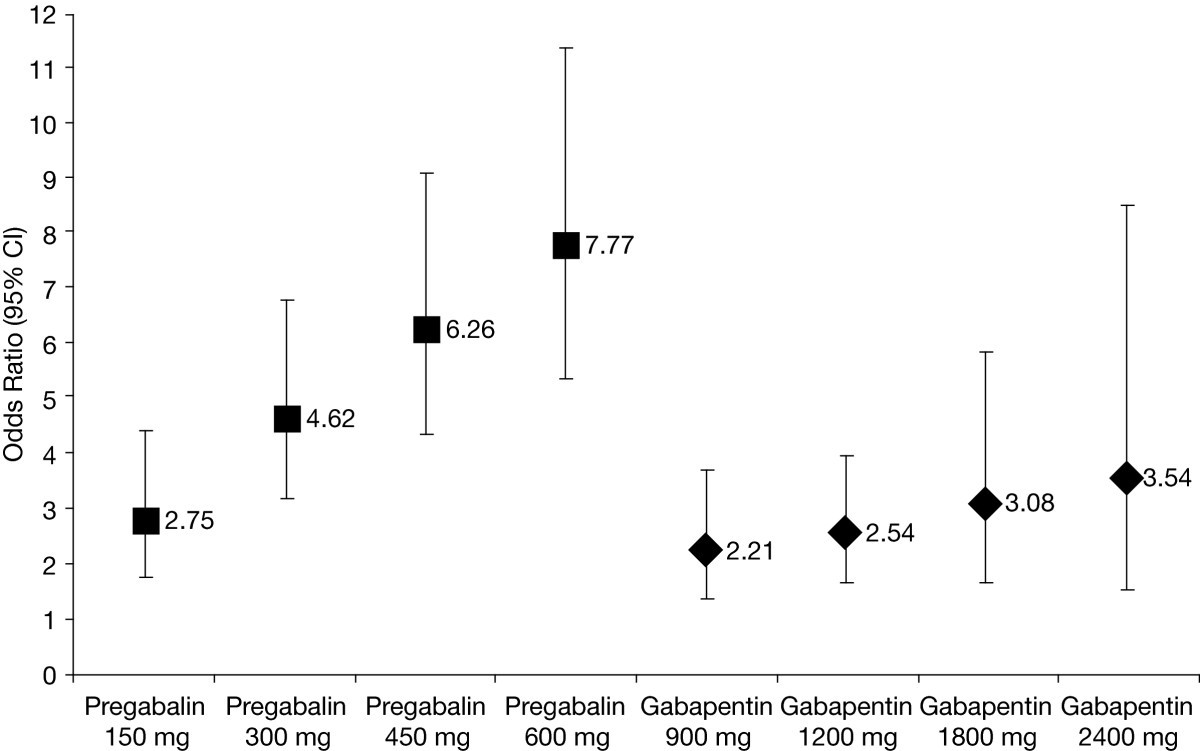
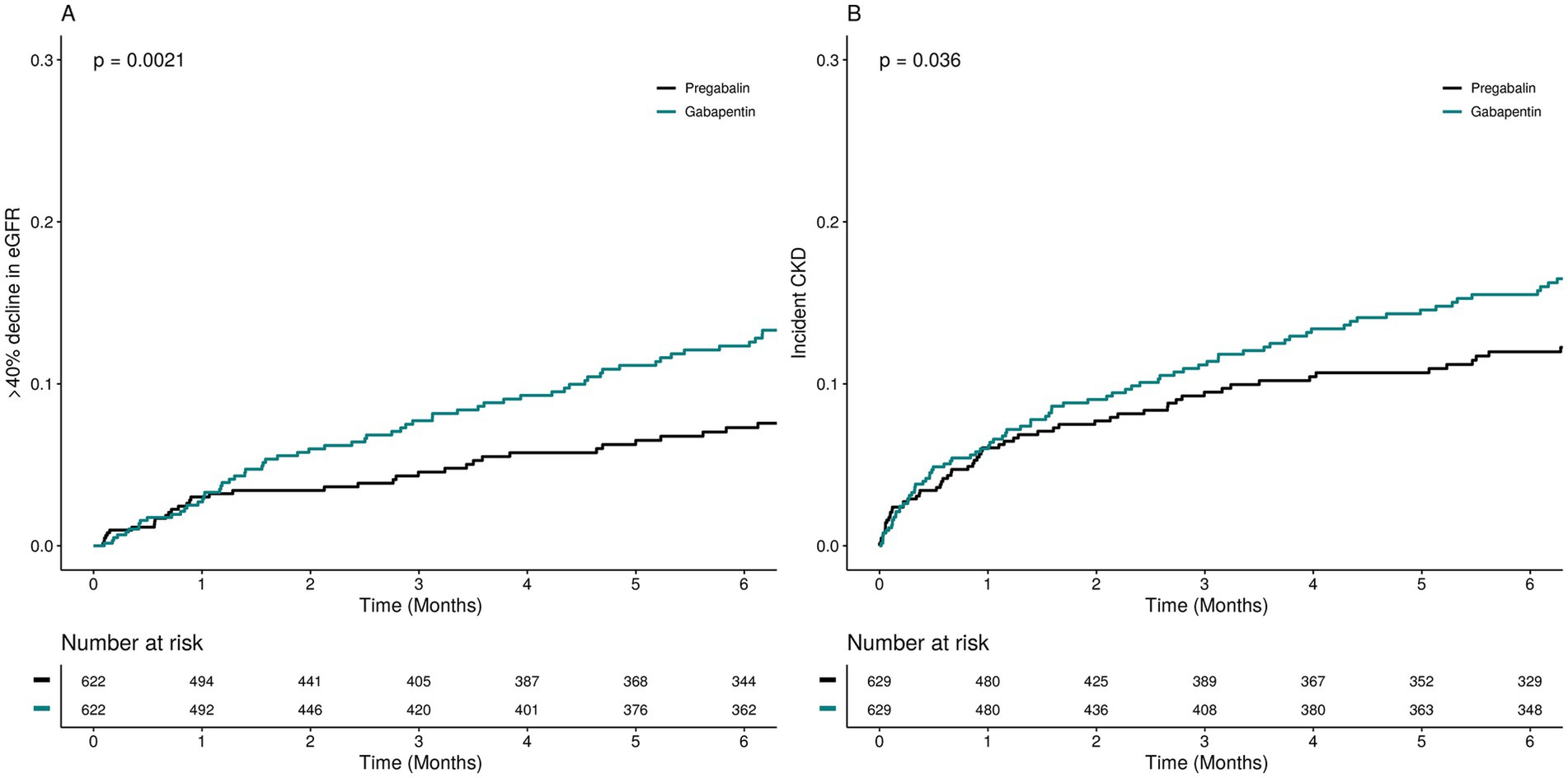
Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with m Learn the similarities and differences of pregabalin vs gabapentin in treating neuropathic pain and seizures. Get informed for better treatment decisions. Note that pregabalin is currently approved for treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in Europe, but not in the United States. Continue reading for an in-depth comparison of pregabalin versus gabapentin, including an analysis of their respective uses, proven efficacy, dosing regimens, side effects, and more. Pregabalin and gabapentin are often considered first-line treatments for various neuropathic pain syndromes, generally irrespective of cause. Both pregabalin and gabapentin are GABA analogues that bind to presynaptic neuron’s voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), specifically to the alpha-2-delta protein leading to reduced calcium influx at the nerve terminals. This leads to reduced release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Though the compounds are similar they have few important differences that must be considered. Newer anticonvulsants such as Gabapentin and Pregabalin have been proven beneficial in patients with peripheral neuropathic pain. Aims and Objectives: The aim of the study was to compare the efficacy of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in relieving the pain in patients of DPN. Pregabalin binds potently to the α 2 -δ subunit of calcium channels, resulting in a reduction in the release of several neurotransmitters, including glutamate, noradrenaline, serotonin, dopamine, and substance P. In this review, I will discuss the pharmacology of pregabalin and available efficacy studies in pain management. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. The interaction of gabapentin and pregabalin with conventional antiepileptic and analgesic drug targets is likely to be modest, at Gabapentin and Lyrica are effective for managing nerve pain, epilepsy, and fibromyalgia. Gabapentin is more likely than Lyrica to cause side effects such as difficulty speaking, fever, an increased risk of viral infections, unusual eye movements, or jerky movements Lyrica is absorbed faster and starts working more quickly than gabapentin. What are pregabalin and gabapentin? Pregabalin and gabapentin, collectively gabapentinoids, are primarily anticonvulsant drugs. Over the past decade, they have been increasingly prescribed for pain. 1 They are recommended for neuropathic pain in adults 2 3 (table 1), but are commonly used off-label for other pain disorders such as low back pain, sciatica, and migraine. 9 10 Pregabalin was one Clinical pharmacology studies conducted to characterize the pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and drug-drug interaction properties of pregabalin and gabapentin were used to assess the pharmacokinetic similarities and differences between these two drugs. In practice most patients are started on gabapentin and if higher doses are required with little relief they will be transitioned to lyrica. Lyrica and gabapentin are renally cleared but not harmful to the kidney. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain.1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety dis-orders in the United Kingdom. Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with maximum plasma concentrations attained within 3–4 hours. Orally administered gabapentin Abstract Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. The interaction of gabapentin and pregabalin with conventional antiepileptic and analgesic drug targets is likely to be Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. Pregabalin vs. gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of effectiveness and safety Initially developed to generate new treatments for epilepsy, gabapentin, and pregabalin (“gabapentinoids”) were engineered to mimic the action of GABA and to modulate GABA metabolism. Rather than their intended pharmacological action on GABA neurotransmission, instead, they exhibit a high
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |