Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
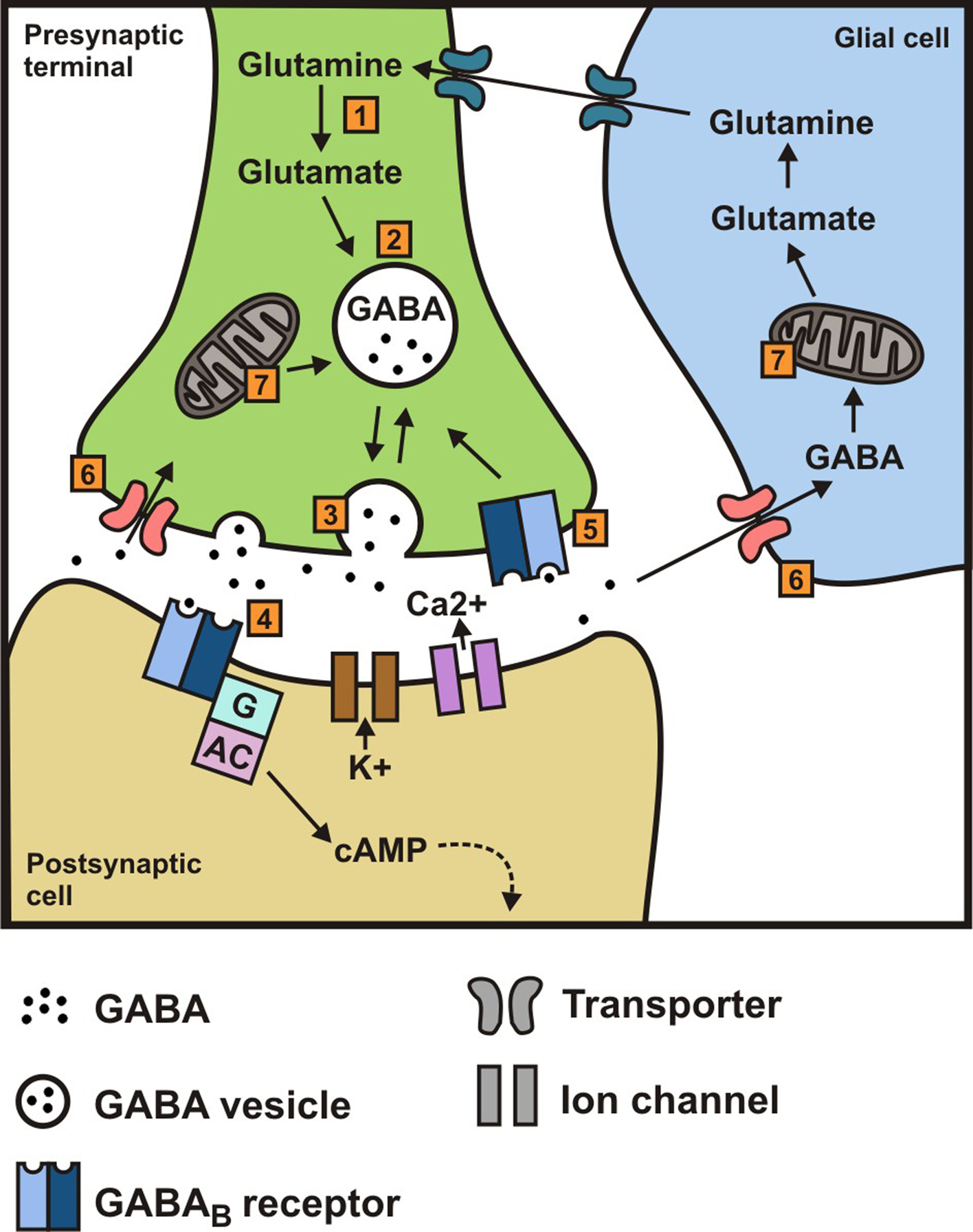
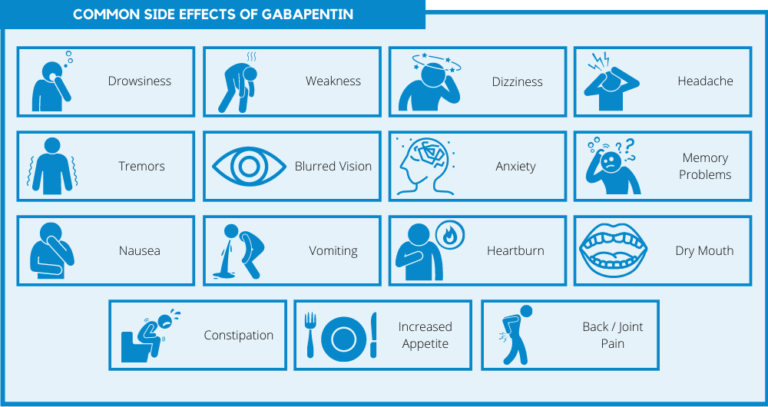
By Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist “GABA” is short for the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. New research Explore the benefits of GABA and compare it with gabapentin. Learn about their effects, potential side effects, and how they influence relaxation, sleep, and mood regulation. GABAPENTIN (NEURONTIN) One of the most extensively used anticonvulsants in the management of neuropathic pain, gabapentin has proven efficacy in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, phantom limb pain, and pain following spinal cord injury (Fig. 346-4). An analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), gabapentin is thought to exert its analgesic effect by modulating Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. Gabapentin is not the same as pregabalin, even though they both belong to the same class of medicine, called gabapentinoids, and work similarly Clinical studies suggest that 120 mg of GABA per day for 12 weeks does not cause side effects. However, it’s a good idea to start low and increase the dose gradually as needed. GABA is not the same as gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement; gabapentin is a prescription medication December 23, 2022 By Trudy Scott 53 Comments Dosage Considerations: If someone decides to try a GABA supplement, it's essential to follow recommended dosages and guidelines. Excessive intake of GABA supplements may lead to side effects or interactions with medications. Dietary sources of Gamma-aminobutyric acid Here are you can find some food sources that contain GABA: Fermented Foods. Similarities between GABA and Gabapentin Both promote relaxation and reduce anxiety. Both have potential applications in managing pain and sleep disorders. Both interact with the nervous system to modulate neuronal activity. Important Considerations While Gabapentin mimics the effects of GABA, it is not a direct replacement. It's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before taking GABA and gabapentin are two fundamentally different compounds that share some important similarities. The first, gamma- or γ-aminobutyric acid (or GABA), is a neurotransmitter that serves as a chemical messenger in the brain. The other, gabapentin, which you may also know as Neurontin, is a so-called analog of GABA, meaning that it was designed to mimic certain qualities of the neurotransmitter. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. The study is based on gaba (gamma - aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin (the active ingredients of Gaba and Gabapentin, respectively). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs or brand names) are also considered. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin are two substances often discussed in the context of brain health and neurological treatments. While they share some similarities in their impact on the nervous system, they are fundamentally different in terms of their structure, function, and applications. This distinction is crucial for understanding their respective roles and benefits. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. On the other hand, gabapentin was created to mimic some of the effects of GABA but it does not appear to affect the same receptors in the brain. Another function of GABA is its responsibility for regulating the body’s muscle tone since it is linked to the pituitary glands which affect human growth hormone (HGH) levels. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Key Takeaways: GABA is a natural supplement that helps alleviate anxiety and physical tension. Gabapentin is a
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |