Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
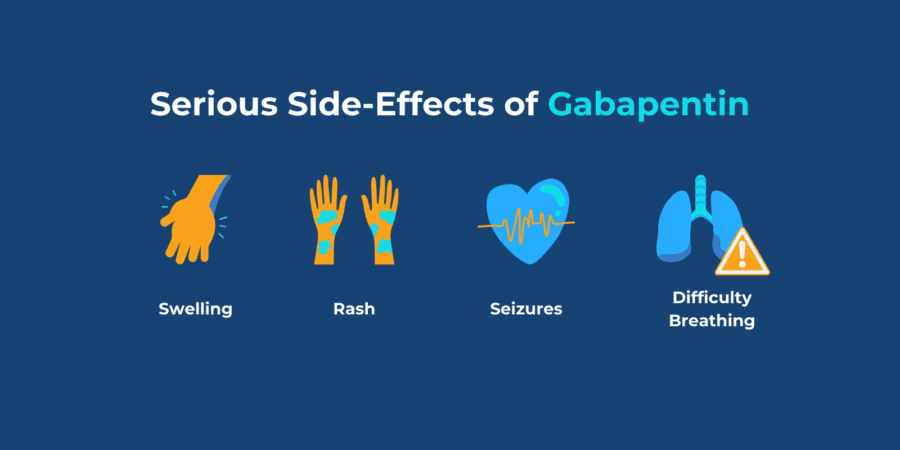
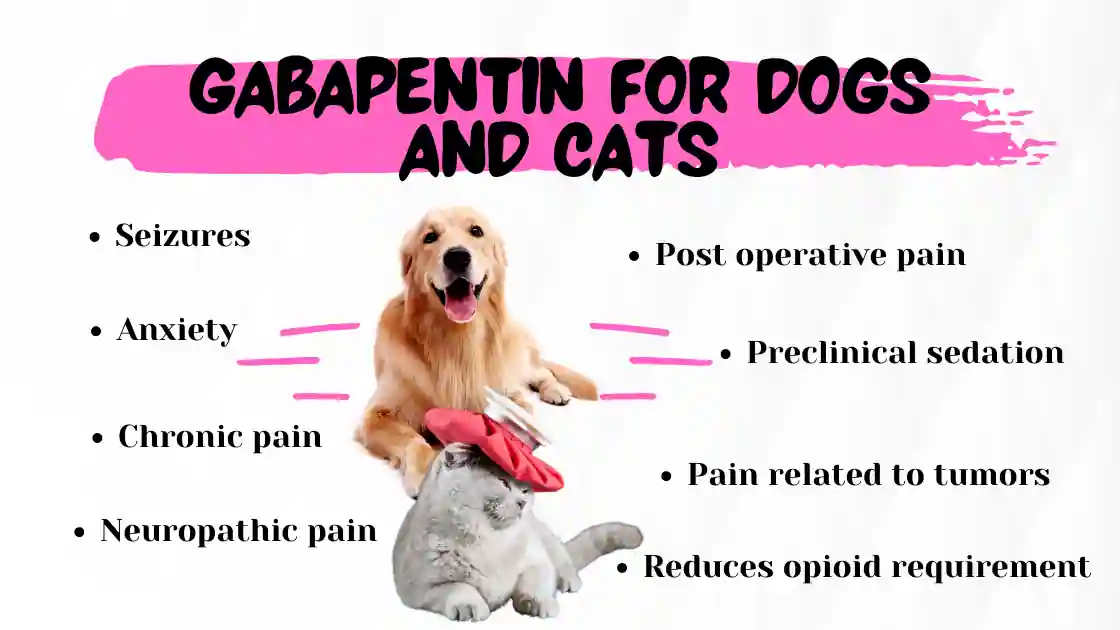
Gabapentin for dogs is an anti-seizure and pain medication commonly prescribed to dogs by veterinarians. Gabapentin for dogs may be helpful for treating chronic pain especially nerve pain that is secondary to neurological diseases such as slipped discs. The most common side effects of gabapentin in dogs include sedation and dizziness. What are the side effects of giving a dog gabapentin? The most common side effects include sedation (sleepiness) and incoordination. Gradual increases of the medication over time is recommended to alleviate these effects. This short-acting medication should stop working within 24 hours, although effects can be longer in pets with liver or kidney disease. The kidneys and liver are needed for the metabolism of gabapentin so it should be avoided by dogs with liver disease or kidney disease. Pregnant or nursing dogs, or dogs taking antacids, hydrocodone or morphine should not take it to avoid drug interactions. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Dogs with liver or kidney disease may have heightened sensitivity to gabapentin, requiring close monitoring and possible dosage adjustments. Additionally, stopping gabapentin suddenly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including increased anxiety and seizures. Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Can gabapentin cause heavy breathing in dogs? How much gabapentin can I give my dog for sedation? Gabapentin should be used with caution for animals with liver or kidney disease, as it will take longer to metabolize. Gabapentin is available in several forms that are human-labeled products: 100 mg (capsules and tablets)Nov 3, 2020. If your dog recently started taking gabapentin and you are wondering about the gabapentin side effects in dogs, this article is for you. Integrative veterinarian Dr. Julie Buzby discusses what side effects to watch for, and how those side effects can be minimized or managed. Plus, she answers seven gabapentin FAQs. Here are some options that are generally considered safer: Gabapentin: Gabapentin is often used for nerve pain and is safe for dogs with kidney disease. It is typically used to manage conditions like arthritis, spinal issues, and post-surgical pain. It does not have significant effects on kidney function, making it a reliable option. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medicine that is used to treat certain conditions in humans. Dive into this vet answer on the use of Gabapentin for dogs. Can gabapentin cause liver or kidney damage in dogs? Gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys in dogs, so it is important to monitor kidney function in dogs receiving long-term gabapentin therapy. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Gabapentin can be used by kidney disease patients, but dosage adjustments are critical. Learn how to safely use gabapentin with kidney issues and discover alternative medications. Dr. Shelby Loos discusses gabapentin for dogs, including what it’s used for, the gabapentin dosage for dogs, and potential side effects. However, this risk is avoided altogether as long as you only give your dog medication that your veterinarian has prescribed. Why might gabapentin not be a suitable medication for my dog? Gabapentin might not be safe in dogs with kidney disease or dogs who are pregnant or lactating. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication for dogs, used primarily to manage chronic pain, especially from conditions like arthritis or neuropathic pain, and to help control seizures. It can be a highly effective treatment option, but when given long-term, some pet owners wonder about the potential side effects. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the long-term effects of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |