Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1182285243-fcfa18e81ea742ae932201ddd6043411.jpg) |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
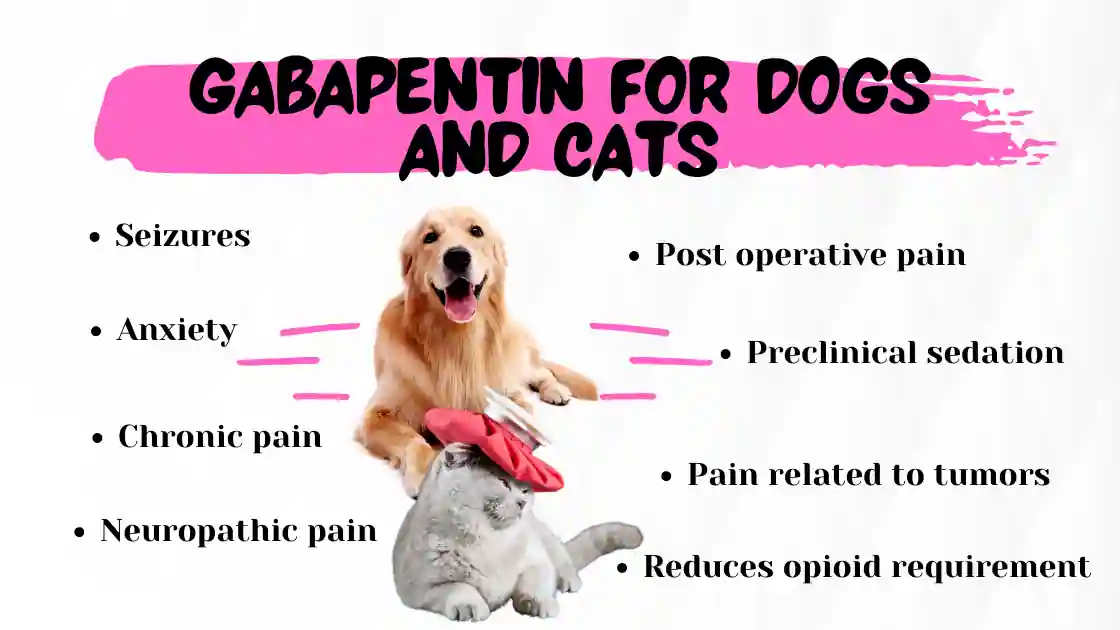
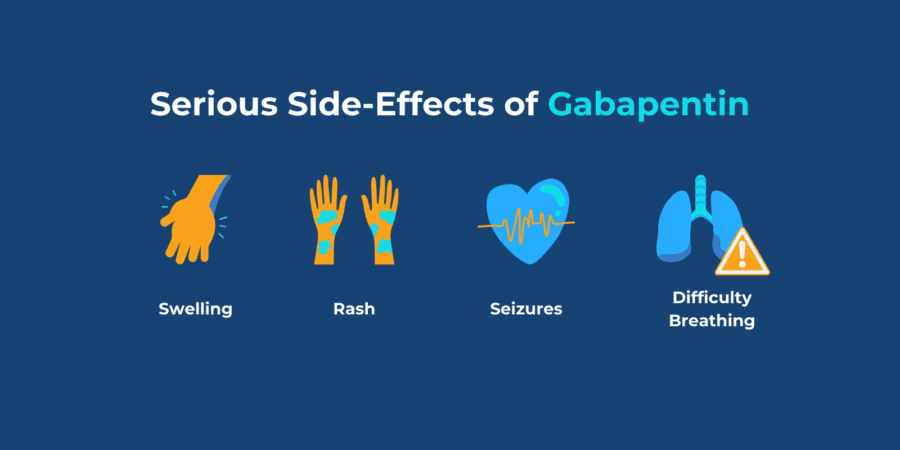
Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin offers notable benefits, particularly in managing seizures and nerve pain, but potential mental health side effects require careful consideration. While primarily prescribed for these conditions, Gabapentin is often used off-label for anxiety and mood-related disorders. Depression Although gabapentin is not a first-line treatment for depression, it is sometimes prescribed in conjunction with other antidepressant medications. It may help alleviate symptoms such as persistent sadness, loss of interest, and emotional numbness. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Understanding Gabapentin Use Gabapentin is a medication primarily utilized for its antiepileptic properties. While its primary use is for the treatment of seizures, this versatile drug has a variety of therapeutic benefits and is also employed for off-label uses. Therapeutic Benefits Gabapentin serves a vital role in managing various conditions related to the nervous system. In addition to its Link between gabapentin and depression Does gabapentin affect your mood and can it cause depressive symptoms? Gabapentin can affect mood and may cause depressive symptoms, though this is considered a rare side effect. Since depression often involves imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, understanding how gabapentin interacts with these systems is crucial for evaluating its efficacy in treating depressive symptoms. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication when used for anxiety. Understanding Gabapentin's Connection to Mood Changes Gabapentin, a medication primarily formulated to treat seizures and manage nerve pain, is often used off-label for various mental health conditions. Despite its benefits, there is ongoing concern about its potential impact on mood and mental health, particularly its association with depression. Gabapentin has gained attention for its use in managing depression, especially in individuals who have treatment-resistant depressive disorders. It is not an FDA-approved indication, but physicians may prescribe it off-label based on clinical judgment. Understanding the effects of Gabapentin on mental health is essential, particularly its potential link to depressive episodes. This medication, often used for pain and seizure management, has a range of side effects that can impact a patient's psychological well-being. Is gabapentin a good option for treating anxiety disorders? This is what research says and why caution is important. Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Discover gabapentin uses and benefits for nerve pain, epilepsy, and anxiety, highlighting its efficacy as an anticonvulsant and neuropathic pain reliever, with related treatments like fibromyalgia and restless leg syndrome management. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is not commonly used to treat depression, but some recent studies indicate it may treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and alcohol use disorder. A normal dose of gabapentin for adults can be anywhere from 100 mg to 3600 mg each day. Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, weakness, and upset stomach.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1182285243-fcfa18e81ea742ae932201ddd6043411.jpg) |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |