Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
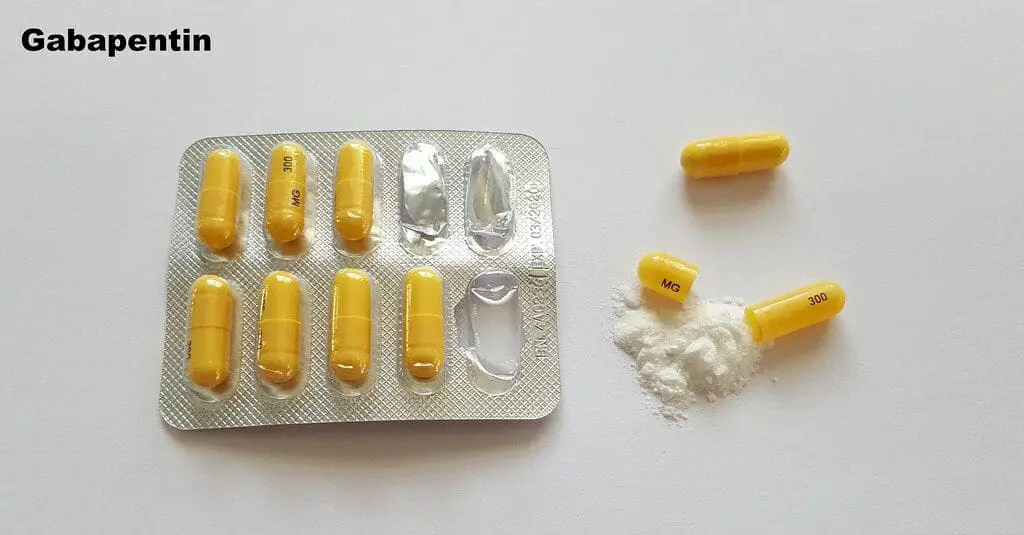
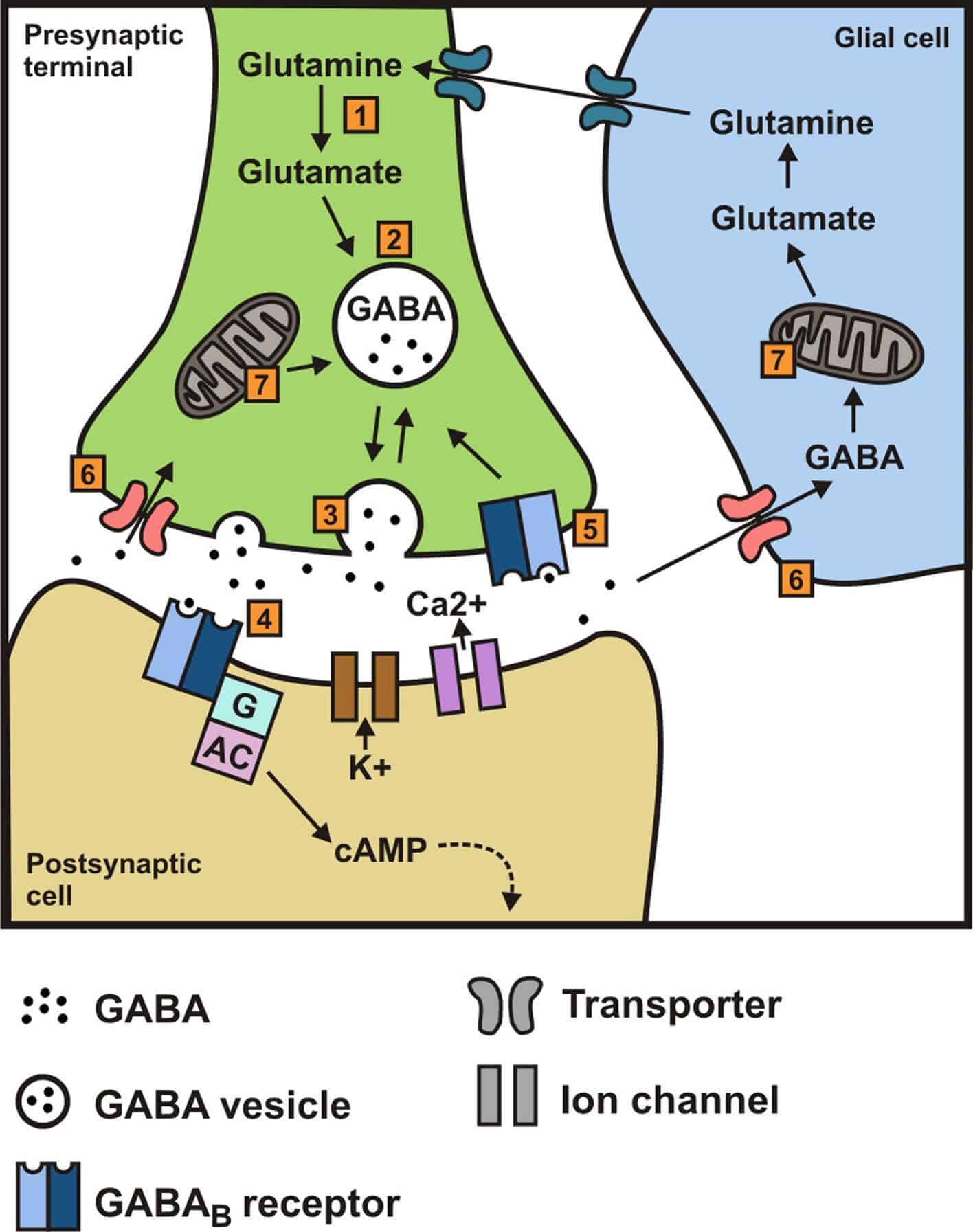
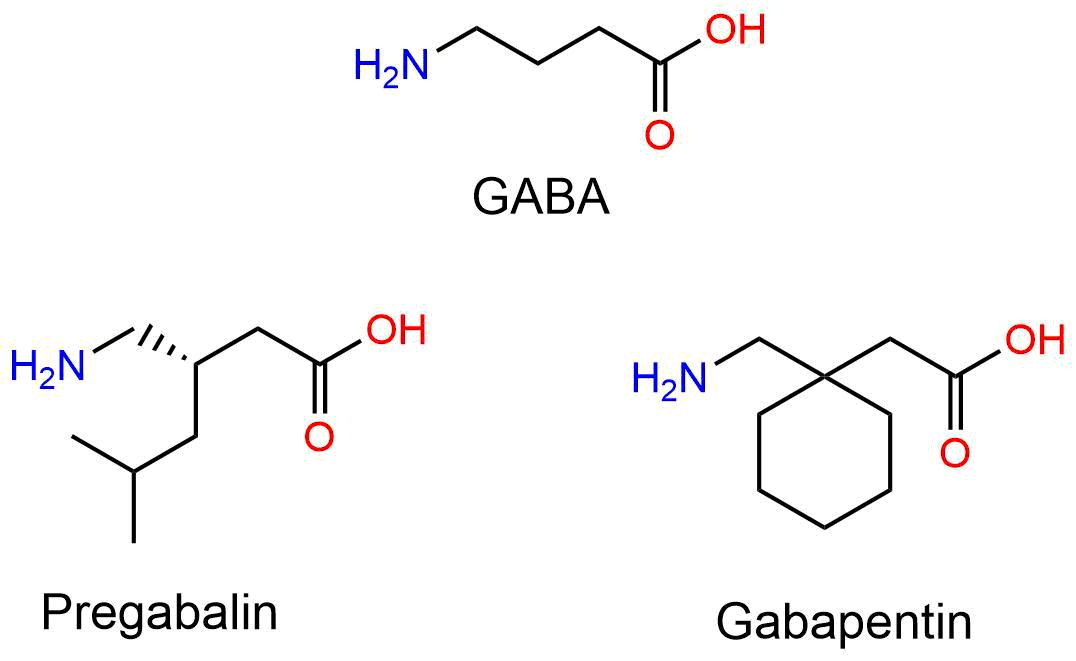
Gabapentin users often report more consistent sleep patterns and reduced nighttime awakenings, particularly those with chronic pain conditions. Long-term efficacy and safety considerations are crucial when evaluating these medications for ongoing sleep therapy. Have you used Gabapentin for sleep or insomnia? If you’ve used gabapentin to treat a sleep disorder such as insomnia or to enhance sleep, be sure to share your experience in the comments section below. Sleep problems questionnaire (SPQ) scores before and after medication treatment with trazodone vs. gabapentin. Matched letter pairs indicate significant (p<0.05) differences between baseline and follow-up for the trazodone (a) and gabapentin (b) groups, and between medication groups for change scores (c) and follow-up scores (d). The SPQ individual item scores were dichotomized because of Studies have shown that GABA supplements can increase GABA levels in the brain, leading to a range of benefits, including improved sleep quality, reduced anxiety, and enhanced mood. This promising potential of GABA supplements offers hope to those struggling with sleep and anxiety issues. What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. While endogenous (naturally produced) GABA is more effective at activating inhibitory brain receptors, there is promising evidence that supplemental GABA can also cross the blood-brain barrier and contribute to a relaxation response, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.* GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both compounds that play important roles in the functioning of the central nervous system. While GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, Gabapentin is a synthetic drug that is structurally similar to GABA. Better Sleep Quality: GABA may promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, particularly in people with insomnia. One study found that those who took GABA supplements fell asleep faster and experienced an increase in deep sleep. Millions of Americans struggle with sleep problems, and data from the CDC shows that over 8% of adults take sleep aids multiple times per week. Dietary supplements are one type of sleep aid, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) supplements are often advertised as a way to improve sleep. GABA plays a crucial role in preparing the body for sleep by reducing excitability. GABA supplements are available, but their effectiveness as sleep aids still requires research. What Is GABA? GABA, or Gamma-Aminobutyric acid, is an amino acid produced naturally in the brain. While gabapentin may help improve sleep for some people (especially if you have another health condition that worsens sleep), it’s unlikely to be the first medication your healthcare provider recommends. Similarly, Gabapentin vs Xanax for Sleep: Comparing Effectiveness and Safety is another comparison worth considering. Xanax (alprazolam) is primarily an anti-anxiety medication that can also help with sleep, but it carries a higher risk of dependence and more severe withdrawal symptoms compared to gabapentin. Special Considerations and Precautions Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. Improves sleep: GABA facilitates sleep onset and maintains sleep quality by promoting relaxation and reducing brain activity. Reduces pain perception: GABA plays a role in pain management by modulating the transmission of pain signals in the spinal cord. Results Effects of GABA and l -theanine on sleep latency and duration in the pentobarbital-induced sleep model Sleep latency and duration time following GABA or l -theanine administration were measured in the pentobarbital-included sleep model to identify the optimal combination ratio for sleep enhancement (Figure 1). Learn about the difference between GABA and gabapentin, a neurotransmitter and an inhibitory medication often used for seizures and neuropathic pain. Both melatonin and GABA liposomal supplements are powerful sleep support and help to improve the quality, duration and time it takes to fall asleep. GABA supplementation can be a valuable component of this approach, working in harmony with other sleep-promoting habits to create a more restful and rejuvenating sleep experience. As research in the field of sleep science continues to evolve, our understanding of GABA and its potential applications for sleep improvement will undoubtedly grow.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |