Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
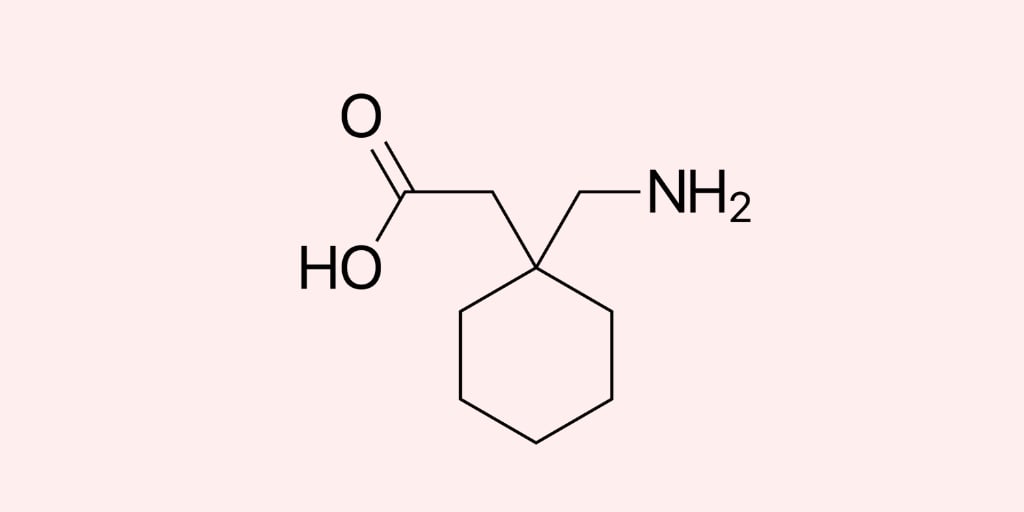
Learn about important nursing considerations for gabapentin, including dosage, side effects, potential drug interactions, and patient education. By understanding gabapentin’s pharmacology, indications, and nursing considerations, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and enhance patient quality of life. Continuous vigilance, patient-centered education, and interdisciplinary collaboration are key to successful gabapentin therapy. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin Related Nursing Diagnoses Acute pain Risk for injury Risk for infection (related to decreased white blood count) Risk for suicide, impaired oral mucous membrane, constipation as potential side effects of gabapentin Nursing Assessment Assess for allergies to gabapentin Monitor for changes in neurological status, changes in mood, or thoughts of suicide Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin is one of the top 100 drugs prescribed in the US, so there’s a very good chance it will show up on NCLEX or your nursing school exams. Let’s go through the key things you need to know about this medication using the Straight A Nursing DRRUGS framework. D: Drug Class Gabapentin (brand name Neurontin) is classified therapeutically in a few different ways. As an anticonvulsant, an The Eleventh Edition of Lehne’s Pharmacology for Nursing Care provides a thorough understanding of key drugs and their implications for nursing care. This text, written by renowned nursing educators, helps you comprehend and apply pharmacology principles. Nursing considerations Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output Interventions Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. Introduction In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. What is the generic name? GABAPENTIN What is the Trade Name for GABAPENTIN? Neurontin What are the Indications for GABAPENTIN? 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE NEURONTIN ¬Æ is indicated for: Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Identify appropriate indications for use of gabapentin. Relate general characteristics of gabapentin to specific patient situations. Apply nursing process considerations for gabapentin to specific patient situations. Correctly calculate dosage for gabapentin. Gabapentin (Neurontin) MoA: Increases release of GABA into the synapse. Indications: Seizures Side Effects: Fatigue, Xerostomia, Dizziness Drug Interactions: Antacids Nursing Implications: Monitor for possible suicidal ideation. Educate Patient on reporting changes in vision, hallucinations, and fever to their healthcare provider. Neurontin Pre-Administration Assessment: Post Administration Evaluation: Nursing Considerations: Gabapentin Medication GridNCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Pharmacology [Internet]. 2nd edition. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2023. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |