Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH.GettyImages-94965543-787c7e1d9cac423095e520bbd834079f.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
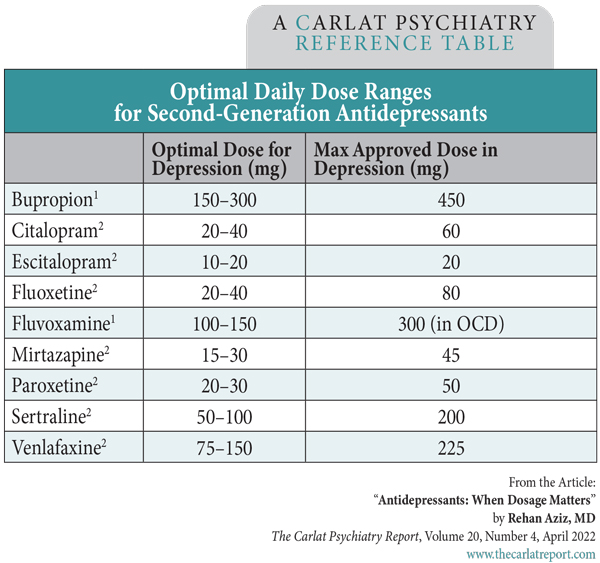
Compare the effectiveness of gabapentin vs. venlafaxine hydrochloride for chronic pain based on the experiences of 822 members of the chronic pain research community. Venlafaxine is used to treat depression. Venlafaxine extended-release (long-acting) capsules are also used to treat generalized anxiety disorder (GAD; excessive worrying that is difficult to control), social anxiety disorder (extreme fear of interacting with others or performing in front of others that interferes with normal life), and panic disorder (sudden, unexpected attacks of extreme fear Effexor XR (venlafaxine) is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety, and panic disorder. Includes Effexor XR side effects, interactions and indications. We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Venlafaxine hydrochloride and Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 567,749 people who take Venlafaxine hydrochloride and Gabapentin, and is updated regularly. Venlafaxine tablets are prescribed for depression and social anxiety disorder. Learn about dosage, side effects, how it compares with Xanax, and more. Studies have shown that Effexor is generally more effective in treating depression than Gabapentin, with a higher response rate and a greater reduction in symptoms. However, Gabapentin may be more effective in reducing anxiety symptoms, particularly in individuals with co-occurring anxiety disorders. Detailed Venlafaxine dosage information for adults. Includes dosages for Depression, Panic Disorder, Generalized Anxiety Disorder and more; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Compare Gabapentin vs Venlafaxine head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Easy-to-read patient tips for venlafaxine covering how it works, benefits, risks, and best practices. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and venlafaxine (Effexor XR) are both prescription medications that can treat nerve pain caused by diabetes (diabetic neuropathy). But they belong to different drug classes and are approved for different conditions in addition to nerve pain. Learn about venlafaxine usage and dosing. Read the latest news and reviews about the drug as well as potential side effects and popular alternatives. Description Venlafaxine is used to treat depression. It is also used to treat general anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder. Venlafaxine belongs to a group of medicines known as serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI). These medicines are thought to work by increasing the activity of a chemical called serotonin in the brain. This medicine is available (1) Gabapentin is efficacious in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy; (2) and (3) in patients who do not respond to gabapentin monotherapy, the addition of venlafaxine is also efficacious. Compare Venlafaxine and Gabapentin: which is more effective for treating anxiety and depression? Learn their differences and benefits in this informative guide. Patients with diabetic neuropathy treated with gabapentin in combination with venlafaxine reported pain relief and improvements in quality of life compared to those in a placebo group and to those who received gabapentin and placebo [77]. Venlafaxine is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety, and panic disorder. Learn about side effects, interactions and indications. Find patient medical information for Venlafaxine (Effexor) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Venlafaxine, sold under the brand name Effexor among others, is an antidepressant medication of the serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class. [5][9] It is used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. [9] Studies have shown that venlafaxine improves post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a recommended Brand-name gabapentin and venlafaxine were both significantly associated with longer persistence than generic: 7.3 versus 6.3 months, P <0.001; and 8.8 versus 8.1 months, P <0.05, respectively. Our data suggest that monotherapy or adjuvant therapy with venlafaxine is comparable to gabapentin for NeP management. We advocate for head-to-head, randomized, double-blinded studies of current NeP therapies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH.GettyImages-94965543-787c7e1d9cac423095e520bbd834079f.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |