Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
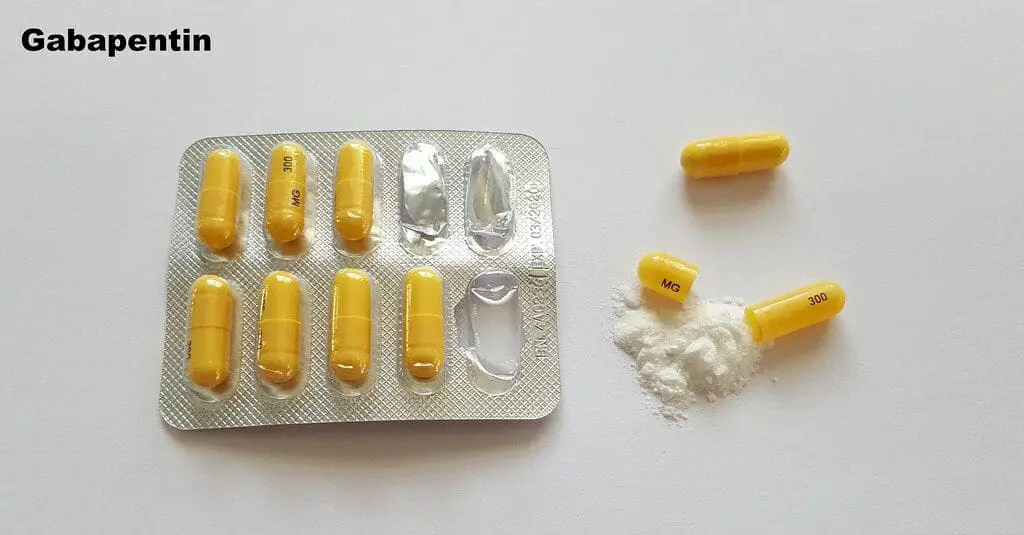
Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication. Pregabalin and gabapentin are both FDA approved as an add-on treatment for partial-onset seizures. But pregabalin is approved for adults and children as young as 1 month old, whereas gabapentin is approved for adults and children who are at least 3 years old. Comparative Evaluation of Oral Gabapentin versus Oral Pregabalin Premedication for Anxiolysis, Sedation, and Attenuation of Pressor Response to Endotracheal Intubation Gabapentin and pregabalin are both used to treat partial-onset seizures and nerve pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia). Additionally, gabapentin and pregabalin are used off-label to treat a variety of mental health and pain disorders. Analgesic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin is well-defined in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Postoperative pain after lumbar spine surgery limits the function of patients in the postoperative period, for which the search for ideal analgesic resent study was to compare pregabalin and gabapentin as a pre-emptive analgesic in elective lumbar spine surgeries. Material and Methods: In this randomized prospective study, 75 patients were allocated into three groups of 25 each. Group G, group PG, and group P received two capsules of gabapentin 300 mg each, two capsules of pregabalin 150 mg each, and two multivitamin capsules Pregabalin and gabapentin are often considered first-line treatments for various neuropathic pain syndromes, generally irrespective of cause. This randomized clinical trial assesses the effect of gabapentin vs pregabalin in leg pain intensity and compares adverse events among adults with chronic sciatica. The primary objective of the study was to compare pregabalin and gabapentin versus placebo with regard to a visual analogue scale (VAS) score for postoperative pain for 24 hours, time to first rescue analgesia, and total analgesic consumption over 24 hours. The level of sedation with the help of a modified Ramsay sedation score was also compared. Clinical studies showed the Schedule V controlled substance to be efficacious for reducing acute feline fear during transportation and veterinary visits. Healthy cats exhibited minimal sedation and side effects. Compared with gabapentin, pregabalin is more potent, requires a smaller dose, and has a longer duration of action. Take-Home Points Reduction in central sensitization by gabapentinoids that include gabapentin and pregabalin may reduce acute postoperative pain. The aim of this study is to evaluate postoperative analgesic benefit and efficacy in patients administered with oral Gabapentin and pregabalin are both effective options for managing neuropathic pain, but their differences in efficacy, side effect profiles, dosing schedules, and indications can make one more suitable than the other for specific patients. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both effective treatments for neuropathic pain and other conditions, but they differ in several key aspects. Pregabalin has faster absorption, onset of action, and greater potency, making it more effective for some patients. This is the first trial aimed at comparing gabapentin with pregabalin in NLBP. Although the results are preliminary, in our pilot study pregabalin was found to be superior in pain reduction, gabapentin demonstrated better effect on anxiety, insomnia and fatigue symptoms. Pregabalin has a higher affinity for the alpha-2-delta subunit making it a more potent analgesic for neuropathic pain. 7 Pregabalin also demonstrates improved pain reduction as doses are increased up to 600mg/day. 6 Gabapentin, on the other hand, begins to exhibit a plateau effect in pain reduction once doses reach 1,800mg/day. 6 Both gabapentin and Lyrica may interact with alcohol and drugs that cause sedation including narcotic pain medications. Gabapentin also may interact with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This study has been undertaken to compare the efficacy of 2 drugs namely Pregabalin and Gabapentin given orally 1 hour prior to surgery in not only attenuating the stress responses to intubation but also to lessen the anxiety levels of the patients and provide sedation. Abstract OBJECTIVE To compare the effects of oral pregabalin versus gabapentin on sedation quality and anesthesia recovery times in cats in a typical perioperative setting. ANIMALS 50 healthy cats with > 1 kg body weight presenting for elective surgery. METHODS In this randomized, prospective clinical trial, cats presenting to the University of California-Davis Veterinary Medical Teaching This systematic review and network meta-analysis evaluates the associations of pain, opioid consumption, and adverse events with different dosages of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients undergoing spine surgery. Both Lyrica and gabapentin are used as anti-epileptic medications and to treat nerve pain. But there are several differences between them. The main differences between Lyrica and gabapentin are: Lyrica is a brand name for pregabalin. Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |