Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
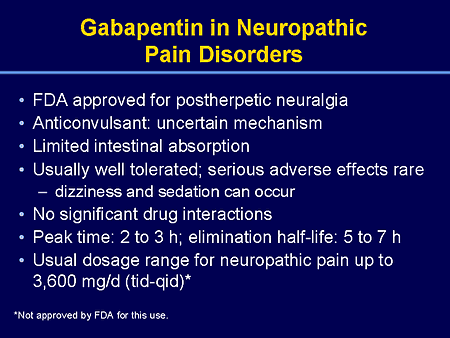 |  |
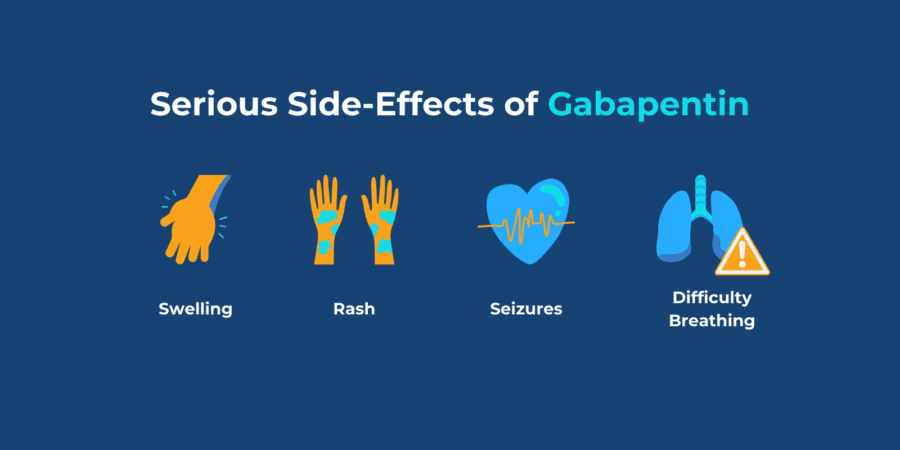
Discover how gabapentin helps alleviate peripheral neuropathy symptoms, a common condition causing numbness, pain, and tingling in hands and feet. Gabapentin was shown to be better than placebo across all studies for IMMPACT outcomes. The review concentrated on gabapentin doses of 1,200 mg/d or greater and reported that doses at or above this threshold were reasonably effective for treatment of various neuropathic pain types. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. At high dosages, gabapentin is moderately effective for neuropathic pain, although adverse effects are experienced as often as benefit. Gabapentin is widely used for the treatment of pain, Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that has been used for a number of off-label indications, including neuropathic pain. It is thought to act by binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, or by blocking new synapse formation. Neuropathic pain tends to be chronic, is complex, and can be difficult to treat effectively. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). Millions of people suffer from the burning, tingling, and numbness of a form of neuropathy called idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. A recent study directly comparing four medications produced disappointing results, but is a step in the right direction. While gabapentin doesn’t heal nerve damage, it can play a valuable role in managing symptoms. For many patients, it reduces the intensity of nerve pain, allowing them to focus on other healing strategies like physical therapy, lifestyle changes, or alternative treatments. Gabapentin is primarily used for: Neuropathic Pain: Effective in alleviating pain from nerve damage. Postherpetic Neuralgia: Reduces pain following shingles. Seizure Disorders: Acts as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures. Restless Legs Syndrome: Helps manage the uncomfortable urge to move legs, especially at night. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain following shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. This has been used as a treatment for peripheral neuropathy in Europe for years and there is some evidence that it can be helpful in those with painful diabetic neuropathy. Discuss using alpha-lipoic acid with your health care professional because it can affect blood sugar levels. Other side effects can include stomach upset and skin rash. In the 2016 report, most of the available randomized control trial (RCT) data pertained to diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), it was concluded that for DPN there was greater reduction in neuropathic pain and increased risk of adverse events associated with gabapentin compared with placebo. Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, easily titrated, has few drug interactions, and does not require laboratory monitoring. Patients suitable for gabapentin should have a clear neuropathic pain syndrome, characterized by sharp, shooting, lancinating and/or burning pain, in a nerve root (radicular) or stocking/glove distribution. One, from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom, includes the use of gabapentin as a first-tier treatment for all neuropathic pain. 14 Similarly, the European Additional benefits include improved sleep and increased daily activity in patients with severe neuropathic pain. Even with low doses of 100mg to 300mg, patients saw improvement in their pain. Although Gabapentin does not increase food intake, its use can help alleviate the severe pain that often results in reduced appetite, making it difficult to eat or swallow. This is especially true for Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Therapeutics Letter 75 examines new evidence from unpublished trials on the use of gabapentin for pain. Conclusions and recommendations Misleading promotion pushed gabapentin to blockbuster status; scientific evidence suggests gabapentin has a minor role in pain control. Gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by < 1 point on a 0-10 point scale and benefits about 15% of carefully selected patients Gabapentin at a dose of 1800 to 3600 mg daily (1200 to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin has sufficient evidence showing its efficacy and safety in treating neuropathic pain. Effective treatment doses of gabapentin for neuropathic pain tend to be higher compared to effective treatment doses for other conditions. Gabapentin is a relatively safe medication. The most prevalent effects seen are drowsiness, somnolence, and A further report (170 participants) used an experimental formulation of intrathecal gabapentin. Thirty‐seven studies (5633 participants) studied oral gabapentin at daily doses of 1200 mg or more in 12 chronic pain conditions; 84% of participants were in studies of postherpetic neuralgia, painful diabetic neuropathy or mixed neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |