Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
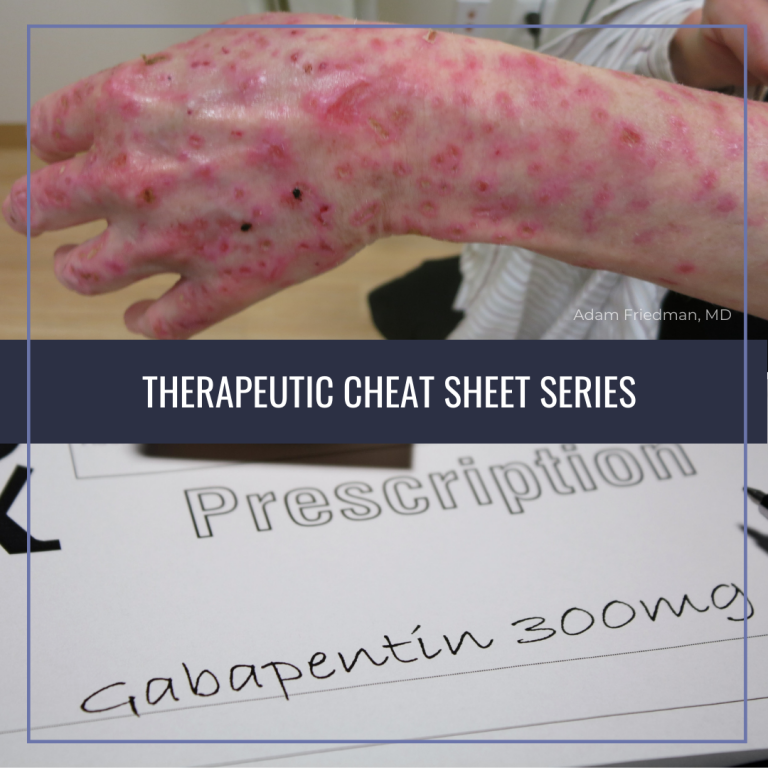
Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), restless legs syndrome (RLS), a painful movement disorder in the legs partial seizures in adults and children Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Neurontin: Treats pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) and, when combined with other seizure medications, treats partial-onset seizures in adults and children over 3 years old. Gabapentin may cause vision changes, clumsiness, unsteadiness, dizziness, drowsiness, sleepiness, or trouble with thinking. Make sure you know how you react to this medicine before you drive, use machines, or do anything else that could be dangerous if you are not alert, well-coordinated, or able to think or see well. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin is an oral capsule sold under the brand name Neurontin or as a lower-priced generic drug. It’s primarily used to treat partial seizures in adults and children. Is gabapentin a good option for treating anxiety disorders? This is what research says and why caution is important. Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. Gabapentin is a prescription antiseizure medication and nerve pain medication. Learn more about whether or not it is effective against arthritis pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Learn more about how gabapentin is used in sciatica treatment. Gabapentin is available in 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg capsules, and in 600 mg and 800 mg tablets. The dose of gabapentin to treat epilepsy with partial onset seizures in patients 12 years of age and older is up to 600 mg three times daily. The dose of gabapentin may then be increased gradually if needed to a maximum of 3600 mg each day. Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat neuropathic pain and seizures. It works by reducing the abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can cause these conditions. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat seizures and nerve pain caused by the herpes virus. Includes Neurontin side effects, interactions and indications. If you suddenly stop taking gabapentin tablets, capsules, or oral solution, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, nausea, pain, and sweating. If you are taking gabapentin to treat seizures and you suddenly stop taking the medication, you may experience seizures more often. Gabapentin Capsules or Tablets Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Talk to your provider about medications you currently take to avoid drug interaction. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Gabapentin, available in both branded and generic forms, is used to treat partial seizures, postherpetic neuralgia following shingles and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Gabapentin does have an advantage over some other medicines used for add-on therapy, because the doctor won't have to change how much of the first medicine is prescribed.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |