Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
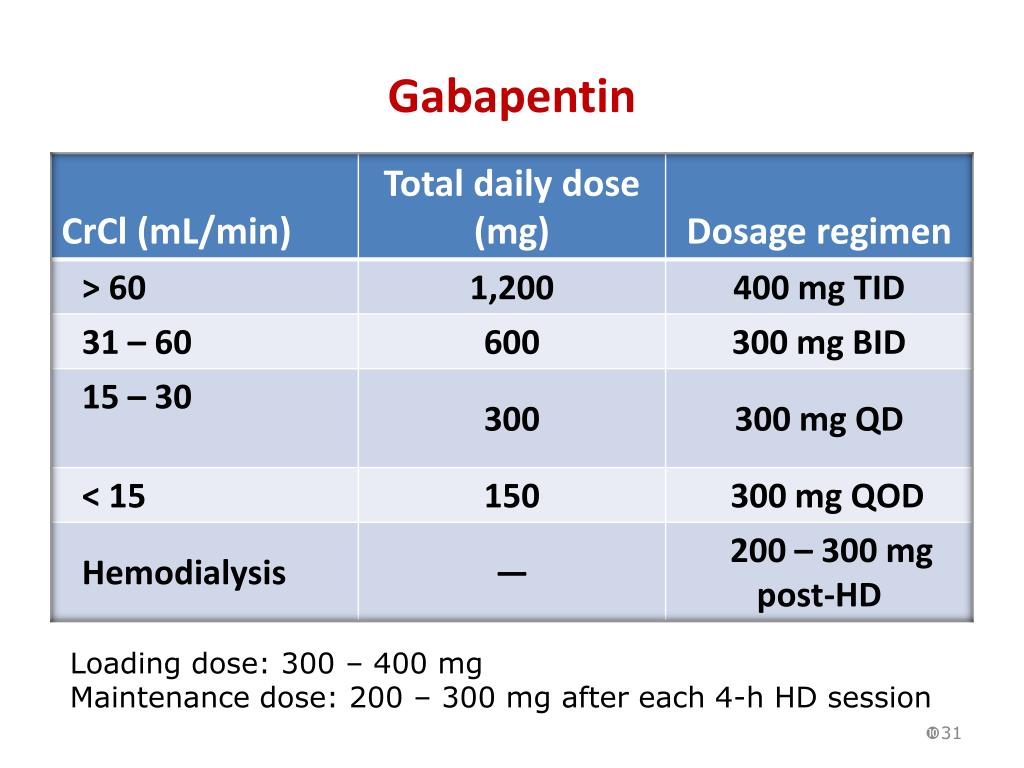
Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with analgesic effects. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1994 as an adjunctive agent for partial seizures and subsequently in 2002 as an analgesic for postherpetic neuralgia. In recent years, gabapentin has been increasingly used off-label for expanded indications, including migraine headache,1 phan-tom limb pain,2 cancer-related pain,3 Pharmacology Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors in Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has garnered attention for its efficacy and safety profile. However, concerns about its potential impact on kidney health have emerged, especially among patients with pre-existing kidney conditions. Understanding the relationship between gabapentin and kidney function is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease Mena Raouf,1 Timothy J Atkinson,1 Meredith W Crumb,1 Jeffrey Fudin2–5 1VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, Murfreesboro, Nashville, TN, 2Stratton VA Medical Center, 3Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Albany, NY, 4Western New England University College of Pharmacy, Springfield, MA, 5Scientific and Clinical Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has no harmful effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. In people with renal impairment, gabapentin can be harder to clear from the body. Gabapentin can be removed from plasma by hemodialysis. Gabapentin affects kidney function as it is primarily eliminated by the kidneys and its clearance is directly proportional to creatinine clearance. This means that patients with impaired renal function may have reduced gabapentin clearance, leading to increased drug levels and potential When kidney function declines, the clearance of Gabapentin can be affected, leading to increased levels in the bloodstream. For patients with normal kidney function, Gabapentin's half-life—approximately 5 to 7 hours—allows for effective dosing without significant accumulation. Gabapentin toxicity and side effects are well-known among nephrologists and fully described in the literature as myoclonic twitches, myopathy, neurotoxicity, etc., particularly in dialysis patients. 2,4 Rhabdomyolysis with associated acute renal failure is an uncommon side effect, but it has been described in earlier cases. 1,3 Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. While gabapentin itself doesn't directly damage the kidneys, it can cause side effects like dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema that may be more pronounced in those with kidney disease. Regular monitoring of kidney function is advisable when using gabapentin in patients with renal impairment or other risk factors for kidney disease. Introduction Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication, commonly used to manage neuropathic pain, and it also finds widespread off-label use in treating various pain and sleep disorders. Notably, gabapentin is exclusively excreted through the kidneys, making its dose reduction essential when given to patients with impaired renal function.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |