Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
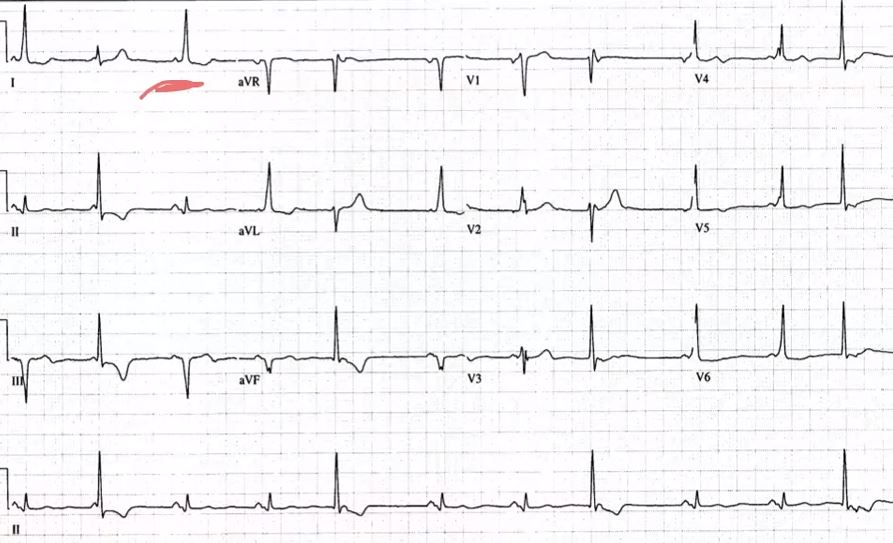
Funds go solely to hosting and development costs that allow medical practitioners around the globe to freely access WikEM. Some protocols call for higher dosing - 1200 mg (400 mg t.i.d.) of gabapentin for three days then 800 mg (400 mg b.i.d.) for day 4 [11] Similar efficacy to lorazepam in decreasing craving and anxiety [12] Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . UpToDate UpToDate Other agents Baclofen, clonazepam, valproic acid, lamotrigine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, topiramate Surgery Posterior fossa microvascular decompressive surgery Approximately 50% of patients will require surgery Successful in 70% of patients Disposition Typically outpatient See Also Headache References J Pain Symptom Manage 2001; 21 (6):506-510. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years. ↑ Epocrates. Gabapentin Monograph. Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue [1] Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat partial seizures, neuropathic pain, hot flashes, and restless legs syndrome. [2][3] It is recommended as one of a number of first-line medications for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain. [8] About 15% of Gabapentin is a questionably effective medication, but is low cost and has a relatively tolerable side effect profile March 2017 systematic review revealed gabapentin is not beneficial [5] Effective treatments include duloxetine, venlafaxine, pregabalin, oxcarbazepine, TCAs, atypical opioids (tapentadol) Consider also gabapentin (titrate slowly) or TCAs (nortriptyline, amytriptyline) Gabapentin Oral: Immediate release: 400mg-1200mg PO TID Spinal stenosis Treatment is the same as for musculoskeletal back pain Cauda equina syndrome Immediate spine surgery consultation for spinal decompression to avoid permanent bowel/bladder/neurologic injury Antiepileptics - gabapentin, topiramate TCAs - amitriptyline, nortriptyline Duloxetine (especially if TCAs contraindicated) Pregabalin NSAIDs and Tylenol Second line medications (temporary relief, not long term) Tramadol Muscle relaxants - cyclobenzaprine, methocarbamol, diazepam Refer to pain specialist for multidisciplinary approach Gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal symptoms, including management strategies and clinical considerations, are discussed in this comprehensive resource. Comprehensive guide on overdose management, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for various substances. Essential resource for healthcare professionals. Neuropathic Pain 600mg PO load in ED Discharge with 300mg → 900mg per day divided tid (as in post-herpetic neuralgia regimen) Discharge with pain specialist follow-up Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue [1] General Type: Anticonvulsants; GABA analog Dosage Forms: capsule, tablet, oral solution 250mg/5mL Common Trade Names: Neurontin, Gralise Physical therapy NSAIDs +/- gabapentin if patient has neuropathic pain May benefit from referral for steroid or botulinum toxin injection [2] Disposition Outpatient See Also External Links References ↑ Boyajian-O'Neill LA, McClain RL, Coleman MK, Thomas PP. Diagnosis and Management of Piriformis Syndrome: An Osteopathic Approach. Make an edit and help make WikEM better for everyone. Step1. Mild Pain, Nonopioid, +/- Adjuvant. Step2. Mod Pain, Opioid for mild/mod pain, +/-nonopioid, +/-Adjuvant. Step3. Severe Pain, Opioid for mod/sev pain, +/- nonopioid, +/-Adjuvant. ^In elders, use a bulk laxative and give instructions regarding activity, hydration and close follow-up. Reloading Dose (mg) = ideal body weight (kg) X Vd X [desired level - current level (mcg/mL)] Volume of Distribution Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |