Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 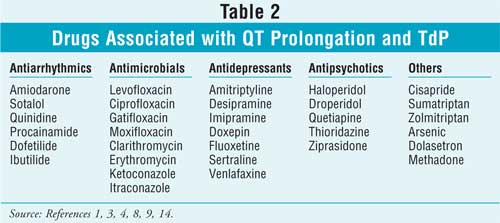 |
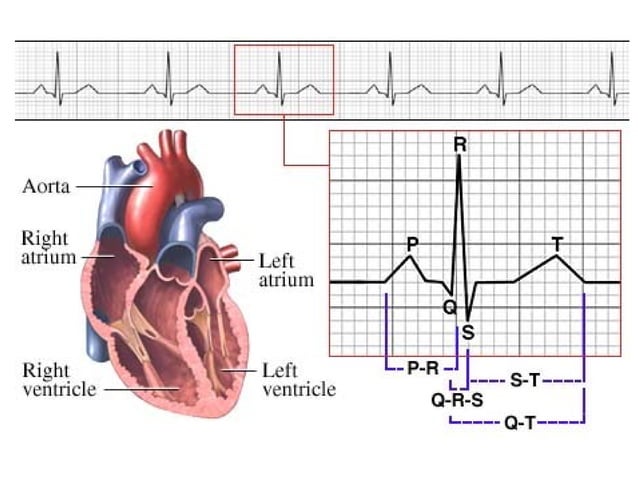
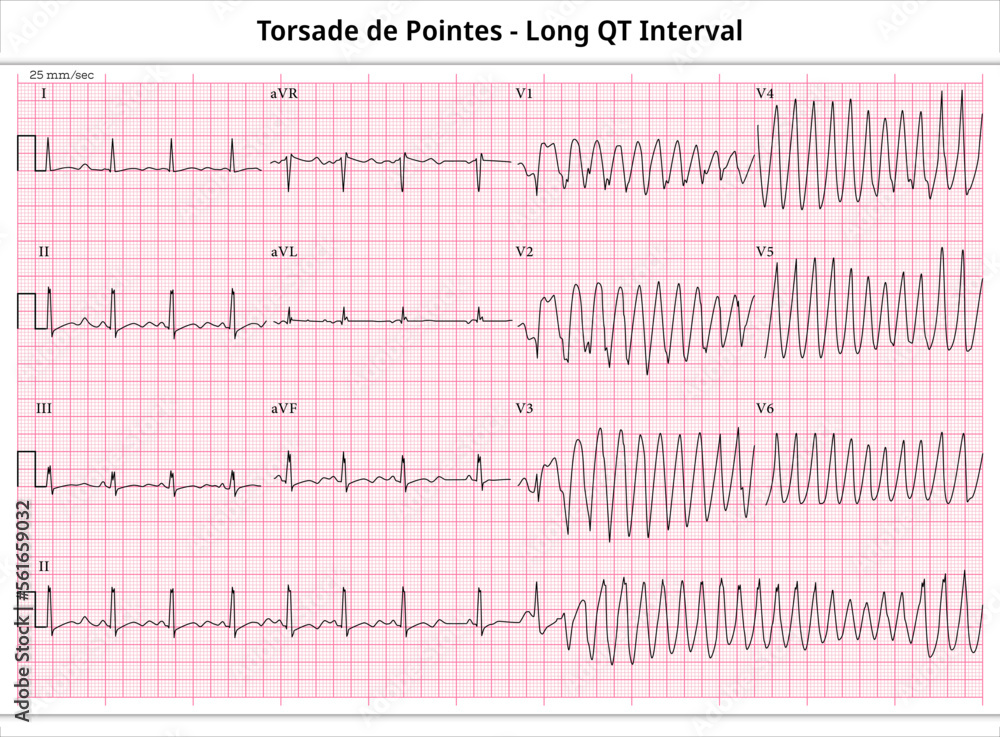
A comprehensive list of conditions and drugs that may prolong the QT interval, and cause torsade de pointes (TdP) and long QT syndrome (LQTS) is presented below. Slow heart rate prolongs the repolarization phase, making an individual vulnerable to drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval. Heart failure has been associated with extended action potentials by blocked IKr channels, leading to an increased risk of drug-induced arrhythmias. A QT-concentration relationship was reported with moxifloxacin. Gabapentin exposures were dose-proportional with gabapentin enacarbil doses of 1200 and 6000 mg. The most commonly reported adverse events with gabapentin enacarbil 6000 mg were dizziness and somnolence (60.0% and 54.0%, respectively). Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a cardiac conduction disorder characterized by prolongation and increased dispersion of ventricular repolarization, manifested by lengthening of the QT interval on the surface electrocardiography (ECG). Pregabalin (PRG) is a new antiepileptic drug that has been used as supportive therapy for partial seizures in patients. Although many neuro-psychiatric and non-cardiac drugs are known to prolong ventricular repolarization as manifested by QTc prolongation on ECG of which provokes torsades de pointes Many drug therapies are associated with prolongation of the QT interval. This may increase the risk of Torsades de Pointes (TdP), a potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. As the QT interval varies with a change in heart rate, various formulae can adjust for this, producing a 'corrected QT' Prolongation of the QT interval can lead to a life threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsades de pointes which can result in sudden cardiac death. The risk of torsades de pointes depends on patient factors and current medication. The unexpected and catastrophic cardiovascular effects of psychotropic drugs are well described albeit uncommon. The list of drugs which have been associated with prolonging QT interval and hence potentially causing Torsades de pointes is Prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG is also associated with arrhythmia risk and sudden cardiac death. Congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS) comprises a group of arrhythmia disorders, arising from cardiac channelopathies in both sodium and potassium channels. Summary: Long qt syndrome is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Long qt syndrome when taking Gabapentin. A definitive QT/QTc study of healthy human subjects showed no effect on QTc interval after either a single low dose (1200 mg) or high dose (6000 mg) of oral gabapentin enacarbil (Fig. 1) [17 ••]. Case reports suggest the potential for these drugs to enhance QTc prolongation in patients receiving one or more known QTc–prolonging medications. Antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers and some antidepressants are known to interact badly with it. Drugs which people with Long QT Syndrome should avoid; Below is a list of the drugs that people with Long QT Syndrome should avoid. A similar list can also be found by clicking here. The length of the QT interval represents the time required for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Prolongation of ventricular repolarization can result in fatal ventricular arrhythmias [3]. Faster heart rates can shorten the QT interval [4], so it is often adjusted for rate and reported as the heart rate corrected (QTc) interval. The degree of QT prolongation is correlated to the level of risk, with severe prolongations being associated with much higher risk. The most common etiology is acquired prolongation due to medication use, followed by electrolyte abnormalities. Definitions for QT prolongation vary in the literature, but for men QTc >440 msec and for women QTc >470 msec are commonly used. The risk of TdP increases with increasing QTc, for every 10 msec increase, there is a ~5-7% increase in the risk of arrhythmic events. When QTc is greater than 500 msec for both men and women and/or an increase of >60 msec from baseline, risks are higher, and urgent Prolongation of the QT interval above 470 ms for men and 480 ms for women should be regarded as abnormal [4]. Several risk factors for QT prolongation have been identified, including female sex, advanced age, drug-drug interactions, genetic predisposition, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart failure, and bradycardia [5, 6]. Christoph Klivinyi and Helmar Bornemann-Cimenti Long QT syndrome is a cardiac repolarization disorder and is associated with an increased risk of torsades de pointes. The acquired form is most often attributable to administration of specific medications and/or electrolyte imbalance. This review provides insights into the risk for QT prolongation associated with drugs frequently used in the Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines INTRODUCTION Many drugs are notoriously known to prolong the QT interval, especially those used in cardiology and psychiatry practice. QT prolongation can remain asymptomatic or lead to torsades de pointes (TdP), a rare tachyarrhythmia which can be life-threatening or nearly fatal due to ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death. In 2005, the International Conference on Harmonisation Some psychotropic medications have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval and QT prolongation, especially in those with medical illness, and are linked to lethal ventricular arrhythmias, such as Torsades de Pointes (TdP). In 2013, we published a review of QT prolongation, TdP, and psychotropic medications.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |