Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |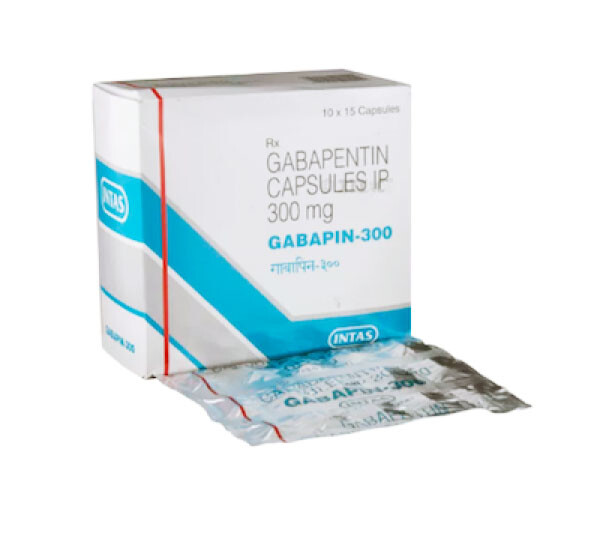  |
Having a seizure during pregnancy could harm both mother and baby. Tell your doctor if you become pregnant. If you are pregnant, your name may be listed on a pregnancy registry to track the effects of gabapentin on the baby. Ask a doctor if it is safe to breastfeed while using gabapentin. Advice and warnings for the use of Gabapentin during pregnancy. FDA Pregnancy Category C - Risk cannot be ruled out There was an increased risk of preterm birth among women exposed to gabapentin either late (RR=1.28 [CI 1.08-1.52], p < 0.01) or both early and late in pregnancy (RR=1.22 [1.09-1.36], p < 0.001). Key takeaways Gabapentin may cause different side effects in women than in men due to the different hormonal make-ups of women, as well as differences in metabolism and body composition. Women may be more likely than men to experience dizziness, tiredness, edema, and mood swings from gabapentin. It’s not clear whether gabapentin is safe during pregnancy, but it’s unlikely to impact In this large population-based study, we did not find evidence for an association between gabapentin exposure during early pregnancy and major malformations overall, although there was some evidence of a higher risk of cardiac malformations. Maternal use of gabapentin, particularly late in pregnancy It has not been known to cause any side effects in breastfed babies. If your baby is not feeding as well as usual, seems unusually sleepy, has a stomach upset, or if you have any other concerns about your baby, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, health visitor or midwife. While gabapentin can pass into breast milk in small amounts, it is often considered relatively safe for use during breastfeeding if the potential benefits to the mother outweigh the risks to the infant. In a cohort study of pregnant women included in the US Medicaid Analytic eXtract (MAX) dataset, Elisabetta Patorno and colleagues investigate neonatal and maternal outcomes associated with gabapentin exposure during pregnancy. However, it could have adverse effects, including mood swings, drowsiness, and vertigo. Women who are pregnant should ask their doctor if they can take gabapentin while pregnant. Doctors also consider the risk during pregnancy if a woman is trying to conceive or is currently in the early stages. Gabapentin is a prescription pain medication often used to treat various forms of pain and pain caused by shingles. It is a Schedule V controlled substance that carries a lower risk of addiction than other prescription pain medications. Many people are afraid to take prescription medications while pregnant due to the risk of adverse effects on the developing fetus. But should you take A study from the European Gabapentin Registry included prospective and retrospective data with a total of 51 outcomes and 44 live births of women with epilepsy and other disorders exposed to gabapentin during pregnancy. Results from this large cohort study suggest that gabapentin exposure during early pregnancy does not appear to be associated with teratogenic effects, although a moderately higher risk of cardiac malformations—in particular, conotruncal defects—cannot be excluded. If you become pregnant while taking gabapentin, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334. Can Gabapentin Be Used During Pregnancy or While Breastfeeding? The safety of gabapentin during pregnancy is unknown. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant before taking gabapentin. Gabapentin passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding while using gabapentin is not recommended. If a male takes gabapentin, could it affect fertility or increase the chance of birth defects? Sexual dysfunction, such as loss of desire to have sex and loss of ability to have an erection, ejaculate, and/or have an orgasm, has been reported in people using gabapentin. Gabapentin may be used during pregnancy only when the benefits outweigh the potential risks. In animal studies, gabapentin has been shown to increase the risk for fetal malformation, particularly delayed bone formation. Some of the most commonly affected parts include the skull, backbone and the extremities. Pregnancy-related problems, such as preterm delivery (birth before week 37) or low birth weight (weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces [2500 grams] at birth) have been reported in some studies looking at the use of gabapentin during pregnancy. Animal studies suggest gabapentin could have adverse effects on a fetus. A population-based cohort study found no increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in babies born to mothers who took gabapentin during pregnancy. Animal studies have shown that gabapentin intake during pregnancy increases the risk of embryo fetal toxicity, specifically on mice. For rats, adverse effects on offspring development were common among those who had gabapentin during pregnancy. Talk to your doctor about taking gabapentin if you are pregnant or are planning on being pregnant. Your doctor may have alternative medication (s) to
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |