Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
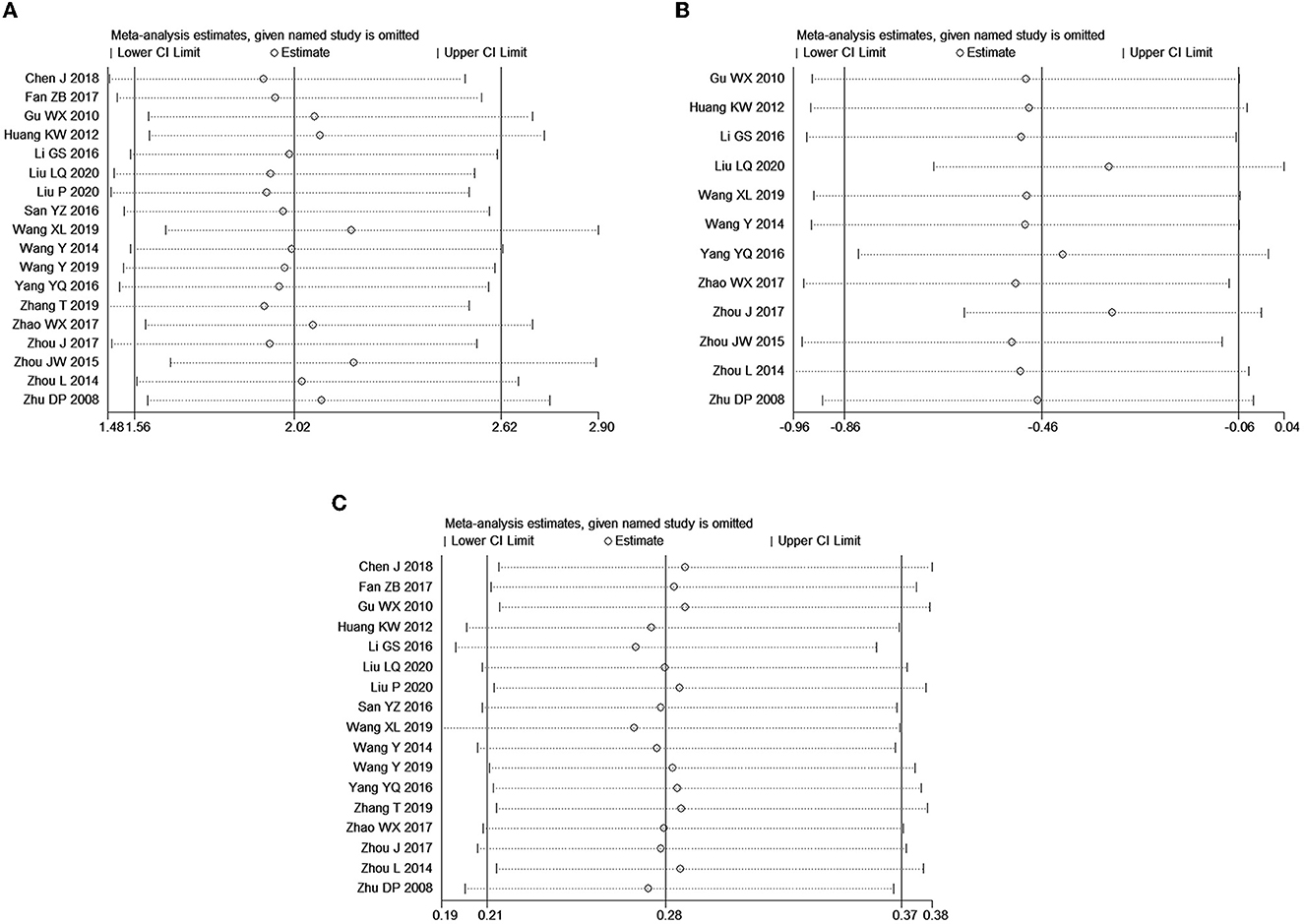 |  |
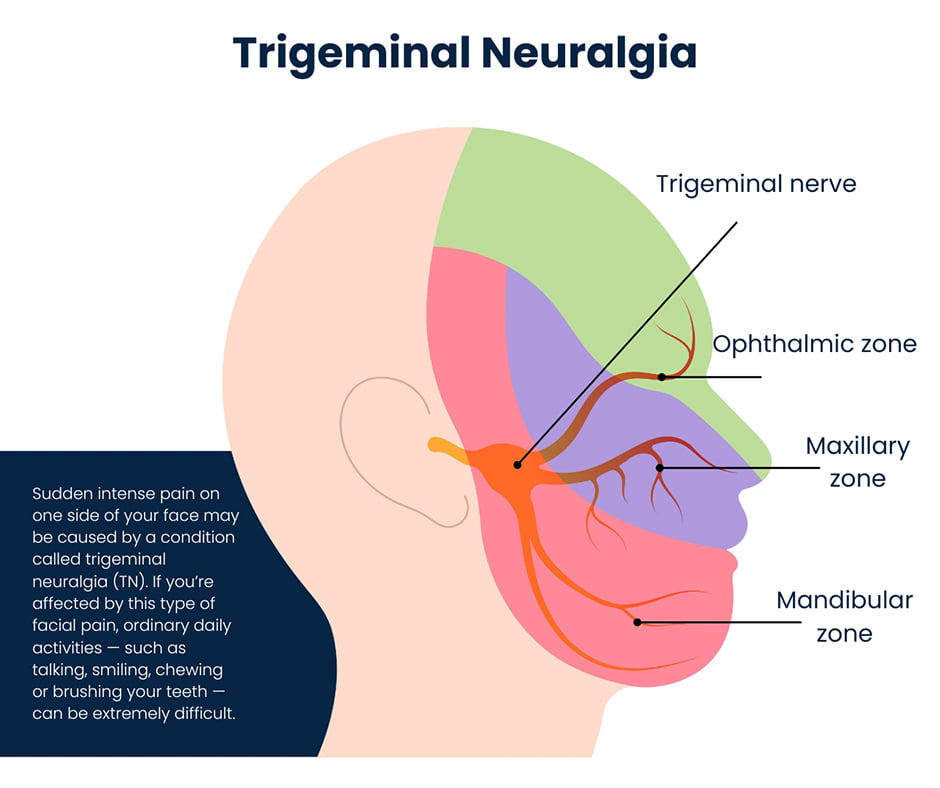
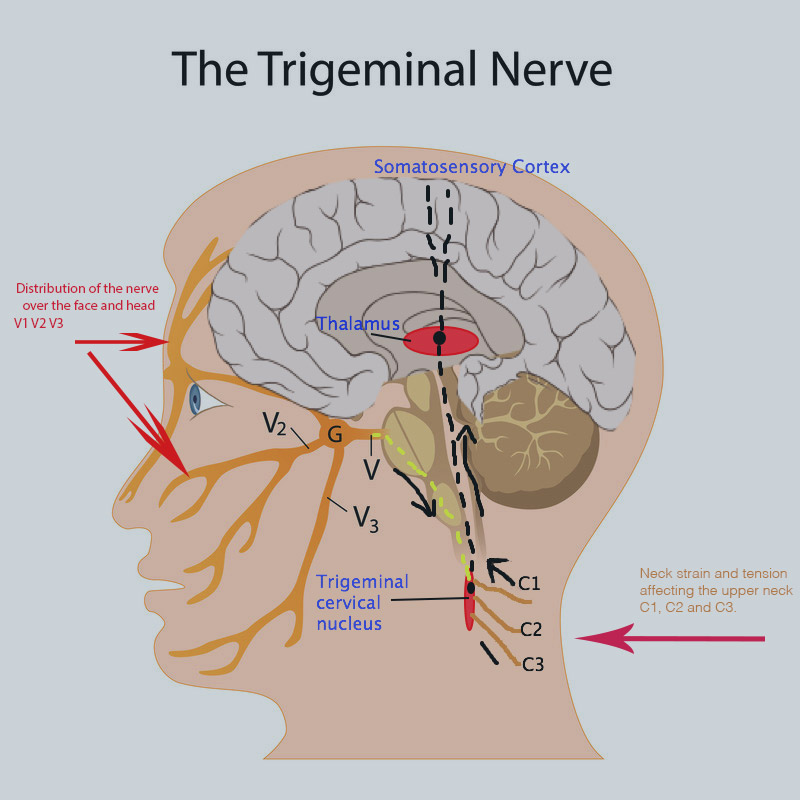
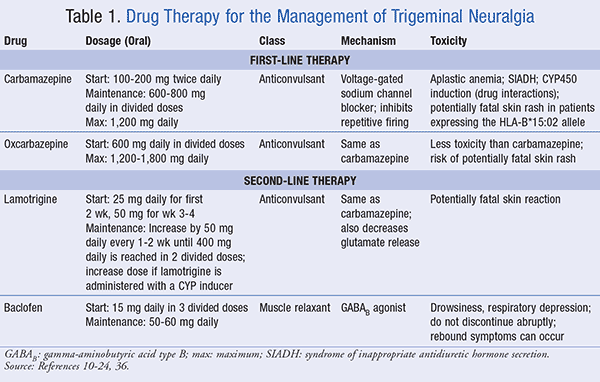
Plain Language Summary Trigeminal neuralgia is a really excruciating neuropathic pain condition. Although sodium channel blockers are efficacious in most of the patients, the poor tolerability profile and the limited efficacy in patients with concomitant continuous pain represent a major issue over the long-term treatment. Gabapentin and other α2δ ligands, which have been shown to be Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. 38 reviews submitted with a 7.3 average score. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin (brand name: Neurontin) is a medication often used to treat nerve pain, including trigeminal neuralgia. While it’s not a first-line treatment, it is effective in 50 – 60% patients who cannot tolerate other medications or need additional pain control. Today, trigeminal neuralgia is usually treated with drugs called anti-convulsants, which include carbamazepine (Tegretol®), phenytoin (Dilantin®), and gabapentin (Neurontin®). Phenytoin was first introduced in 1942, and in 1962 carbamazepine became the most commonly used drug. Baclophen (Lioresal®) may add to the effectiveness of these drugs. ABSTRACT Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) advocate for a multidis-ciplinary team approach to improve the care of patients with acute and chronic TN. Evidence-based discussions and decisions are encouraged to establish care pathways for prompt diagnosis and treatment, and long-term outcomes data collection to improve care. The guidelines Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN), or tic douloureux, is a rapid onset of stabbing, unilateral facial pain, lasting seconds to minutes, triggered by simple activities such as eating, brushing teeth, talking, or being exposed to a burst of cold air. ABSTRACT: Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) is a sudden onset, short-duration, yet debilitating neuropathic pain arising from the compression of the fifth cranial nerve, precipitated by daily activities such as chewing and speaking. This chronic condition is most common in older females, affecting up to 27 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. It is also indicated for the treatment of neuropathic pain inclusive of diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia and trigeminal neuralgia in adults ≥18 yrs. Dosage: The recommended dose for Epilepsy: Adults and children >12 yrs: Initially 300 mg tds on day 1 or by titrating dose as: 300 mg once daily on day 1, 300 mg bd on day 2 and 300 Neurontin, also known as gabapentin, is a medication that has been shown to be effective in managing the symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia. It works by altering the way that nerve signals are transmitted to the brain, which can help to reduce the frequency and severity of pain episodes. William P. Cheshire, Jr Abstract: The preferred treatment for trigeminal neuralgia consists of antiepileptic drugs. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple Low-dose gabapentin combined with either lamotrigine or carbamazepine can be useful therapies for trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis. Eur Neurol. 2000;44 (1):45–48. doi: 10.1159/000008192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is treated on an outpatient basis, unless neurosurgical intervention is required. Management of this condition must be tailored individually, based on the patient's This article discusses the efficacy and safety of gabapentin versus carbamazepine in treating trigeminal neuralgia through a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The efficacy of α2δ ligands, gabapentin and pregabalin, has been assessed in seven controlled or open-label studies. Despite the low quality of evidence, the favorable tolerability profile and the possible action on concomitant continuous pain make this drug category of interest for future trials in trigeminal neuralgia. The aim of this systematic review was to determine the efficacy of gabapentin (GBP) in the treatment of pain of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (TN). A comprehensive literature search was conducted using the Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature (EBSCO Industries), Emcare (Ovid), The fact that gabapentin was well-tolerated and without serious side effects is an important advantage when prescribing for elderly patients. The present study suggests that gabapentin can be effective as first or second line treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, even in cases resistant to traditional treatment modalities. The preferred treatment for trigeminal neuralgia consists of antiepileptic drugs. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a condition causing severe, unilateral, episodic facial pain. The diagnosis of TN is clinical, and patients typically report brief, lancinating attacks triggered by eating, drinking, talking, touching the face, or even a puff of wind. Recently, Neurontin®, (gabapentin) has been widely used because of reduced side effects, although is more expensive and somewhat less effective then Tegretol®. The anti-convulsants are thought to reduce TN attacks by decreasing the hyperactivity of the trigeminal nerve nucleus in the brain stem. Gabapentin is a recent antiepileptic drug that was introduced in 1994 for the treatment of partial seizures with and without secondary generalization. Several anecdotal case reports and preliminary clinical series have described relief of trigeminal neuralgia in some patients treated with gabapentin. 14, 25, 26, 27, 31 This study surveys the cumultative experience with gabapentin for patients
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |