Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
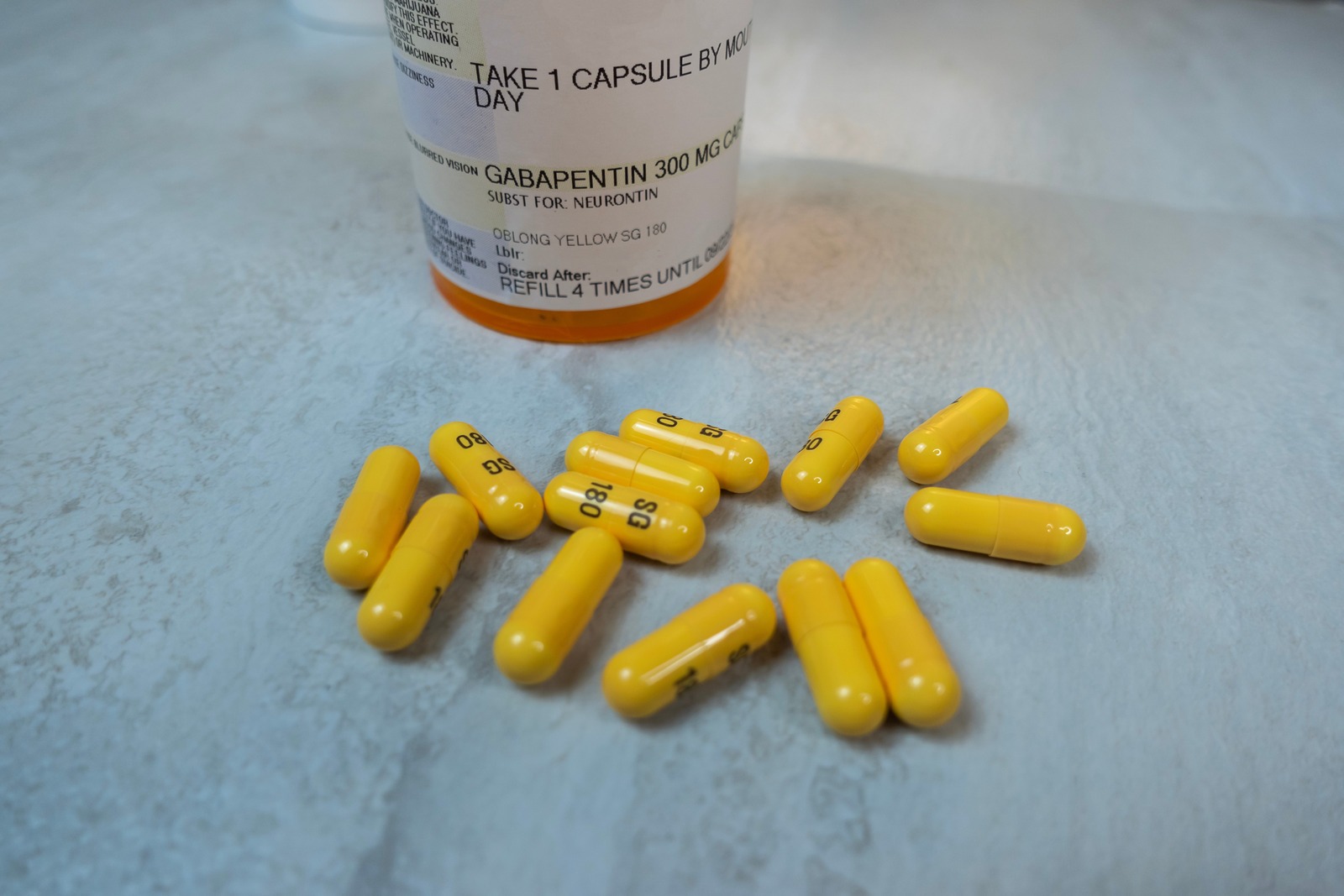 |  |
Explore gabapentin's potential psychological side effects, factors influencing mental health impacts, and strategies for managing risks in this comprehensive guide. Abstract Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Gabapentin and pregabalin have often been prescribed off-label in spite of Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Understanding the effects of Gabapentin on mental health is essential, particularly its potential link to depressive episodes. This medication, often used for pain and seizure management, has a range of side effects that can impact a patient's psychological well-being. Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. Can gabapentin cause brain fog? Yes, gabapentin can cause brain fog in some individuals. Cognitive issues, such as a decrease in alertness, may occur as side effects, often accompanied by dizziness and drowsiness, affecting about 10% of users. While gabapentin is used to manage conditions like nerve pain and menopause symptoms, its impact on cognitive function is a concern for some patients Gabapentin can affect mood and may cause depressive symptoms, though this is considered a rare side effect. While it is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain, some individuals have reported experiencing feelings of sadness or worsening depression during treatment. Furthermore, other measurements of mood, depression, anger-hostility, fatigue, and physical functioning were more effectively managed with gabapentin compared to a placebo. During the same time, Backonja et al reviewed the effect of gabapentin in 165 diabetic neuropathy patients. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Conclusion: It is imperative to screen, identify, and appropriately manage patients with underlying psychiatric disorders prior to initiating pain management with gabapentin. Therefore, it is crucial to raise awareness of gabapentin as a potential cause of depression, aggressive behavior, and suicidal ideation. Gabapentin has gained attention for its use in managing depression, especially in individuals who have treatment-resistant depressive disorders. It is not an FDA-approved indication, but physicians may prescribe it off-label based on clinical judgment. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Discover whether gabapentin effectively treats depression symptoms. Learn about its dosage, side effects, and potential as a depression treatment here. While studies don’t typically show effectiveness for improving symptoms of depression, there is evidence that gabapentin may have some benefit for anxiety disorders. A rat study found that gabapentin produced behavioral changes suggestive of anxiolysis, or feelings of calmness. Today, gabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for various mental health conditions, joining the ranks of other mood-stabilizing medications like lamotrigine, which has shown promise in treating bipolar disorder and depression. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment. Unveiling Gabapentin's Link to Depression and Suicidal Thoughts Investigating the association between gabapentin use and depression Gabapentin is primarily prescribed as an anticonvulsant for seizures and neuropathic pain, but its role in treating depression remains unclear. Despite being used off-label for mood disorders, significant evidence directly linking gabapentin to effective treatment Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
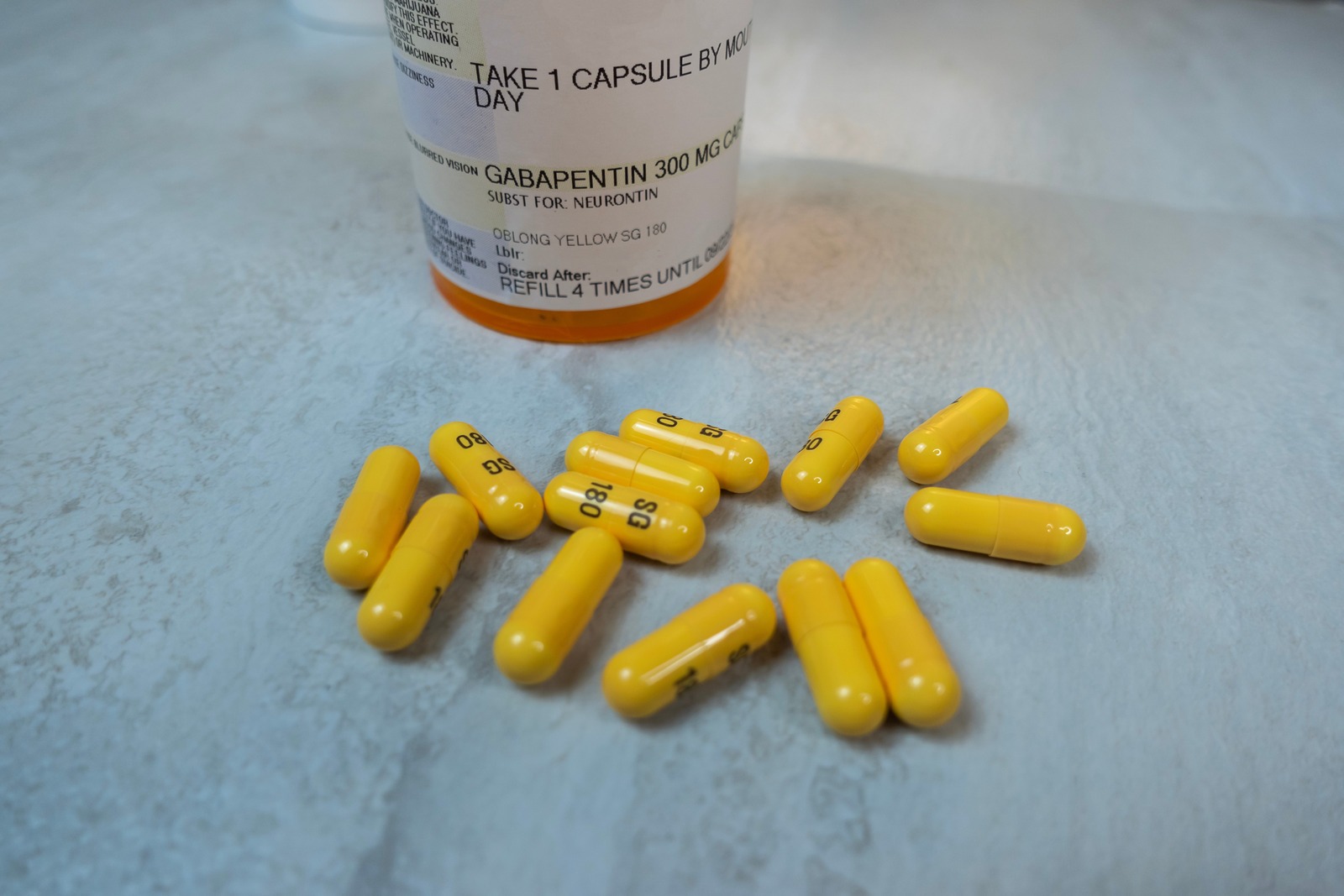 |  |