Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | /woman-s-feet-in-pink-socks-sticking-out-from-under-a-blanket-570140745-59fb54798a84c5001998b804.jpg) |
 | |
 |  |
/GettyImages-596435371-571cce6e5f9b58857db64e3a.jpg) |  |
 |  |
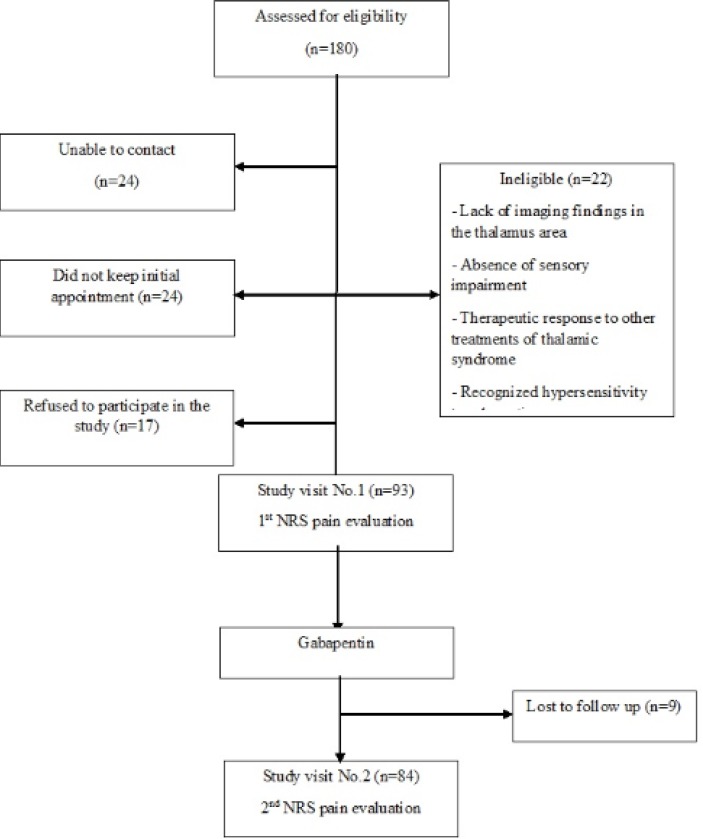
The primary treatment focus after an ischemic stroke, a stroke caused when a clot blocks blood flow and neurons die in the affected brain region, is re-establishing blood flow in the brain as quickly as possible. For some patients, this is accomplished through a combination of drug therapy and surgery which is then followed by weeks and often months of rehabilitation therapy to regain movement The study found that administering gabapentin, an anticonvulsive medication, soon after a stroke helps the brain more effectively work around damaged areas. Thalamic pain syndrome, a type of central post-stroke pain (CPSP), may develops after a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke and results in impairment of the thalamus. There is limited experience about gabapentin in treatment of central pains like CPSP. In a prospective observational study, the intensity The outcomes of patients taking either gabapentin or pregabalin with stroke diagnoses are compared to patients with stroke diagnoses who were not taking either medication. Kruskal-Wallace and X2 were used for statistical analysis. This blog post will delve into the potential impact of Gabapentin in recovery, providing hope and insight for stroke survivors and their families. The Role of Gabapentin in Stroke Recovery Gabapentin, traditionally used to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, has shown promise in enhancing stroke recovery 12. Gabapentin is a medication sometimes used post-stroke. Learn about its uses, side effects, and precautions to take for a safe recovery. Thalamic pain syndrome, a type of central post-stroke pain (CPSP), may develops after a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke and results in impairment of the thalamus. There is limited experience about gabapentin in treatment of central pains like CPSP. Gabapentin is often prescribed to stroke patients to alleviate post-stroke pain and improve recovery. Learn about its benefits, dosage guidelines, and potential side effects. A study evaluating data from Statistics Sweden showed that gabapentin and pregabalin were the most commonly used antiepileptic drugs among patients who underwent stroke after stratification by the diagnosis of neuropathic pain (Karlsson Lind and von Euler, 2021). Gabapentin, a medication commonly prescribed to control seizure activity, may enhance stroke recovery and restore fine motor function, a new study reports. Finally, chemogenetic silencing of cortical projections originating from the contralateral side of the brain transiently abrogated recovery in mice administered gabapentin, further supporting the conclusion that gabapentin-dependent reorganization of spared cortical pathways drives functional recovery after stroke. Gabapentin increased neuroplasticity and corticospinal tract axonal sprouting, and improved fine motor function, in a rat model of stroke, according to a study published May 23 in the journal Brain. The findings point toward a potential clinical role in stroke rehabilitation for this widely used drug and expand the number of strategies for harnessing the nervous system's own regenerative Gabapentinoid drugs (pregabalin and gabapentin) have been successfully used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and in focal seizure prevention. Recent research has demonstrated their potent activities in modulating neurotransmitter release in neuronal tissue, oxidative stress, and inflammation, wh CPSP is a central neuropathic pain condition occurring after a stroke, characterised by pain and sensory abnormalities. Gabapentin has been found to reduce the intensity of pain in patients with CPSP, with one study finding a significant difference in pain intensity between pre-treatment and post-treatment. The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells, new research in mice suggests.The experiments mimicked ischemic stroke in humans, which occurs when a clot blocks bloo Background Cerebrovascular disorders have occurred more frequently in some Central Nervous System (CNS) disorders, such as epilepsy. Some CNS drugs have been associated with increased stroke risk. Our aim was to estimate the risk of ischaemic stroke in patients exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AED). Methods Population-based matched case-control study using SIDIAP database, based in electronic A study evaluating data from Statistics Sweden showed that gabapentin and pregabalin were the most commonly used antiepileptic drugs among patients who underwent stroke after stratification by the diagnosis of neuropathic pain (Karlsson Lind and von Euler, 2021). Objective: This small clinical trial describes the efficacy of gabapentin therapy in patients with neuropathic pain syndromes after stroke. Background The problem of rehabilitation in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke remains one of the Learn about safe pain medication options for stroke patients. Understand the benefits and risks of different medications and how to manage pain effectively post-stroke. Gabapentin's role in stroke recovery Gabapentin is a drug that has been approved for the treatment of seizures and nerve pain. It has been found to be effective in reducing pain and improving recovery after a stroke. Efficacy in pain reduction Central post-stroke pain (CPSP) is a type of neuropathic pain that occurs after a stroke, affecting 8-14% of patients. It is challenging to manage and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | /woman-s-feet-in-pink-socks-sticking-out-from-under-a-blanket-570140745-59fb54798a84c5001998b804.jpg) |
 | |
 |  |
/GettyImages-596435371-571cce6e5f9b58857db64e3a.jpg) |  |
 |  |