Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
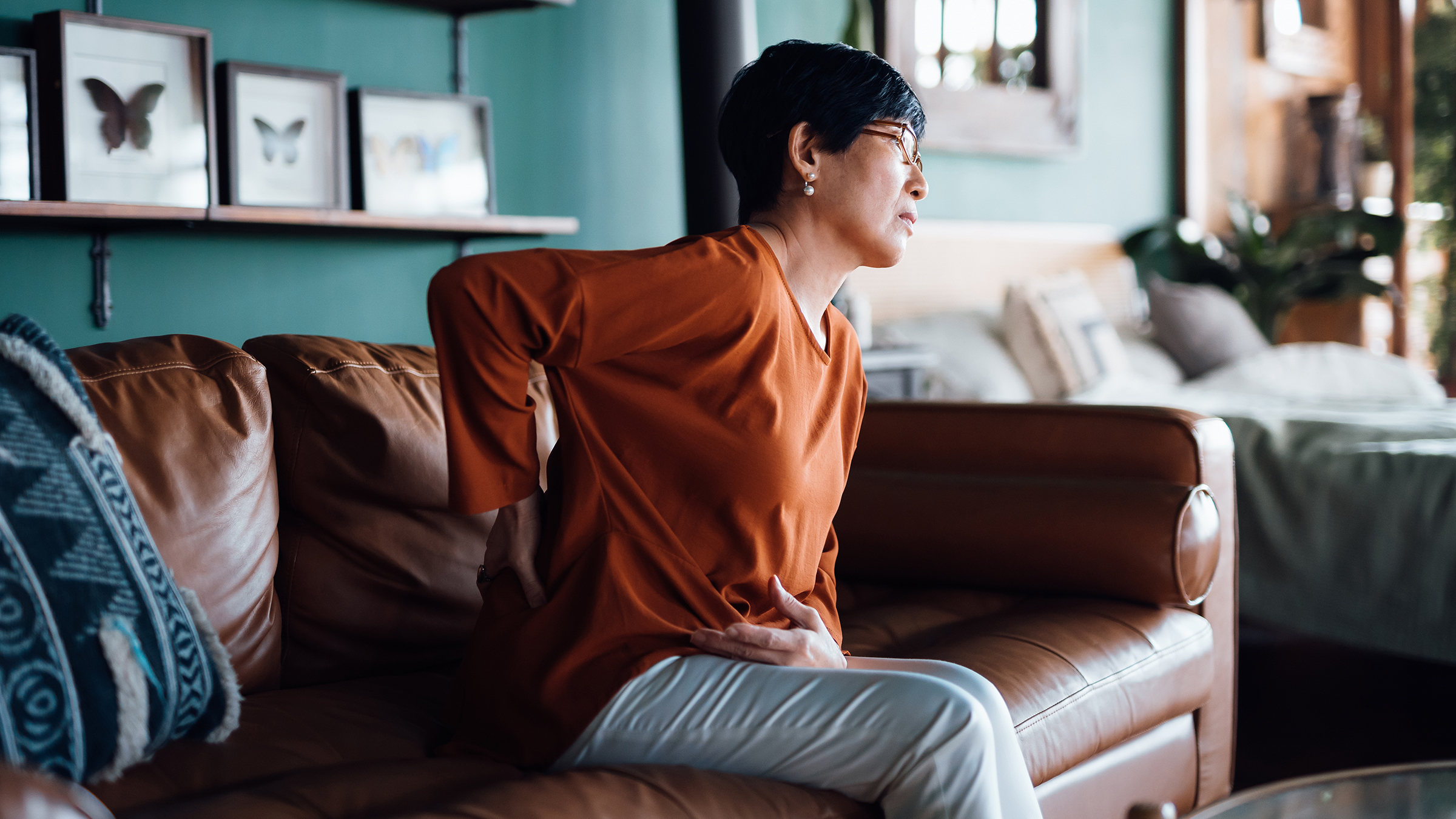
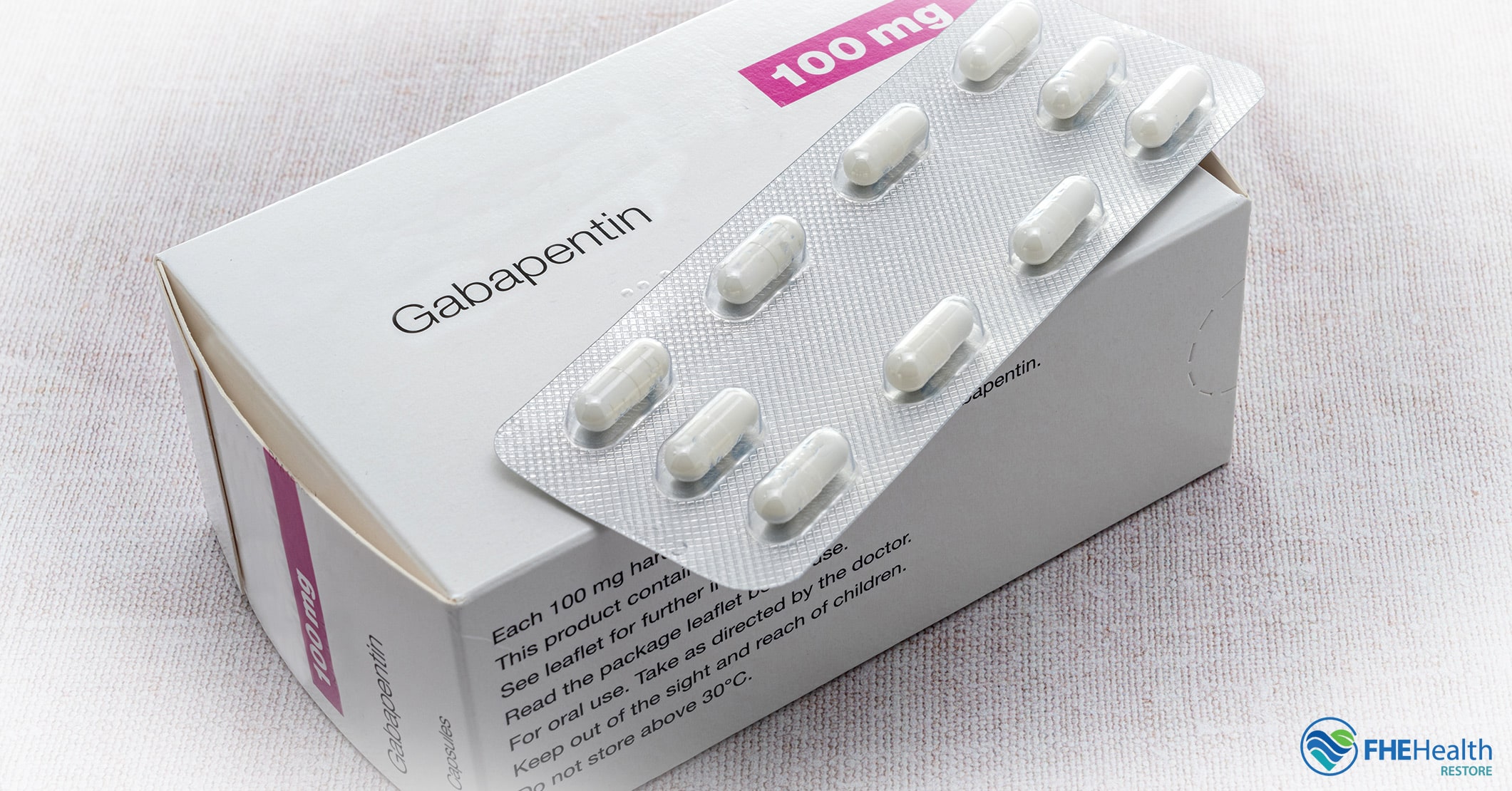
Key takeaways Gabapentin is not commonly used to treat depression, but some recent studies indicate it may treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and alcohol use disorder. A normal dose of gabapentin for adults can be anywhere from 100 mg to 3600 mg each day. Common side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, weakness, and upset stomach. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin was explicitly developed to treat seizures but now has become a valuable option in mental health care. Its ability to provide relief without many of the side effects associated with other medications makes it appealing for various mental health needs. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant primarily used to treat epileptic seizures, but it can also be prescribed off-label to treat a range of mental disorders. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Exploring Gabapentin's Impact on Mental HealthIntroduction: Unveiling the Link Between Gabapentin and Mood Changes Gabapentin is a well-known medication primarily used as an anticonvulsant for treating seizures and relieving nerve pain. It is frequently prescribed off-label for various conditions, including some mood and anxiety disorders. However, concerns about its effects on mental health Although evidence is limited, some studies show gabapentin can help with anxiety symptoms. One 2020 review suggests gabapentin may help with different types of situational anxiety, This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of There are a wide variety of medications for depression available today, and learning more about gabapentin may help you decide if it is the right fit for you. Gabapentin, a medication primarily formulated to treat seizures and manage nerve pain, is often used off-label for various mental health conditions. Despite its benefits, there is ongoing concern about its potential impact on mood and mental health, particularly its association with depression. Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. Understanding the effects of Gabapentin on mental health is essential, particularly its potential link to depressive episodes. This medication, often used for pain and seizure management, has a range of side effects that can impact a patient's psychological well-being. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment. Explore gabapentin's potential psychological side effects, factors influencing mental health impacts, and strategies for managing risks in this comprehensive guide. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Sources GoodRx Health | Gabapentin for Anxiety: Dosing, Side Effects, and More IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology |Gabapentin Innovations in Clinical Neuroscience | Psychiatric Uses of Gabapentin StatPearls | Propranolol Mental Health America | What is GABA? The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry | The Role of GABA in Anxiety Disorders Explore gabapentin's impact on cognitive and emotional well-being, including common side effects, long-term risks, and management strategies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |