Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
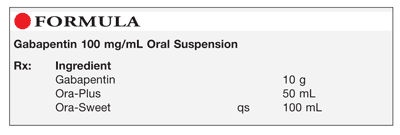 |  |
Your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer's patient information sheet (Medication Guide) when you begin treatment with gabapentin and each time you refill your prescription. You’ve learned about gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications (aka nursing considerations) and patient teachings in this article. In addition, you’ve learned about gabapentin’s mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, dosage, indications, contraindications, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications. This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin Teaching 1979 SN instructed patient about Gabapentin ( Neurontin ). It is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain and hot flashes. It is also used for restless leg syndrome. It is a first line agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain arising from diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain. Most common side effects of gabapentin in Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Gabapentin Enacarbil This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) Patient Information What is this medicine used for? Gabapentin is used to relieve pain from the nerves, from the spinal cord, or from the brain. Gabapentin tablets are used as an anti-epileptic to treat the symptoms of epilepsy and prevent seizures. Read more about gabapentin and its uses at Patient Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp® explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. • Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants which are also used to treat epilepsy. • You may notice that information from the manufacturer may not mention your type of pain. How does Gabapentin work? • Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. By understanding gabapentin’s pharmacology, indications, and nursing considerations, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and enhance patient quality of life. Continuous vigilance, patient-centered education, and interdisciplinary collaboration are key to successful gabapentin therapy. Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications. This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. However, elderly patients are more likely to have unwanted effects (eg, problems with balance or walking, swelling in the feet or legs) and age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Tablets, USP What is the most important information I should know about gabapentin tablets? Do not stop taking gabapentin tablets without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping gabapentin tablets suddenly can cause serious problems.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |