Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 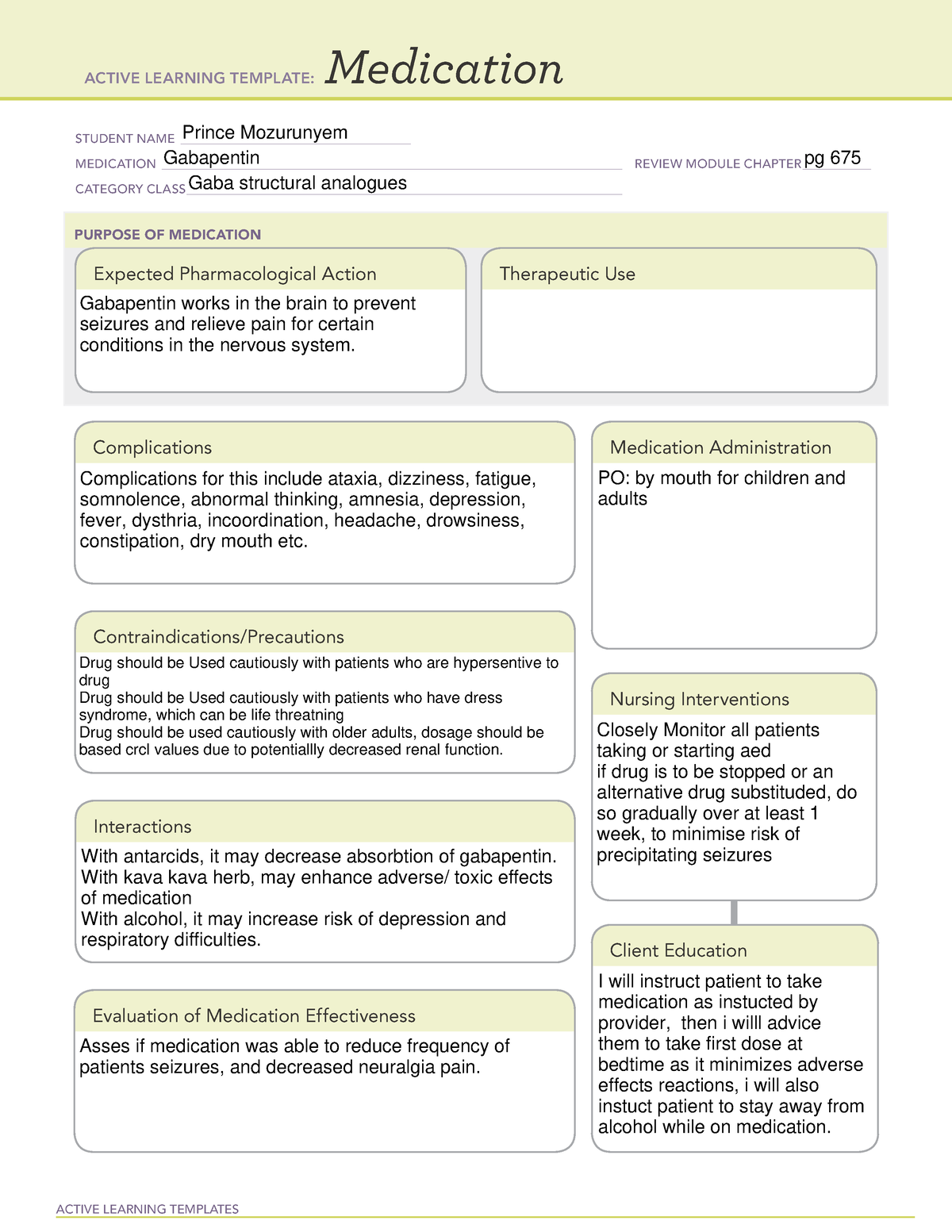 |
Question: How would gabapentin, a nonpolar pain medication, cross the plasma membrane of a cell?It would use facilitated diffusion.It would use simple diffusion.It could not cross the plasma membrane.It would use osmosis. Gabapentin (GBP) is a non-metabolized antiepileptic drug that is eliminated by renal excretion and displays saturable, dose dependent absorption. The · Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to gabapentin. · Use cautiously with lactation, pregnancy. Parosmia is a distortion of the normal sense of smell, where an odor that is usually pleasant may now smell bad. Parosmia typically occurs due to damage to the neuroepithelium and olfactory bulbs. This often transpires after viral infections but may also be a result of brain tumors, head trauma, or neurodegenerative disorders. Treatment of parosmia may include vitamins, minerals, olfactory Pharmacokinetic properties are important to consider in evaluating the usefulness of new antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Gabapentin is a new, water-soluble, antiepileptic agent with properties of an amino acid. This drug is rapidly absorbed and exhibits dose-dependent bioavailability as a result of a sa Purpose of Review In this review, we discuss the mechanism of action of gabapentinoids and the potential consequences of long-term treatment with these drugs on the musculoskeletal system. Recent Findings Gabapentinoids, such as gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) were designed as antiepileptic reagents and are now commonly used as first-line treatment for neuropathic pain and increasingly Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more The best learning experience possible. Osmosis empowers students with our comprehensive video library combined with powerful study tools. Antiepileptics, also known as anticonvulsants, are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy, as well as generalized or partial seizures. On rare occasions, these medications can be used to treat mood disorders. Now, the most commonly used antiepileptics can be subdivided, based on their mechanism of action, into four main groups: sodium channel blockers, calcium channel blockers, GABA These medications include antidepressants like amitriptyline, anticonvulsants like gabapentin, and corticosteroids like dexamethasone, as well as local anesthetics like lidocaine. Now, let’s start with non-opioid analgesics, which include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs, and acetaminophen. The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles can have implications for clinical practice. This article has summarised these key differences. In addition to their use in managing ne Ulnar nerve entrapment is a compressive neuropathy that occurs when the ulnar nerve is trapped or compressed, and can lead to progressive Learn with Osmosis Miller Fisher syndrome can be treated primarily with supportive care, like pain control and physical rehabilitation. For pain control, studies recommend using a combination of pain medications that have different mechanisms of action, such as amitriptyline, gabapentin, and opioids. Physical rehabilitation may include physical and occupational therapy to improve balance and coordination and Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are used along with other medications to help control certain types of seizures in people who have epilepsy. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are also used to relieve the pain of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN; the burning, stabbing pain or aches that may last for months or years after an attack of shingles). Gabapentin extended The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. After oral administration and absorption, gabapentin circulates essentially unbound to serum proteins. In addition, gabapentin does not undergo hepatic metabolism, unlike most other antiepileptic drugs, and is eliminated almost entirely by renal excretion with a clearance that approximates the glomerular filtration rate. Summary Nonbenzodiazepine anticonvulsants are a class of drugs used to treat seizures, headaches, and neuropathic pain. These drugs are also used as mood stabilizers for bipolar disorders. Nonbenzodiazepine anticonvulsants decrease excitatory signals in the brain, primarily by blocking sodium and calcium channels, or by enhancing the actions of GABA. This lead to a decrease in the abnormal
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |