Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
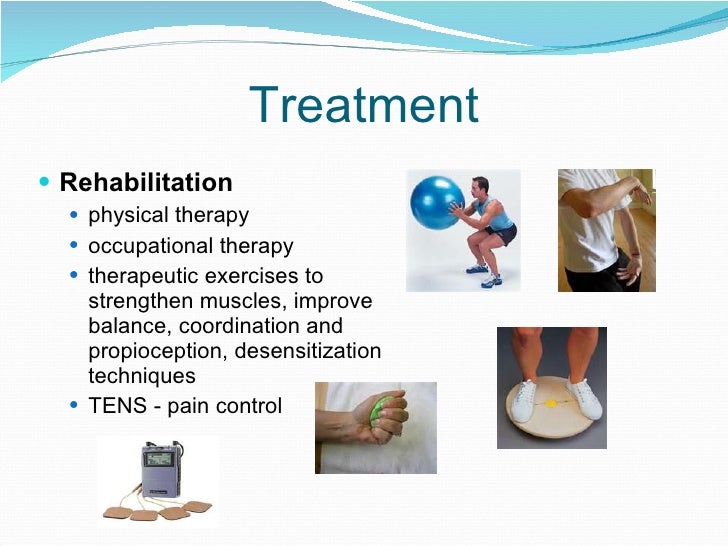
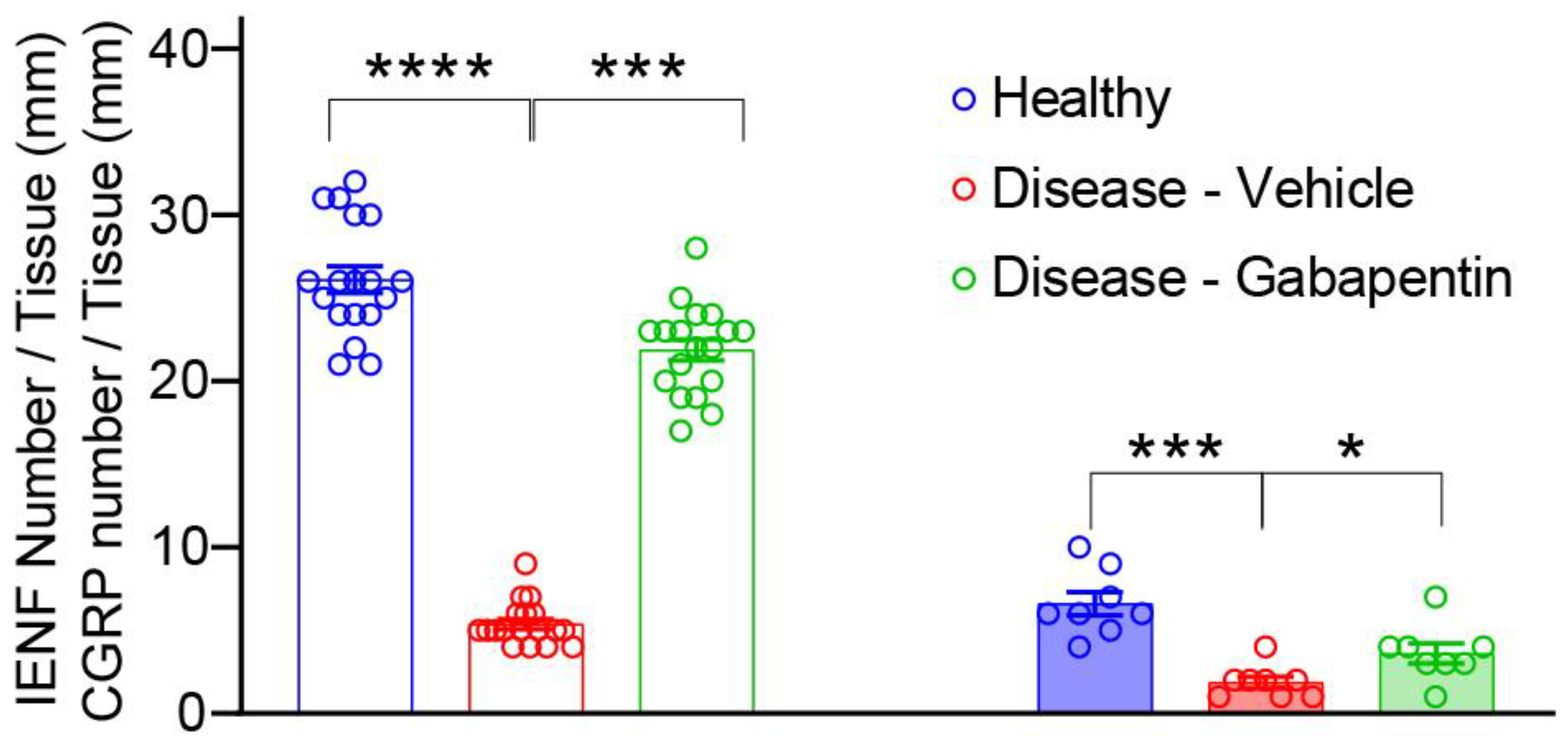
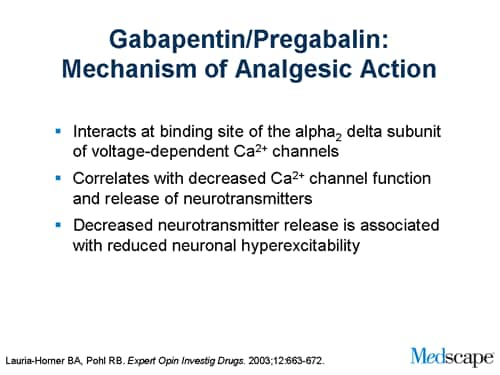
Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Peripheral neuropathy treatment Treatment for peripheral neuropathy depends on your symptoms and what is causing the nerve damage. Treatment is often twofold: treating pain and other symptoms and treating the underlying cause. Your doctor may prescribe medication to relieve pain and tingling. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diabetes mellitus who are treated in the office setting and significantly affects quality of life. It typically Discussion A validated diagnostic screening tool can help identify patients with neuropathic pain. A systematic approach to clinical assessment and investigation will clarify the diagnosis. Good glycaemic control is important in the prevention and management of diabetic polyneuropathy; management options include antidepressants, gabapentinoids and controlled release opioids. Pain that lasts The Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group of the International Association for the Study of Pain recently sponsored the development of evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Tricyclic antidepressants, dual reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine, calcium channel α2-δ ligands (ie, gabapentin and pregabalin), and topical lidocaine were Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other neuropathic pain syndromes. It relieved symptoms of allodynia, burning pain, shooting pain, and hyperesthesia. Adverse effects were typically mild to moderate and usually subsided within approximately 10 days from the initiation of treatment. Despite advances in treatment options, many patients remain undertreated, highlighting the need for individualized, multimodal approaches and continued research into the complex pathophysiology of neuropathic pain conditions. Keywords: chronic neuropathic pain, nerve injury, neuropathic pain, nociception, peripheral nerve injury, neuropathy 1. For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diabetes mellitus who are treated in the office setting and significantly affects quality of life. It typically Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for If your peripheral neuropathy stems from a condition like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, gabapentin alone won’t resolve the root issue, and your pain may continue—or worsen—without a comprehensive treatment plan. Several studies have evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, yielding contradictory results. On one hand, it has been observed that gabapentin is more effective, especially at higher doses, compared to pregabalin (8, 9). Medicines such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, often improve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness. For short-term treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be as effective as tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, or pregabalin (based on indirect evidence). Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Millions of people suffer from the burning, tingling, and numbness of a form of neuropathy called idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. A recent study directly comparing four medications produced disappointing results, but is a step in the right direction. Gabapentin (GBP) is a Health Canada approved antiepileptic drug. 5 In the UK, GBP is licensed for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults and in the US it is marketed for post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). 3 The mechanism of action for GBP relates to its ability to bind with high-affinity to the alpha-2-delta subunit of vo Gabapentin treats seizures by decreasing excitement in the brain and has been studied for its effect in patients with cancer who have neuropathic pain or symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. It also has been studied for its effect on anxiety and hot flashes. A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak [60].
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |