Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
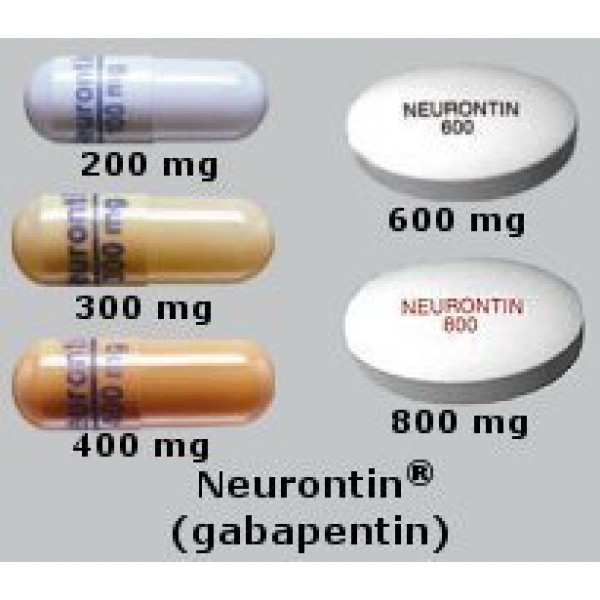 |  |
 |  |
 | /https://cms-prod.s3-sgn09.fptcloud.com/00005247_neurontin_300mg_7760_6066_large_fd00df7738.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. A 60 year-old man presented with acute congestive heart failure and atrial fluter 7 days after taking gabapentin prescribed for peripheral neuropathy. Gabapenin was discontinued and he became asymptom-atic after standard therapy for heart failure and atrial fluter ablaion. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to With rapidly increasing usage of gabapentin for approved and off-label indications, it is important to identify unintended adverse effects of this drug as they are considered safe alternatives to opioids. New-onset atrial fibrillation could be induced by gabapentin in young individuals. Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate All cases of peripheral edema or heart failure [Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) Hight-Level Term ‘total volume fluid increased’ or High-Level Group Term ‘heart failures’] involving gabapentin or pregabalin and recorded between January 1, 1994 and April 30, 2020 were selected. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Purpose of Review The objective of this manuscript is to describe the cardiovascular effects of the gabapentinoids gabapentin and pregabalin. Recent Findings The most frequent adverse effects of gabapentin and pregabalin affect the central nervous system, such as somnolence and fatigue. Additionally, pregabalin, and a much lesser extent, gabapentin, may adversely affect the cardiovascular Fibromyalgia, a chronic pain disorder, impacts approximately 2% of adults in the US. Gabapentin and pregabalin are common treatments to manage fibromyalgia-related pain. Our recent study showed the risk of adverse cardiovascular events increased in Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, Heart failure is a common, costly, and debilitating syndrome that is associated with a highly complex drug regimen, a large number of comorbidities, and a large and often disparate number of healthcare providers. All of these factors conspire to increase the risk of heart failure exacerbation by direct myocardial toxicity, drug-drug interactions, or both. This scientific statement is designed Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings In conclusion, the accumulated evidence suggests that both gabapentin and pregabalin may increase the incidence of new onset heart failure. Clinical symptoms may occur days after the beginning of treatment and are mostly reversible upon its discontinuation. A recently published report describes the case of a patient who developed non-ischemic cardiomyopathy following initiation of gabapentin therapy for pain management. Background: Gabapentin is a commonly used medication used as an anti-convulsant or analgesic. The well-known side-effects of gabapentin are dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue. In rare cases, it can lead to development of new onset congestive heart failure (CHF) or decompensation of pre-existing CHF. We present a case of gabapentin induced CHF with rapid resolution after discontinuing the Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and is used to treat seizures and nerve pain, but does gabapentin affect your heart rate? Find out more about the drug here. Objectives & methods: All cases of peripheral edema or heart failure involving gabapentin or pregabalin reported to the French Pharmacovigilance Centers between January 1, 1994 and April 30, 2020 were included to describe their onset patterns (e.g., time to onset). In patients with diabetic neuropathy who were prescribed gabapentin and pregabalin, there is an increased risk for heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism with long-term use. Our findings suggest that increased risk fo Then, peripheral edema developed associated with the recommended dose of gabapentin, which was used in place of pregabalin. Despite the lack of any published evidence, the New York Heart Association issued a warning about using caution when prescribing pregabalin to type III-IV heart failure patients.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | /https://cms-prod.s3-sgn09.fptcloud.com/00005247_neurontin_300mg_7760_6066_large_fd00df7738.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |