Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
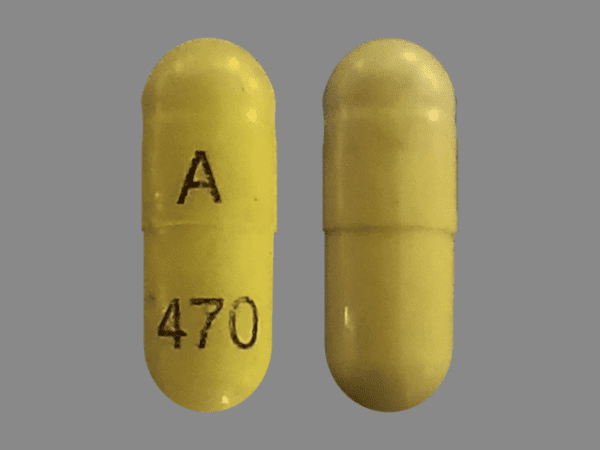 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
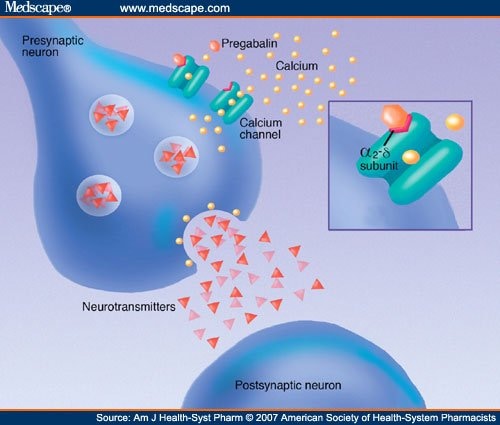
Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. It’s fast becoming the go-to drug for addicts in search of a stronger high — and it is not even an opioid. Gabapentin, a purportedly nonaddictive painkiller primarily used to treat shingles While Gabapentin is not classified as a controlled substance, evidence suggests that it may lead to misuse or dependency in some individuals. Cases of withdrawal symptoms, such as anxiety, insomnia, and nausea, have been reported when discontinuing the drug after long-term use. In 1993, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the oral prescription drug gabapentin (NEURONTIN) as an add-on treatment for focal (partial) seizures [1] — a type of epilepsy that begins in one side of the brain — and subsequently approved the drug in 2002 to treat pain that occurs as a late complication of shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) in adults. [2] The agency later approved Discover why Gabapentin may be considered "bad." Learn about its potential risks, side effects, impact on sleep, mental health, and physical health. Explore alternatives and legal concerns. Gabapentin was approved in 1993 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) initially only for treatment of epilepsy as an adjunct to anticonvulsant therapy, but in 2004 was also approved as an analgesic for post-herpetic neuralgia (8). Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Gabapentin is a drug that has helped countless individuals manage nerve pain and seizures. However, for some, it has turned into a nightmare, leading to unexpected consequences. We will explore what gabapentin is, its potential side effects, and why some people desperately state such things as “Gabapentin ruined my life.” We'll dive into its risks, challenges, and provide a clear overview By Ryan Jackson High doses of gabapentin can pose significant risks to health. As gabapentin becomes more widely prescribed, understanding its potential side effects is crucial. While this medication is often used to manage nerve pain and seizures, misuse and overdose can lead to severe consequences. Neurological Side Effects of Gabapentin Overdose Can you overdose on gabapentin? large amounts Here's who gabapentin was originally approved for, what it's used for today and why it's becoming a drug of increasing concern for abuse and misuse. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects A POPULAR nerve and back pain medicine has been linked to an increased risk of dementia by scientists. The risk was associated with patients who had received six or more prescriptions of the drug. Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. Gabapentin and Lyrica, both sold by Pfizer, have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat only four debilitating pain problems: postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin isn’t inherently dangerous, but it can be habit-forming for those prone to addiction. While gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication with legitimate medical uses, misuse and dependence have become increasingly common. So, why is gabapentin bad for you? Regular gabapentin use appeared to increase risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by 85%, researchers reported July 10 in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. What’s more, the risk was more than doubled in people normally considered too young to suffer from brain aging, those 18 to 64, results show. Gabapentin drug interactions: Along with side effects, gabapentin has possible interactions to know about. Gabapentin FAQs: Experts answer common questions about taking gabapentin, from if you should take it with food to what to do if you miss your dose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |