Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
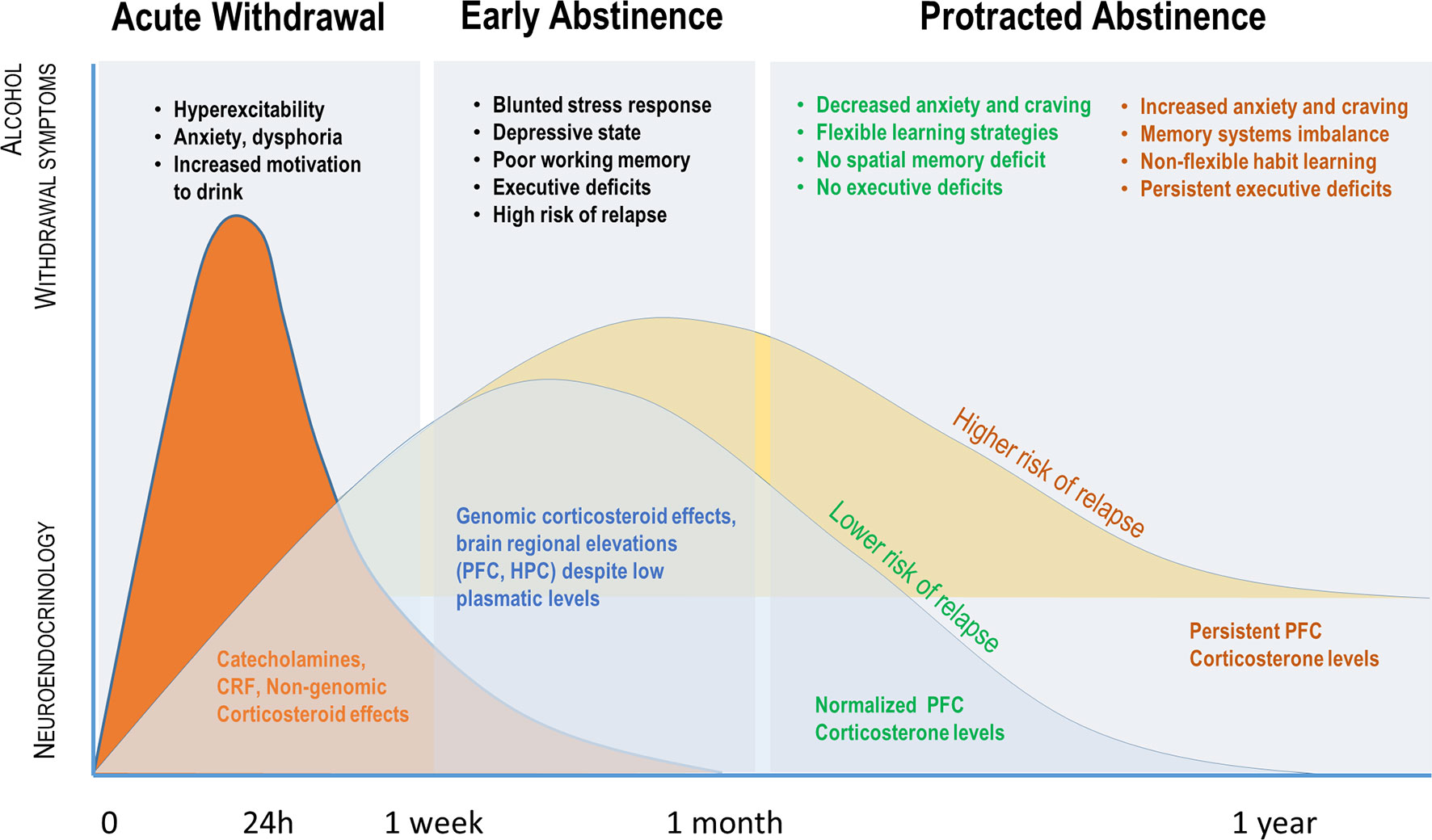
Explore pharmacologic management strategies for alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and outcomes, on this comprehensive resource. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Learn about the effectiveness of using gabapentin for alcohol cessation and how it can help individuals overcome alcohol addiction and withdrawal symptoms. Alcohol use disorder (AUD), a chronic condition that affects many people worldwide, is characterized most commonly by a preoccupation with alcohol, an irresistible craving for or the inability to control the consumption of alcohol, and the marked Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Gabapentin shows promise in treating mild to moderate alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), either alone or alongside traditional therapies. Studies over the last two decades indicate it effectively reduces withdrawal symptoms and improves patient comfort. Alcohol with gabapentin as a substitute has shown to be effective at alleviating or preventing the following symptoms: This lifestyle works by increasing the production of GABA in the brain, essentially aiding brain cells that are too damaged to perform this crucial function. While benzodiazepines are considered the standard of care for alcohol withdrawal, gabapentin is a valuable alternative that can also help with cravings and abstinence long term. Read on to find out more. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from Gabapentin can reduce your desire to drink and can help you stop drinking. Gabapentin may also help improve symptoms of anxiety and dificulty sleeping that may occur when stopping alcohol use. There are no targeted therapies to halt the progression of alcohol related liver disease other than abstinence from alcohol, thus supporting patients in achieving alcohol cessation is the first-line therapy for ALD. Figure 4: Alcohol-related deaths during the COVID 19 pandemic. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: A clinical trial showed that people with We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Abstract Alcoholic patients suffer from harmful allostatic neuroplastic changes in the brain causing an acute withdrawal syndrome upon cessation of drinking followed by a protracted abstinence syndrome and an increased risk of relapse to heavy drinking. Benzodiazepines have long been the treatment of choice for detoxifying patients and managing alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Non Gabapentin’s anxiolytic and sedative properties along with its overall safety profile suggest that it may be a viable adjuvant to lorazepam in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin may reduce these symptoms and help pre-vent early relapse. This clinical trial eval-uated whether the combination of nal-trexone and gabapentin was better than naltrexone alone and/or placebo during the early drinking cessation phase (first 6 weeks), and if so, whether this effect persisted. Gabapentin, a nonbenzodiazepine anticonvulsant GABA analog, has shown some recent promise in the treatment of alcoholism. Preliminary clinical data suggest that gabapentin may be effective in reducing symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal and some symptoms of protracted abstinence (Furieri and Nakamura-Palacios, 2007).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |