Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 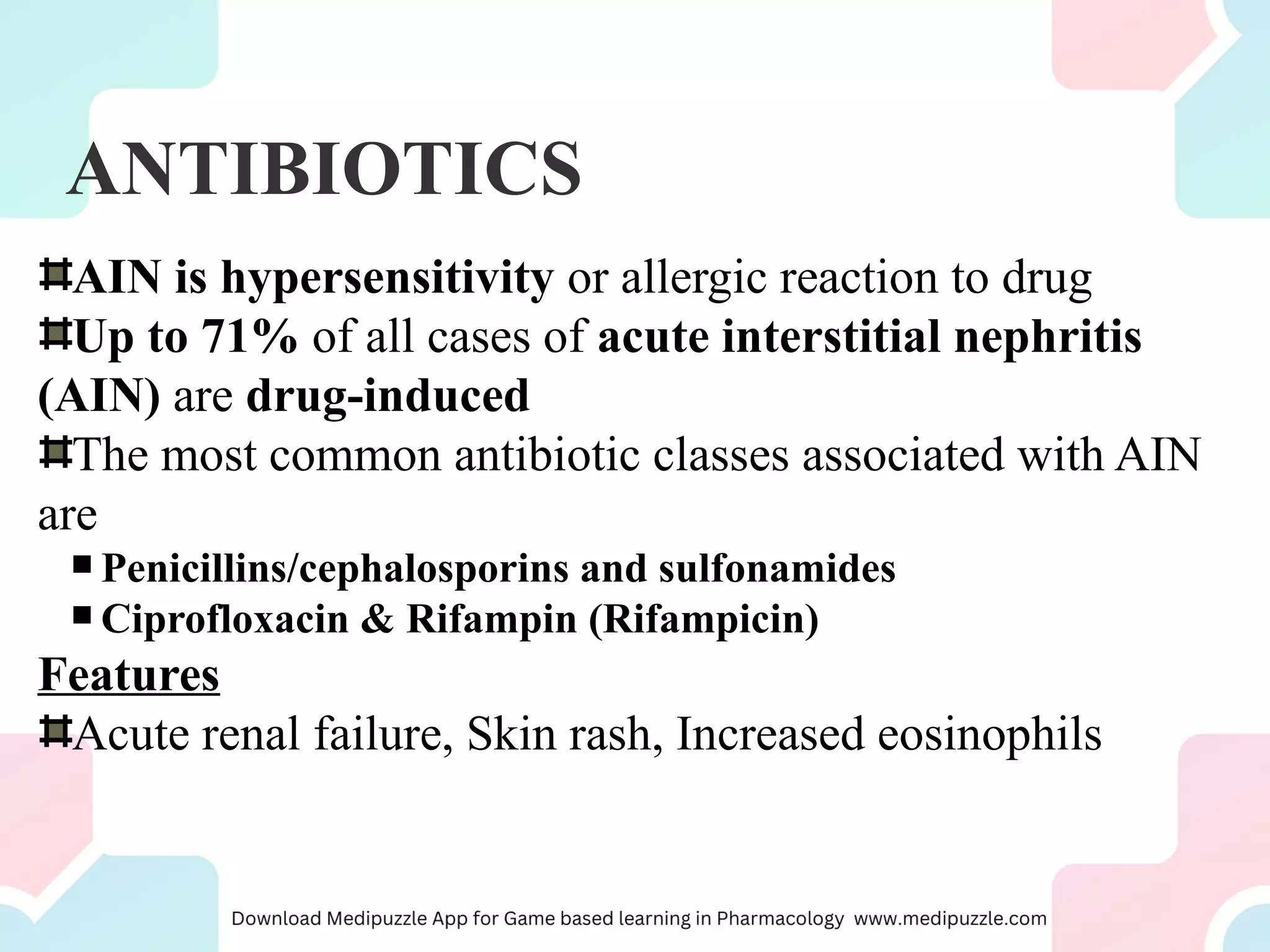 |
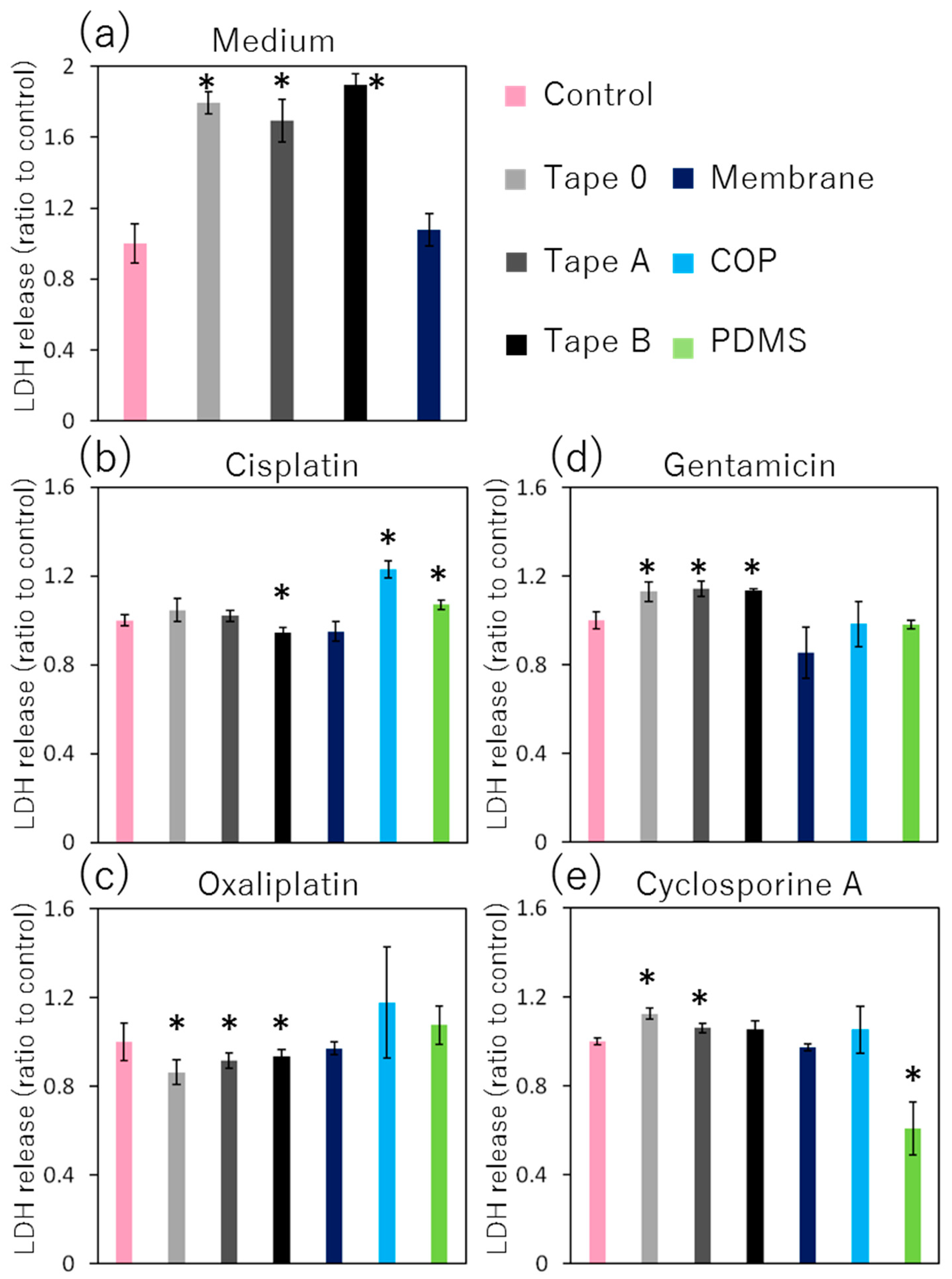
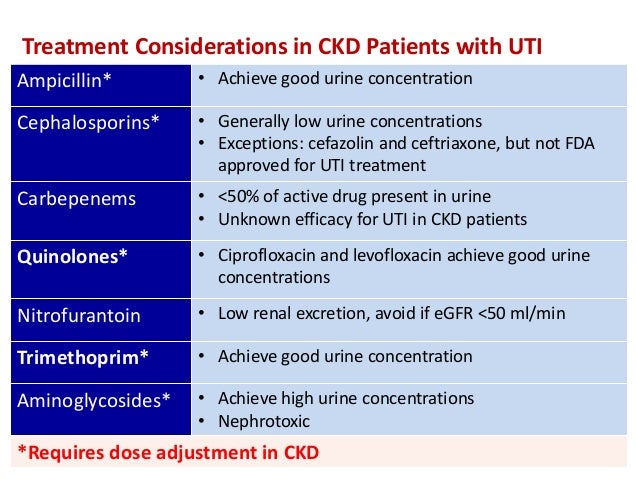
Identify the main drugs that are more likely to be nephrotoxic and how clinicians should proceed with treatment. Outline some renal pathologies that can become a result of nephrotoxic drug administration. Review the importance of care coordination amongst the interprofessional team to improve outcomes for patients with renal disease. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. Gabapentin toxicity and side effects are well-known among nephrologists and fully described in the literature as myoclonic twitches, myopathy, neurotoxicity, etc., particularly in dialysis patients. 2,4 Medications that are harmful to the kidneys are called nephrotoxic medications. Some of these medications only slightly worsen kidney function, while others could cause more serious injury. Your risk for kidney damage depends on your individual health conditions and the medication (s) you’re taking. Drugs eliminated via the kidneys can accumulate during acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) and this can lead to further renal impairment or adverse effects. A review of these drugs is therefore required; any drug which can cause or exacerbate renal impairment should be avoided in AKI, and the appropriateness reviewed in CKD. Where care is needed when prescribing in renal Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia pain associated with shingles, restless leg syndrome, and diabetic neuropathy. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. Chronic kidney disease affects renal drug elimination and other pharmacokinetic processes involved in drug disposition (e.g., absorption, drug distribution, nonrenal clearance [metabolism]). Drug Given the importance of proximal tubule transport of these agents, certain drugs that block hOAT1 and cellular uptake (probenecid) may decrease nephrotoxicity (13–15). In contrast, drugs such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that block apical tenofovir efflux through MRP4 increase kidney injury (13–15). Kidney Dysfunction Overview Analgesic prescribing for patients with kidney disease must consider that: (1) some analgesic medications, so called nephrotoxic drugs, can cause kidney injury or worsen kidney function; (2) kidney dysfunction may impair drug elimination, causing or augmenting adverse effects. Acute Kidney Injury - potentially problematic drugs and actions to take in Primary Care Key Messages Overdose effects can result from continuing intake of renally metabolised medicines in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). Prescribers should review the appropriateness of all medicines in patients at risk of AKI and be prepared to stop treatment if AKI develops. Some medicines may need dose adjustment whilst other medicines may need to be withheld until kidney function is However, carambola, with its unspecified toxin, is nephrotoxic while gabapentin does not seem to affect renal function and its duration of effect depends solely on creatinine clearance. In addition, the adverse effects of gabapentin on the central nervous system vary from person to person. The Renal Drug Handbookhas developed into an essential resource for nephrologists, specialist nurses and pharmacists engaged in the care of these patients. As the field moves forward so also do the therapeutic opportunities, and pitfalls. Fortunately successive editions of the handbook have kept pace with these advances - the present Fifth Edition includes over 900 drug monographs, each Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Population-based cohort study. Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin does not inherently damage kidneys but requires careful consideration when prescribed to individuals with existing renal impairments. Monitoring kidney function regularly while adjusting dosages based on eGFR levels can help mitigate potential risks associated with this medication. Renal impairment affects drug handling, which makes dosing of drugs in renal impairment a key aspect in maintaining their safety. If drug doses are not reduced, this can predispose patients to harm; conversely, overly reducing doses can make drugs, for example antibiotics, ineffective. Drugs can also contribute to or cause direct kidney injury, which needs to be considered when prescribing and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |