Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
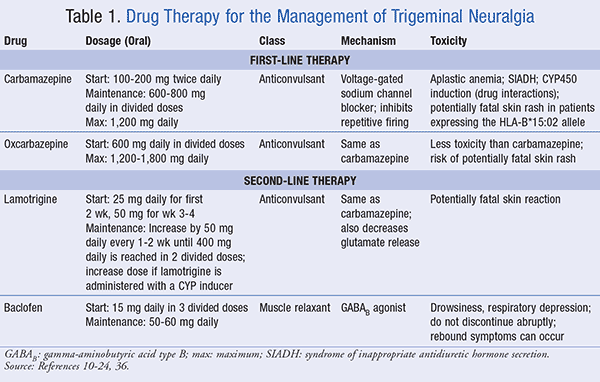
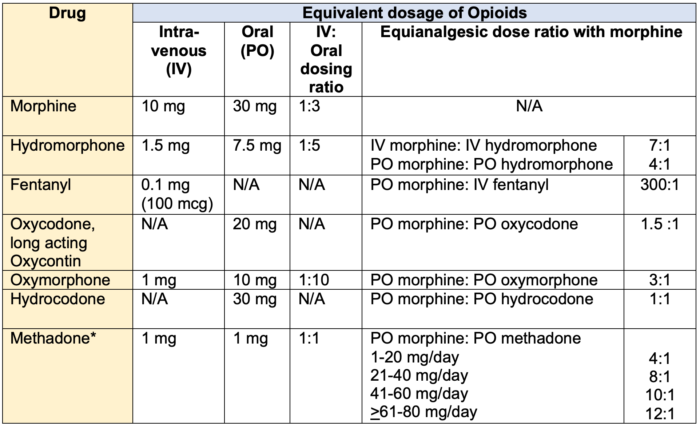
Gabapentin and pregabalin are being massively prescribed for neuropathic pain of all kinds of etiologies. However, if these medications are combined or if given in a high dose, they can lead to adverse effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, weakness, and somnolence. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Pharmacology Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors in Comprehensive drug information on gabapentin, including its uses, side effects, and precautions. An anti-NeP topical cream with ketamine 10%, gabapentin 10%, imipramine 3%, and bupivacaine 5% was shown to resolve NeP symptoms for several hours; it was also successful in reducing flare-ups in a patient with cervicalgia and TGN, refractory to several treatments. 10 Ketamine and gabapentin are more effective together as they mitigate Overview of pharmacologic management of chronic pain in adults, including medication options and treatment strategies. Anesthesiology 2020; 133:265. Fabritius ML, Geisler A, Petersen PL, et al. Gabapentin for post-operative pain management - a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2016; 60:1188. This web page provides an overview of drug choices and general principles for chronic pain syndromes, including neuropathic pain. It mentions gabapentin as an option for neuropathic pain, but does not discuss its use or efficacy in detail. Provides guidance on ambulatory management of alcohol withdrawal, focusing on alleviating symptoms and preparing for the maintenance phase of treatment. Pharmacologic approaches for managing chronic non-cancer pain in adults, including treatment options and considerations. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Comprehensive drug information resource for healthcare professionals. Explore pharmacologic management strategies for alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and outcomes, on this comprehensive resource. UpToDate UpToDate Gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal symptoms, including management strategies and clinical considerations, are discussed in this comprehensive resource. Clinicians, business professionals, and enterprises around the world trust UpToDate evidence-based clinical information solutions to enable the best possible care decisions and improved health outcomes. { {configCtrl2.info.metaDescription}} Gabapentin has been made a Schedule V controlled substance in some states, and a number of states have mandated reporting of gabapentin in their Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs [60]. Gabapentin is a controlled drug in the United Kingdom [61]. Management of chronic pain in advanced chronic kidney disease, including pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic treatments. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and precautions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |