Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 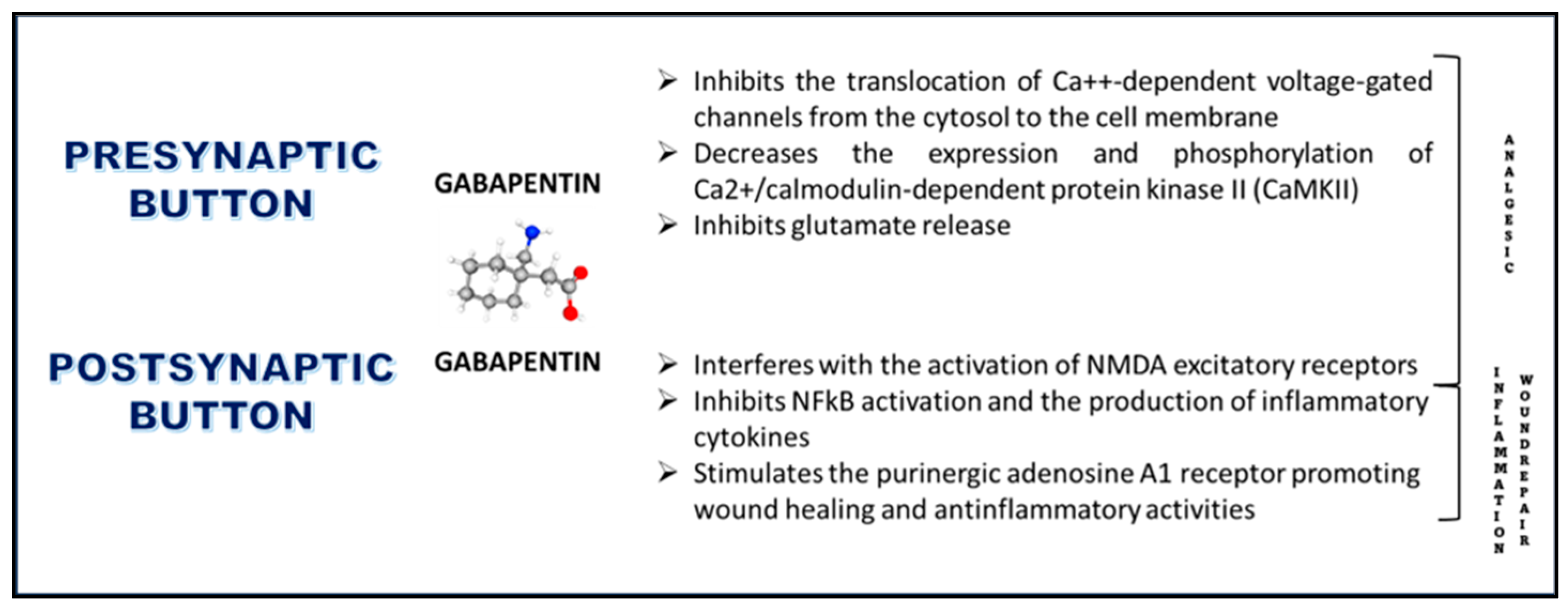 |
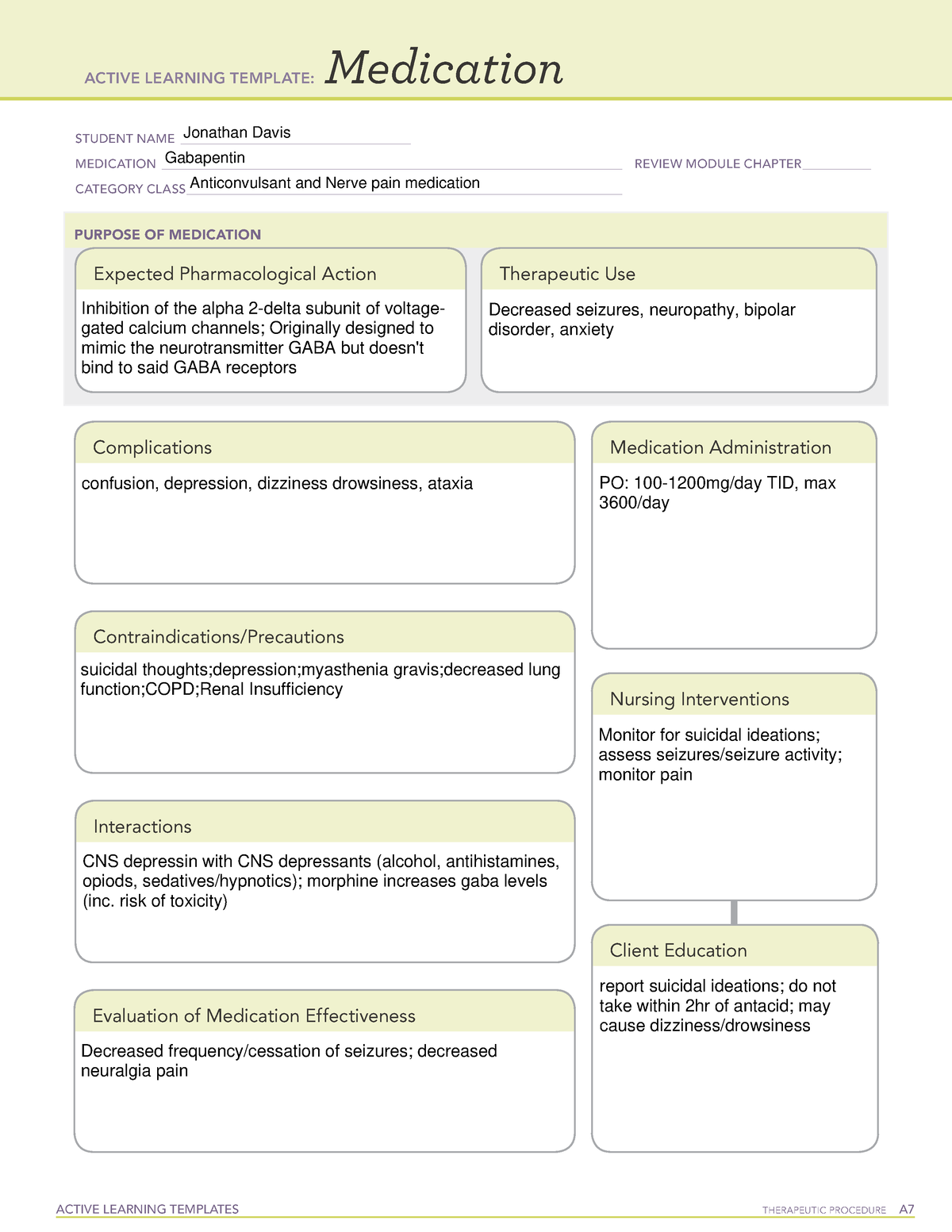
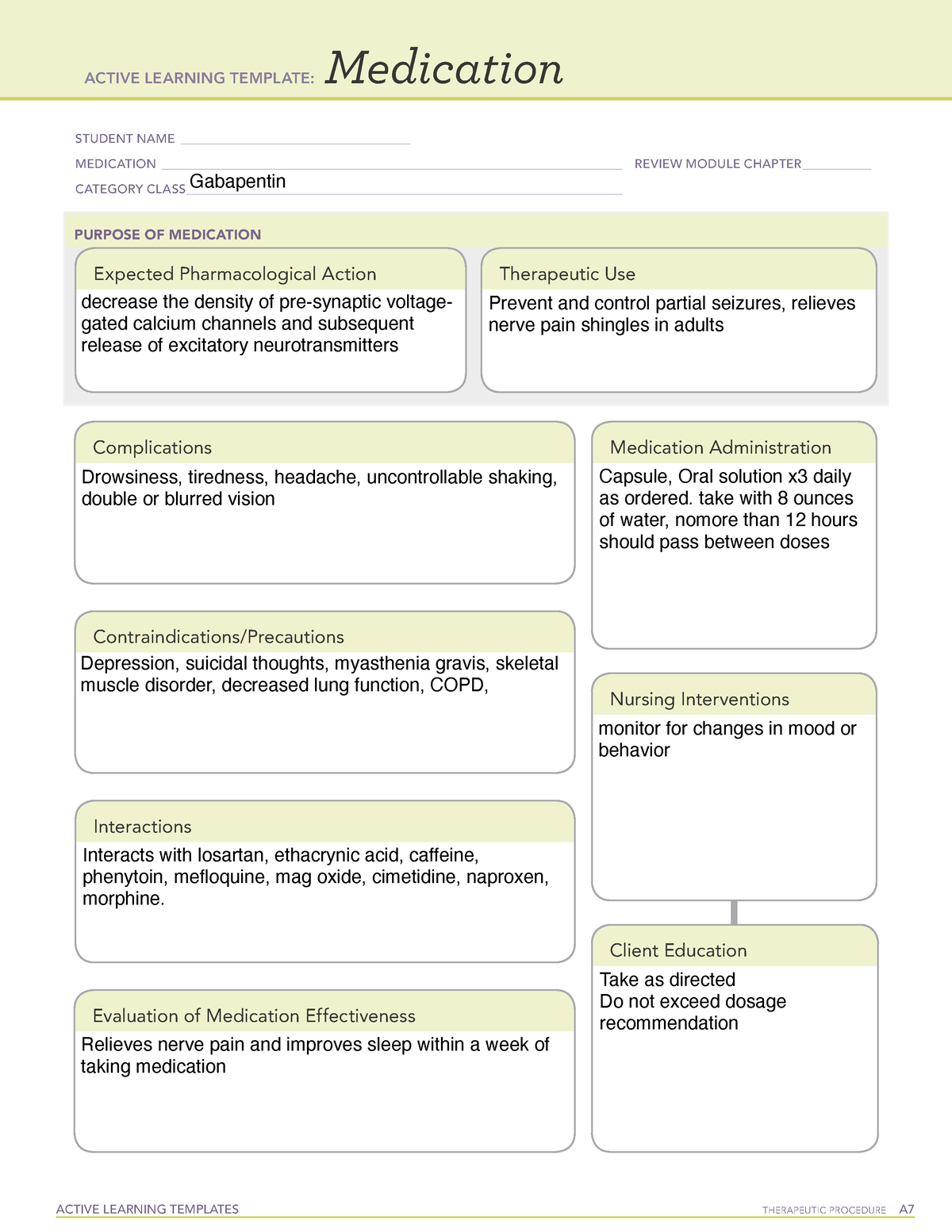
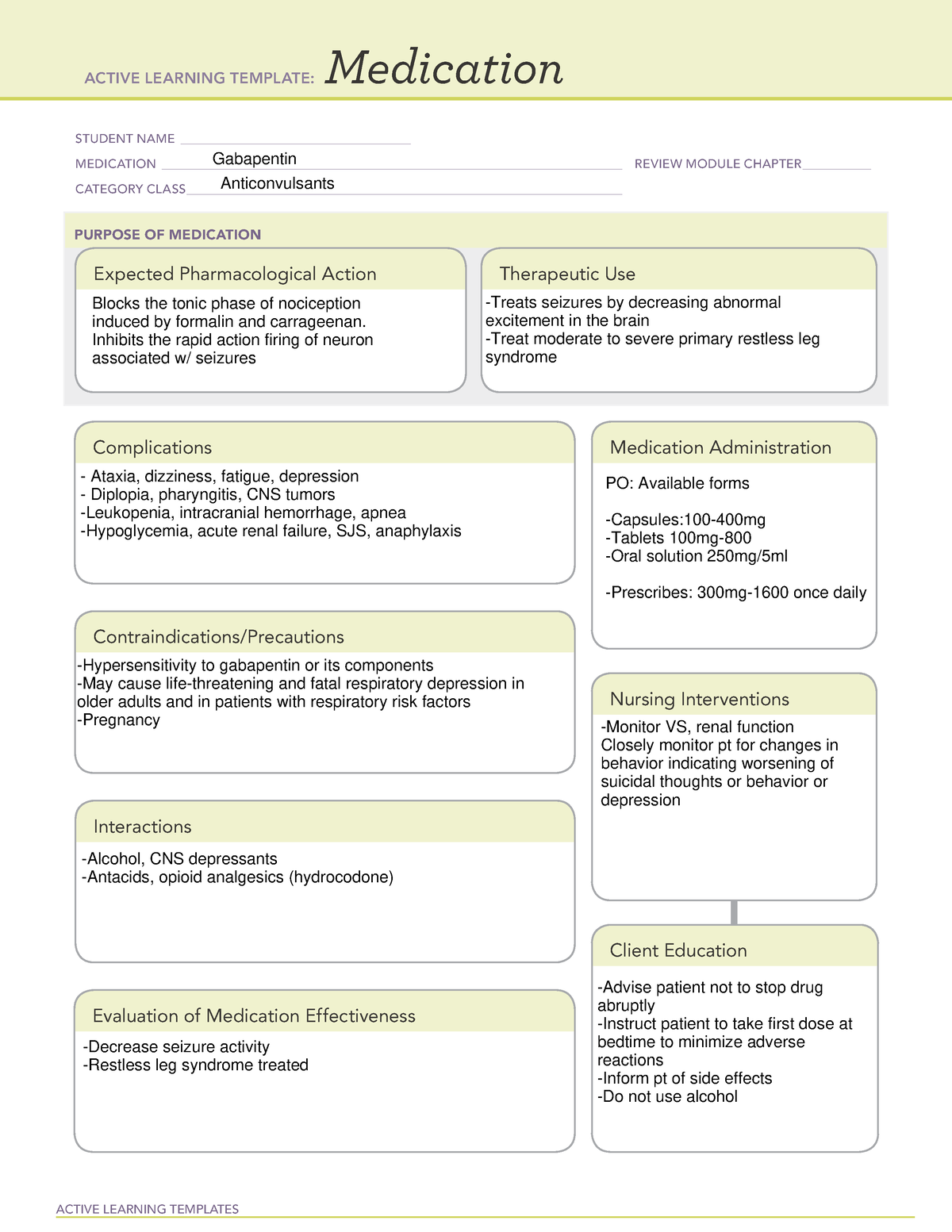
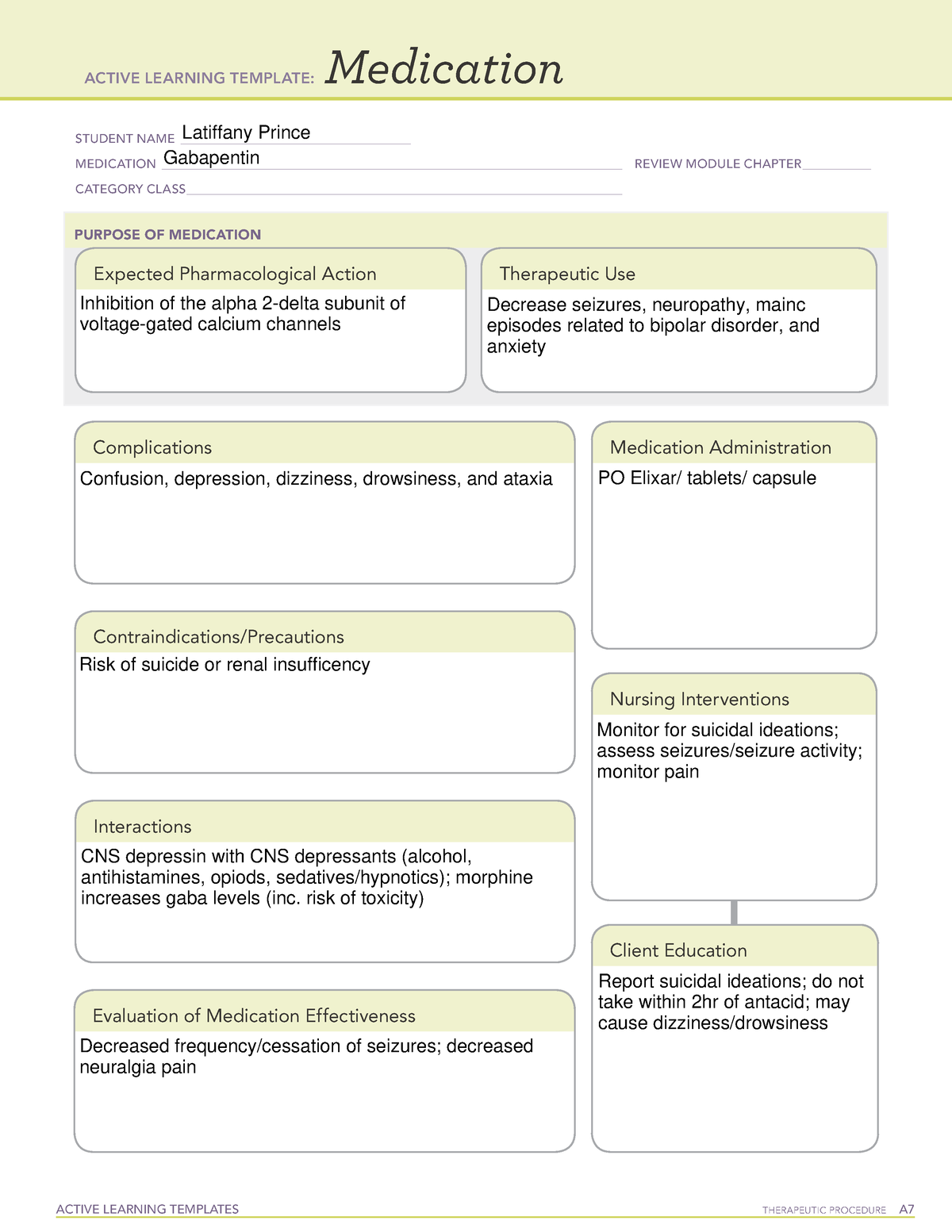
All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin | Deranged PhysiologyGabapentin Gabapentin has been clearly demonstrated to be effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain in diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. This evidence, combined with its favourable side-effect profile in various patient groups (including the elderly) and lack of drug interactions, makes it an attractive agent. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are chemically derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (i.e., GABA analogues) which bind selectively to the α 2 δ protein that was first described as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). [1][2][3][4][5] Clinically used gabapentinoids include gabapentin Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. Gabapentin is a compound produced by addition of a cyclohexyl group to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (McLean 1995). From: Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 1998 gabapentin 1) the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS gabapentin.txt · Last modified: 2024/07/25 18:05 by cclarks Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Generic name : Gabapentin Brand names: Neurontin® Gralise® (gabapentin extended release) Horizant® (gabapentin enacarbil) Therapeutic class: Anti-epileptic, Anticonvulsant Pharmacologic class: 1-amino-methyl cyclohexoneacetic acid, Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue FDA Approved: December 30, 1993 Chemical Formula: C9H17NO2 Pregnancy Category: C Habit forming? No The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles can have implications for clinical practice. This article has summarised these key differences. In addition to their use in managing ne Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Gabapentin is a an Antiseizure Agent belonging to pharmacology class of GABA Analog Class Gabapentin can be used in the treatment of Postherpetic neuralgia, Seizures. It is also used to treat Alcohol use disorder, moderate to severe (alternative agent); Alcohol withdrawal; Cough, chronic refractory Gabapentin extended-release tablets (Horizant) are used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS; a condition that causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move the legs, especially at night and when sitting or lying down). Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |