Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
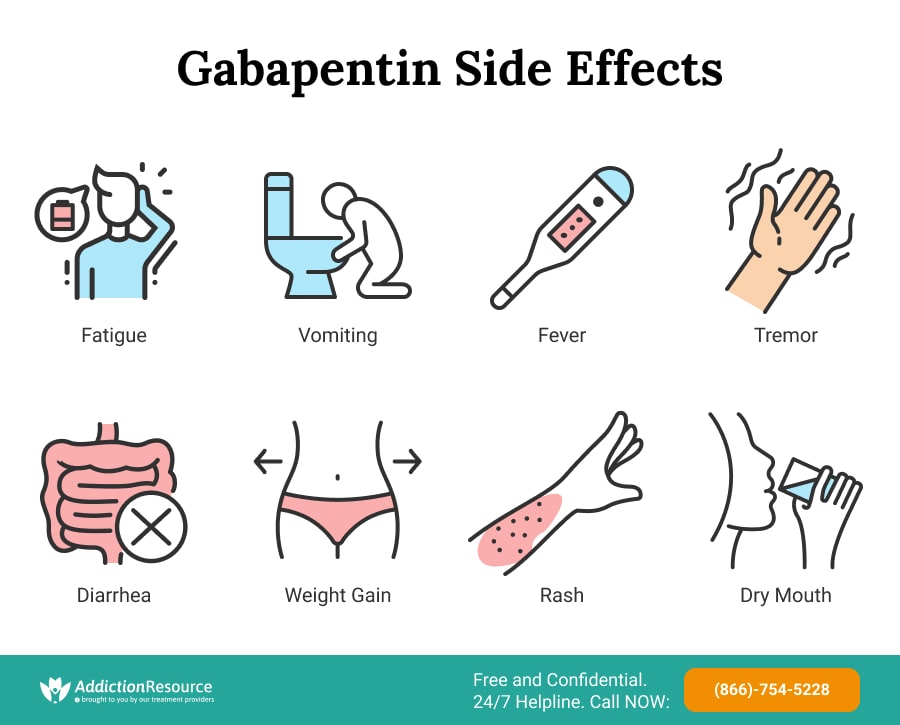
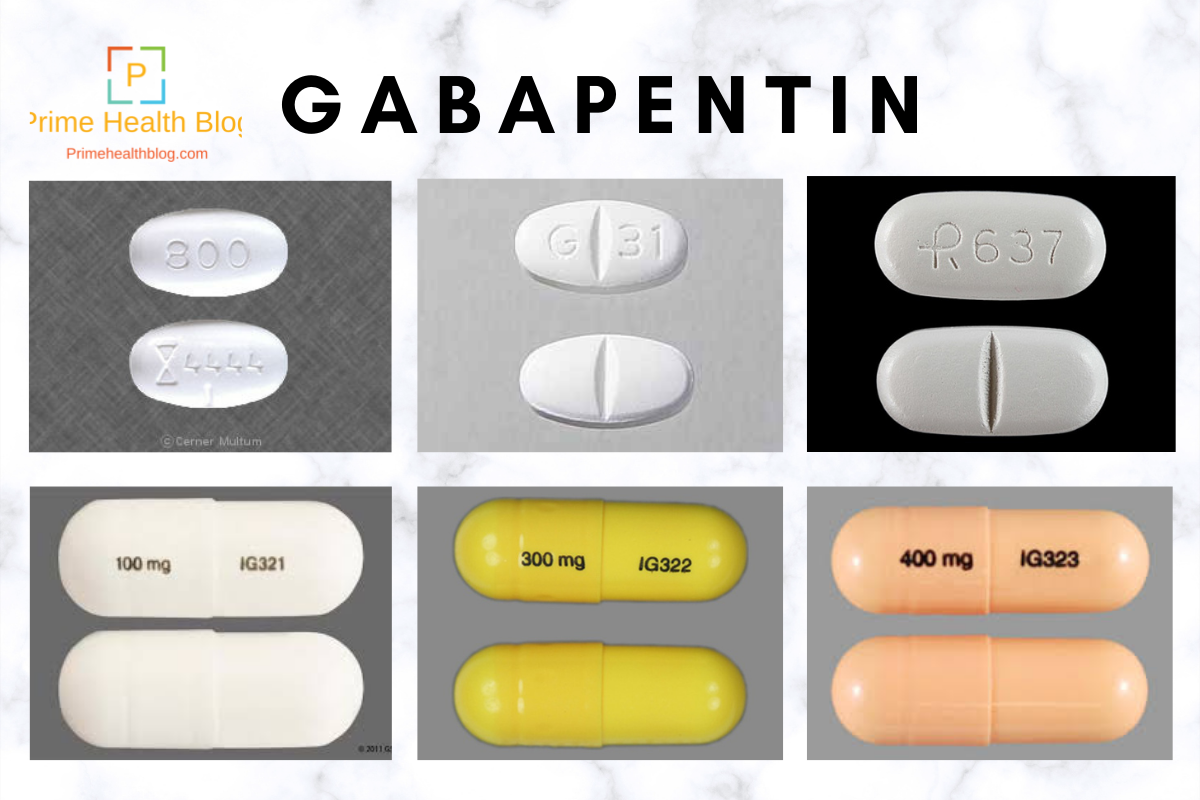
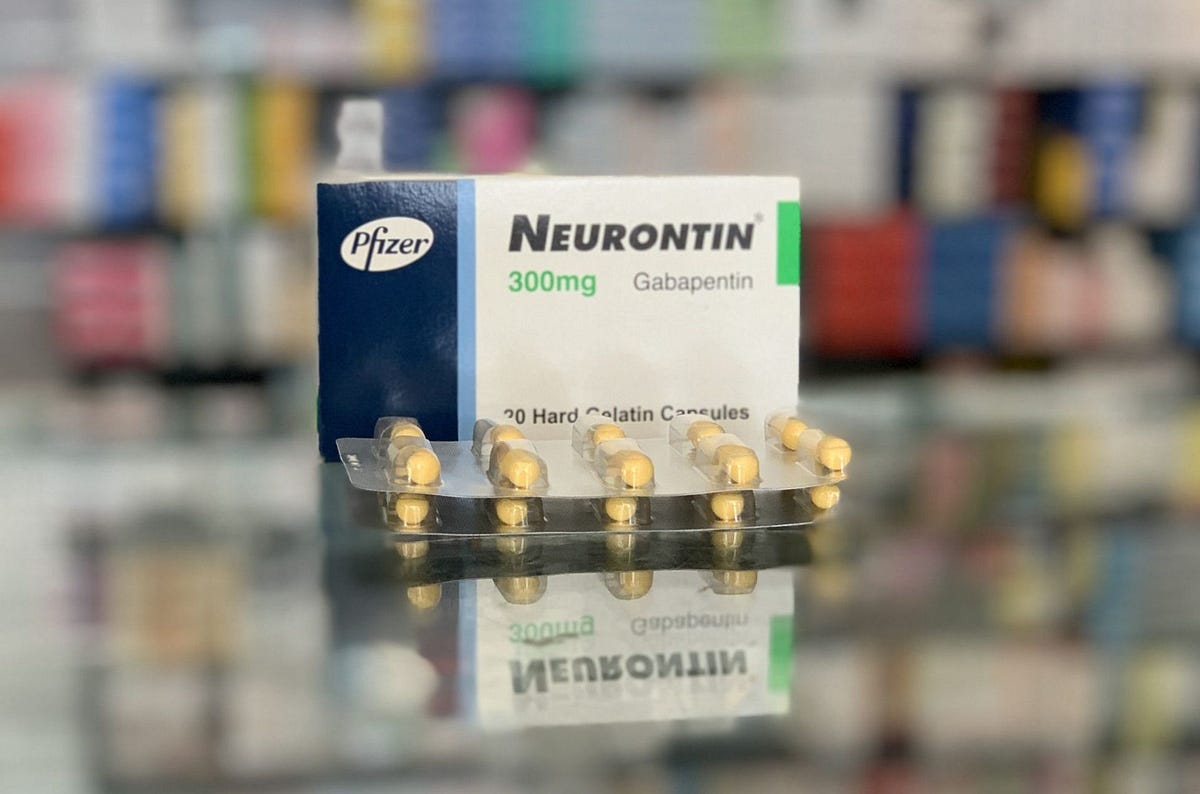
Gabapentin (Neurontin) is prescribed for epilepsy and nerve pain, but some people may take gabapentin for sleep. Learn about whether off-label gabapentin works for sleep disorders. Too many nights of sleeplessness due to insomnia can cause your mood and health to nosedive. Learn how gabapentin can help you sleep. The relationship between gabapentin and its sedative effects is critical to understanding how this medication can be applied in managing insomnia. Originally designed for treating neuropathic pain and seizure disorders, gabapentin has garnered attention for its potential to aid in sleep regulation. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that may help you sleep. That may be why it has been prescribed for people with insomnia, even though it is not approved for that use. However, gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat a sleep disorder called restless legs syndrome (RLS). One of the most common side effects of gabapentin is Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings While gabapentin can be effective for improving sleep quality in some individuals, it’s essential to recognize that using this medication may also introduce certain risks. Many patients report experiencing side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired coordination. Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. Drowsiness is one of the most commonly reported Gabapentin side effects, which is why it is sometimes prescribed as a sleep aid. Research has explored its effects on sleep in people with primary insomnia and insomnia linked to other health conditions. The exact mechanism by which gabapentin can cause insomnia is not fully understood. However, it's thought that the medication may disrupt the normal sleep-wake cycle by affecting the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. NHS medicines information on side effects of gabapentin and what you can do to cope. Insomnia is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Vitamin D3, and have Multiple sclerosis. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. The Timeline of Gabapentin’s Effects Understanding how quickly gabapentin takes effect and how long its benefits last is crucial for patients using the medication for sleep. Gabapentin for Sleep: Timeline and Effectiveness provides a detailed look at the onset and duration of gabapentin’s sleep-promoting effects. Gabapentin Discontinuation Syndrome (aka Withdrawal): No one should ever discontinue gabapentin abruptly. Like so many medications that affect the central nervous system, sudden withdrawal may lead to unexpected side effects. Some that have been reported include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, sweating and even seizures. Sadly, though, the FDA gives very little guidance to prescribers about Gabapentin helps calm the nervous system, which is why it can affect sleep. While prescribed for insomnia, you may experience sleep disruptions when taking it. Learn about the side effects of Neurontin (gabapentin), from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Some studies have found that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical restoration and cognitive function. Additionally, it may reduce sleep fragmentation, leading to fewer nighttime awakenings and improved sleep continuity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |