Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
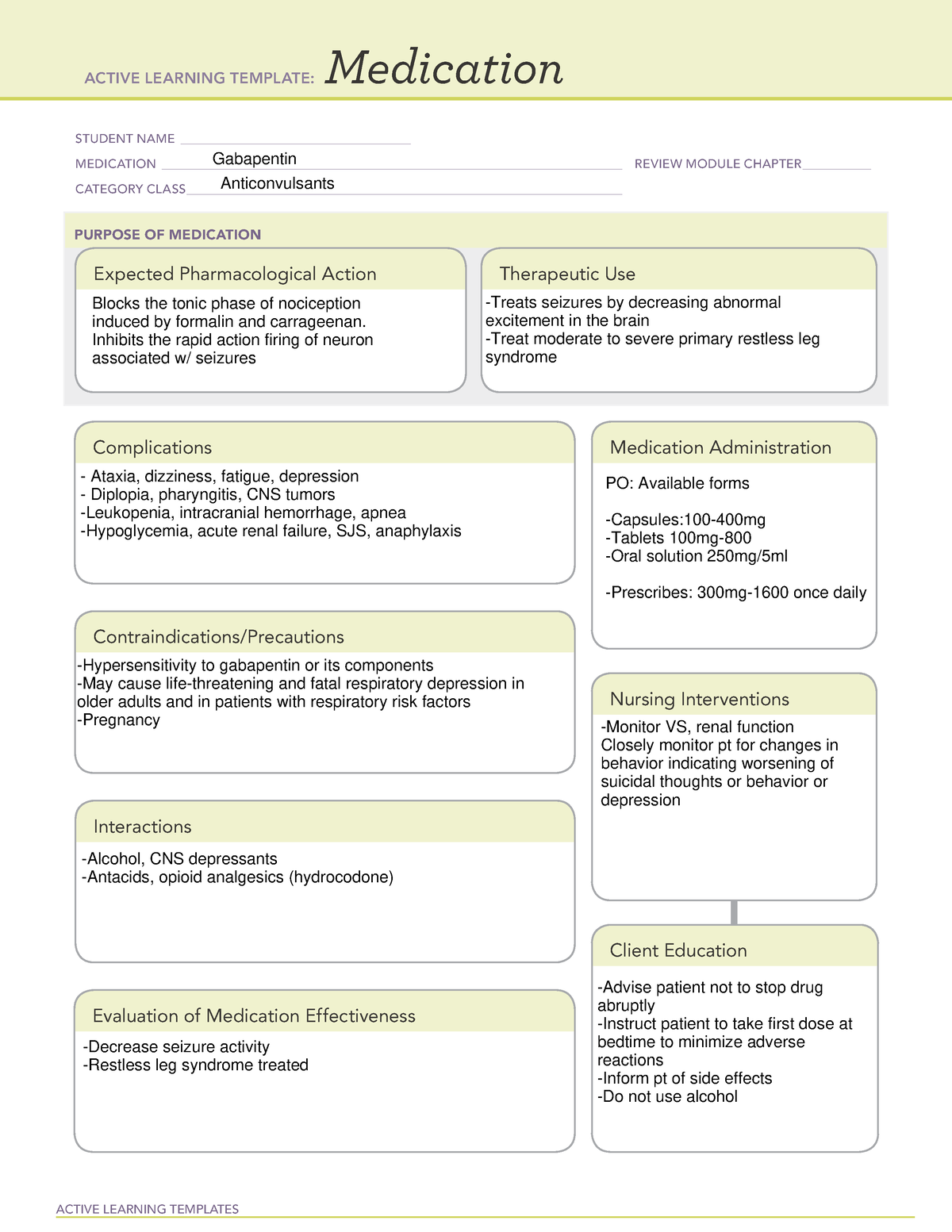
Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Understanding the effects of Gabapentin on mental health is essential, particularly its potential link to depressive episodes. This medication, often used for pain and seizure management, has a range of side effects that can impact a patient's psychological well-being. Potential Link to Depression Gabapentin has been associated with various psychiatric side effects, including depression Intro Gabapentin is a medication that finds its primary application in managing nerve pain. It is commonly prescribed for conditions like neuropathic pain, which can arise from various underlying issues such as diabetes or shingles. However, its role in mental health treatment, particularly regarding depression, deserves careful examination. The relationship between gabapentin and depression GoodRx explains in detail how Gabapentin is used to treat anxiety including dosage, side effects, and more. Today, gabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for various mental health conditions, joining the ranks of other mood-stabilizing medications like lamotrigine, which has shown promise in treating bipolar disorder and depression. In conclusion Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that is prescribed for treating seizures and nerve pain associated with shingles. However, it also is known for producing anti-anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects, which is why gabapentin is often prescribed for treating anxiety. Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent psychiatric disorders and a leading cause of disability. While there continues to be expansive research in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression and schizophrenia, there is a relative dearth of Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Conclusion Gabapentin is a medication that can provide relief for various medical conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless leg syndrome. While concerns have been raised about the potential link between gabapentin use and depression, research on this topic is still ongoing. Gabapentin drug interactions: Along with side effects, gabapentin has possible interactions to know about. Gabapentin FAQs: Experts answer common questions about taking gabapentin, from if you should take it with food to what to do if you miss your dose. Is gabapentin an opioid? Learn the differences and similarities between gabapentin and an opioid medication. Understanding Gabapentin's Connection to Mood Changes Gabapentin, a medication primarily formulated to treat seizures and manage nerve pain, is often used off-label for various mental health conditions. Despite its benefits, there is ongoing concern about its potential impact on mood and mental health, particularly its association with depression. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Why So Popular? Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 as an adjunctive treatment for partial Intro Gabapentin is a medication that finds its primary application in managing nerve pain. It is commonly prescribed for conditions like neuropathic pain, which can arise from various underlying issues such as diabetes or shingles. However, its role in mental health treatment, particularly regarding depression, deserves careful examination. The relationship between gabapentin and depression Easy-to-read patient tips for gabapentin covering how it works, benefits, risks, and best practices. Key takeaways Gabapentin is not commonly used to treat depression, but some recent studies indicate it may treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and alcohol use disorder. A normal dose of gabapentin for adults can be anywhere from 100 mg to 3600 mg each day. Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, weakness, and upset stomach. Outpatient prescription of gabapentin for FDA-approved indications (i.e., partial-onset seizures and postherpetic neuralgia) was less than 1%, and depression and anxiety disorders were the most frequent psychiatric diagnoses among off-label users. Introduction Gabapentin, a widely prescribed medication, is primarily used to manage seizures and neuropathic pain. However, it also comes with a range of side effects, including potential implications for mental health. One of the most pressing concerns among users and healthcare providers alike is whether gabapentin can cause or exacerbate depression. This article delves into the evidence This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Gabapentin, a widely prescribed medication, is primarily used to manage seizures and neuropathic pain. However, it also comes with a range of side effects, including potential implications for mental health. One of the most pressing concerns among users and healthcare providers alike is whether gabapentin can cause or exacerbate depression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |