Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
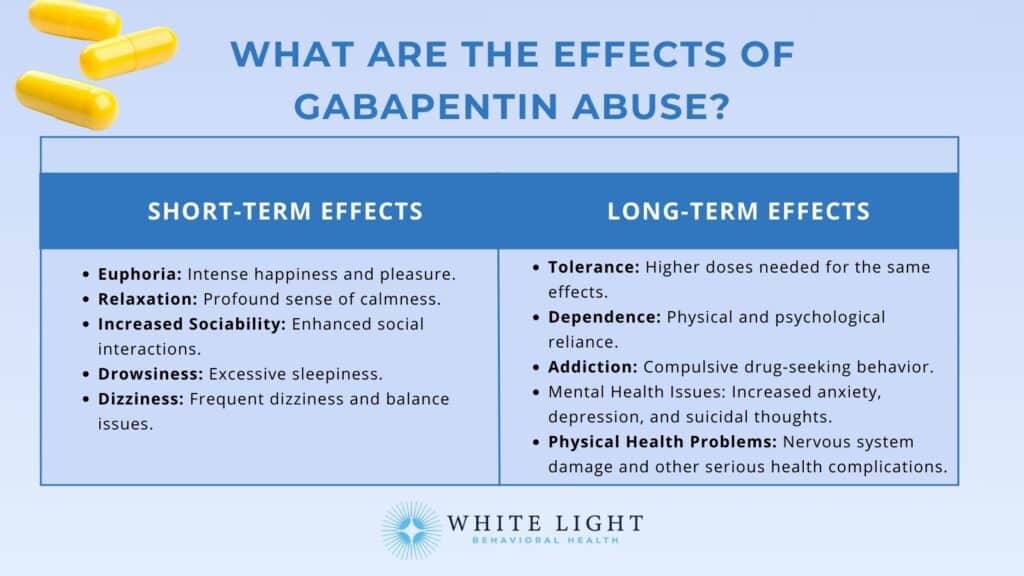
The gabapentin-induced behavioural changes in children and the mood changes with hypomanic fea-tures in adults are both characterized by excessive activity and impulsive behaviour. The behavioural changes in children are distinguished by the absence of elevated or euphoric mood. Characteristically, chil-dren with chronic epilepsy and static encephalopathy with behavioural problems (e.g. ADHD Understanding Gabapentin’s Psychiatric Effects Potential psychiatric side effects of gabapentin Gabapentin, commonly prescribed for seizures and neuropathic pain, has been reported to cause a range of psychiatric side effects. While it is generally considered safe, some users have exhibited significant mood changes, including increases in depression, anxiety, and irritability. Notably Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Gabapentin is not typically considered a mood enhancer. It is primarily used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and, in some cases, mental health conditions like insomnia or bipolar disorder. While gabapentin may help stabilize mood in certain situations, it works in different ways compared to traditional mood enhancers like antidepressants or mood stabilizers. Some people might experience Although Gabapentin has been used to treat seizures, there is evidence to suggest it may be a method for treating anxiety and depression. Learn more! Preamble to Gabapentin Gabapentin has emerged as a significant player in the pharmacological landscape, especially in contexts that relate to pain management and mood disorders. This section is crucial because it lays the groundwork for understanding how this medication interplays with depression, an increasingly common psychological condition. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment. This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. 1. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Clinical trials even found that gabapentin may be a good alternative to Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant. It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder. Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding (84). Exploring Gabapentin's Impact on Mental HealthIntroduction: Unveiling the Link Between Gabapentin and Mood Changes Gabapentin is a well-known medication primarily used as an anticonvulsant for treating seizures and relieving nerve pain. It is frequently prescribed off-label for various conditions, including some mood and anxiety disorders. However, concerns about its effects on mental health Explore the impact of Gabapentin on your emotions and physical sensations. Learn how it affects mood, anxiety, and potential side effects. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Discover how gabapentin affects emotions, from potential benefits to side effects. Learn about managing mood changes and the importance of personalized care. Unveiling Gabapentin's Link to Depression and Suicidal Thoughts Investigating the association between gabapentin use and depression Gabapentin is primarily prescribed as an anticonvulsant for seizures and neuropathic pain, but its role in treating depression remains unclear. Despite being used off-label for mood disorders, significant evidence directly linking gabapentin to effective treatment Gabapentin can cause mood swings in some individuals, particularly during dosage adjustments or when discontinuing the medication. Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures. Over the years, it has gained popularity for a variety of off-label uses, including anxiety and mood disorders. In conclusion, gabapentin’s journey from an anticonvulsant to a tool in mental health treatment is a testament to the complex and interconnected nature of our brains. While it’s not a panacea, it offers hope and potential relief for many individuals battling anxiety, mood disorders, and other mental health challenges.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |