Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
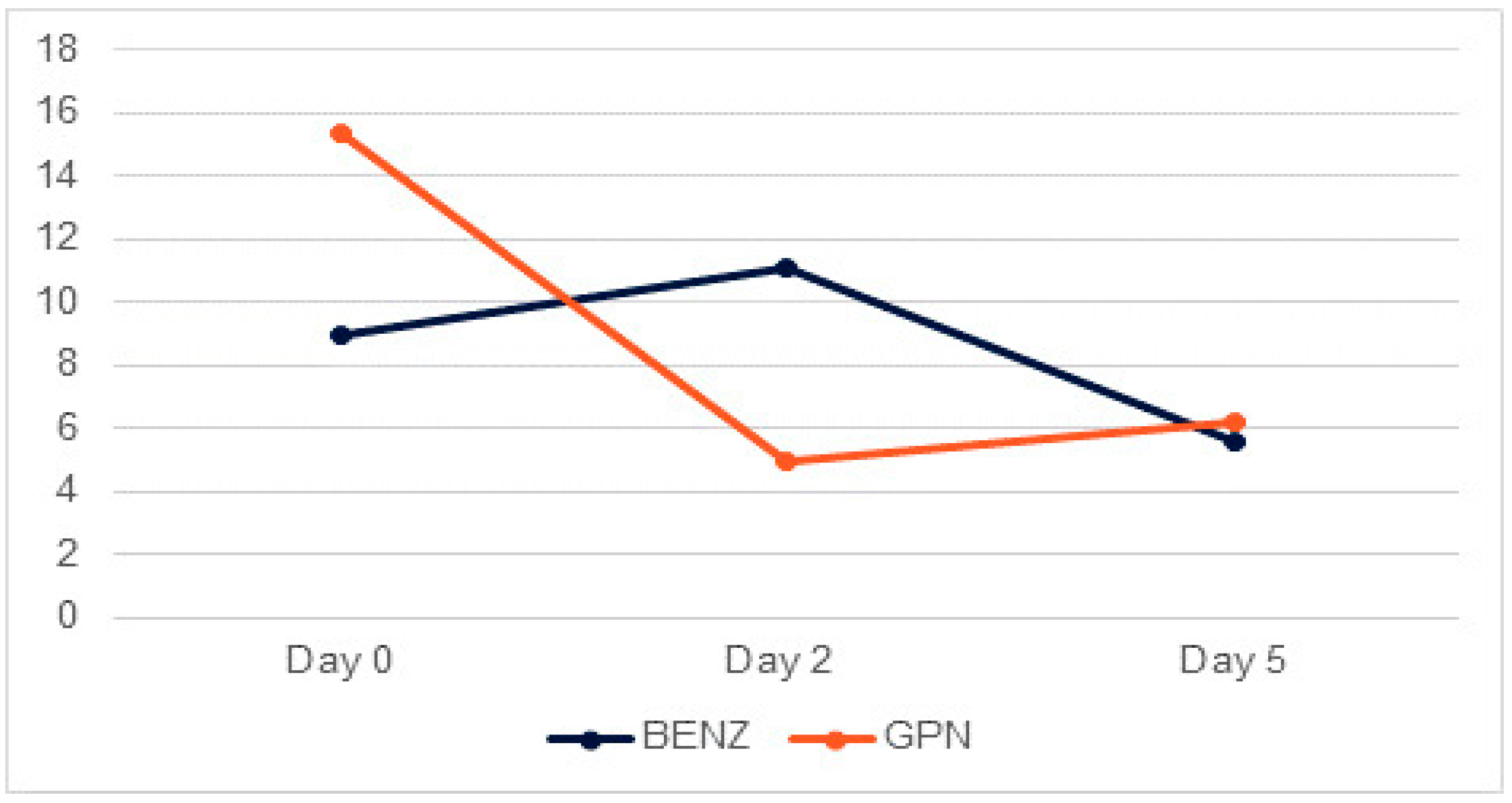
Hi, Last time I talked to my psychiatrist she mentioned that she wanted to try to switch me to a different anti anxiety med instead of Klonapin. This med I think is Gabapentin and she was looking to put me on it long term. I have read that a lot of people have not had good experiences with this a Learn about the use of Neurontin (gabapentin) in managing withdrawals from benzodiazepines and its effectiveness in reducing symptoms and promoting recovery. Similar to alcohol and benzodiazepine withdrawal, gabapentin affects gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a key neurotransmitter in the brain. Common withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, headaches, and irritability. Benzodiazepines are currently the gold standard for treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has growing evidence to support its use in the treatment of alcohol use disorder, however there is limited evidence regarding its role in the treatment Chronic use of a benzodiazepine can cause physiologic dependence and the potential for a withdrawal syndrome upon rapid discontinuation. Benzodiazepine dependance can develop from use of prescribed, illicit (ie, non-prescribed use of compounds used medically), and designer (ie, compounds not used medically) agents. The combination of gabapentin and benzodiazepine can be safe in the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to data presented at American Psychiatric Association annual meeting, which Wanted to see what opinions were on taking gabapentin for the crippling anxiety that comes with benzo withdrawals. I’ve real a couple of success stories where it helped a couple of patients with PAWS and then I’ve also read where the gabapentin didn’t work. al is necessary. Gabapentin, an anxiolytic drug that is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, is a potential candidate for modulating benzodiazepine withdrawal. Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other Background and Objectives: Gabapentin has shown promise as a potential agent for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of gabapentin as a benzodiazepine-sparing agent in patients undergoing alcohol From a few reports I’ve had, patients have been prescribed the anticonvulsant dose of neurontin for benzodiazepine withdrawals. This is cause for concern because such a dose is equivalent to high levels of klonopin (5-15mgs) and could lead to difficulty in tapering from neurontin. There is an increasing interest in anticonvulsants for the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, and among the newer substances gabapentin seems particularly promising due to its gabaergic and its glutamate-antagonistic activity. Benzodiazepine (BZD) use disorders are a common clinical problem among methadone maintenance treatment patients and have adverse effects on clinical outcomes. To evaluate gabapentin for the outpatient treatment of BZD abuse or dependence in Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a prescription anticonvulsant medication that is prescribed to treat neuropathic (nerve) pain and seizures. [1] Although gabapentin abuse is not as common as other forms of prescription drug abuse, studies have documented increasing reports of people misusing the medication with other drugs like alcohol, benzodiazepines, and opioids. [2] Taking gabapentin for long In their study, they compared two groups of patients: One group consisted of patients who were given gabapentin to treat benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms like neuropathic pain and anxiety. Overall, the clinical presentation of gabapentin withdrawal appears to be similar to that of benzodiazepines: agitation and anxiety, diaphoresis, somatic pain, confusion, tremulousness, gastrointestinal distress, and tachycardia or palpitations. These results suggest the potential use of gabapentin as an adjunct to the use of benzodiazepines for treating benzodiazepine withdrawal. The limitations of this study included a small sample size and variability in medication management strategies across the sample. Addition of an anticonvulsant (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin]) should be considered for high-dosage withdrawal. The scientific rationale is profound: by mimicking the brain’s natural regulatory processes at about 80% bioavailability, Gabapentin helps smooth out the intense neurological disruptions caused by benzo withdrawal. We describe six cases where use of gabapentin during benzodiazepine withdrawal resulted in a well-tolerated accelerated withdrawal. A middle-aged female presented to the emergency department after an intentional clonazepam overdose. She reported ingesting thirty 1 mg tablets intentionally. Although trials have examined the use of gabapentin for ethanol withdrawal, [10–15] we are unaware of studies that used gabapentin for benzodiazepine-resistant ethanol withdrawal symptoms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |