Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
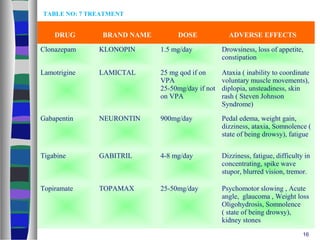
Gabapentin Capsules or Tablets Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Talk to your provider about medications you currently take to avoid drug interaction. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults and the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn about side effects, drug interactions, dosages, warnings, and more. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a prescription drug. It comes as an oral capsule, an immediate- or extended-release oral tablet, and an oral solution. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). How to Calculate Gabapentin Dosage This calculator determines a safe starting dose of gabapentin (Neurontin) based on indication and age, using these guidelines: Typical Daily Dose (mg): View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range of doses Gabapentin is often used for this issue, typically at doses between 900mg and 3,600mg daily. Postherpetic neuralgia is nerve pain that sticks around after a shingles outbreak clears up. The pain can feel like burning, stabbing, or shooting sensations along affected nerve pathways. Gabapentin is also sometimes used to relieve the pain of diabetic neuropathy (numbness or tingling due to nerve damage in people who have diabetes), and to treat and prevent hot flashes (sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating) in women who are being treated for breast cancer or who have experienced menopause (''change of life'', the end of monthly menstrual periods). Talk to your doctor A structured gabapentin taper chart helps ease withdrawal and minimize risks, but knowing what works—and what doesn’t—matters just as much. Learn more. Gabapentin may cause vision changes, clumsiness, unsteadiness, dizziness, drowsiness, sleepiness, or trouble with thinking. Make sure you know how you react to this medicine before you drive, use machines, or do anything else that could be dangerous if you are not alert, well-coordinated, or able to think or see well. This medication is used to relieve nerve pain following shingles (a painful rash due to herpes zoster infection) in adults. This condition is called postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin belongs to a class of drugs known as antiseizure drugs (also called anticonvulsant or antiepileptic drugs). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin therapy may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Learn about gabapentin dosages based on treatment, medical condition, children, and more with GoodRx.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |