Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
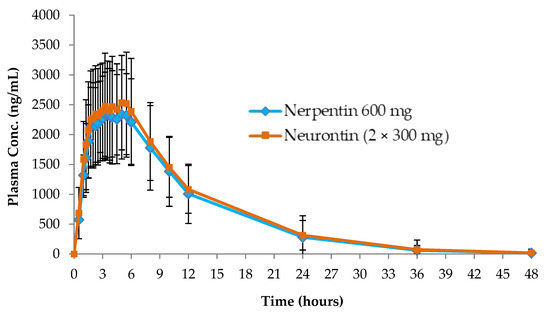 | 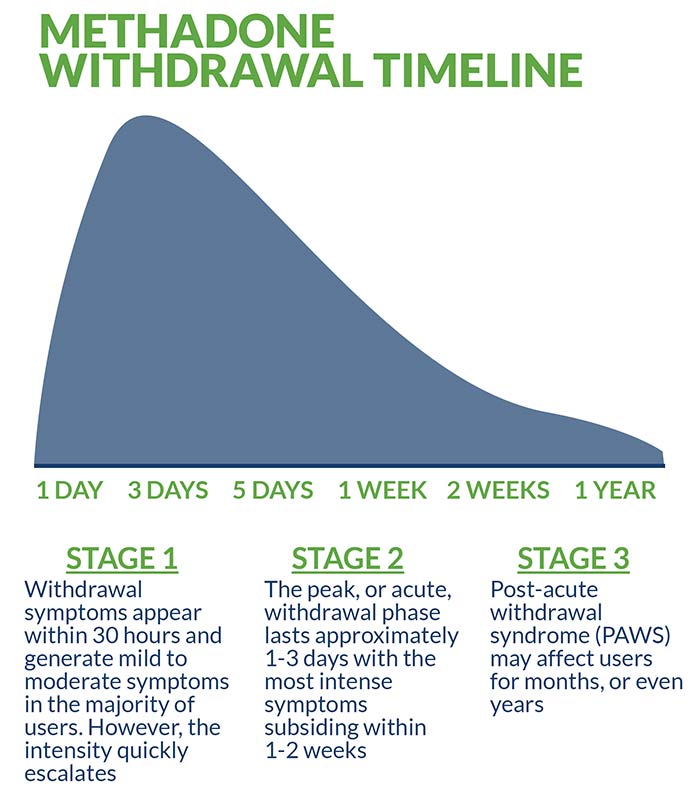 |
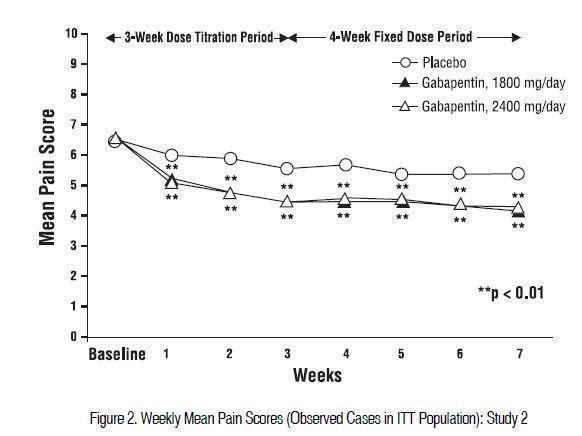
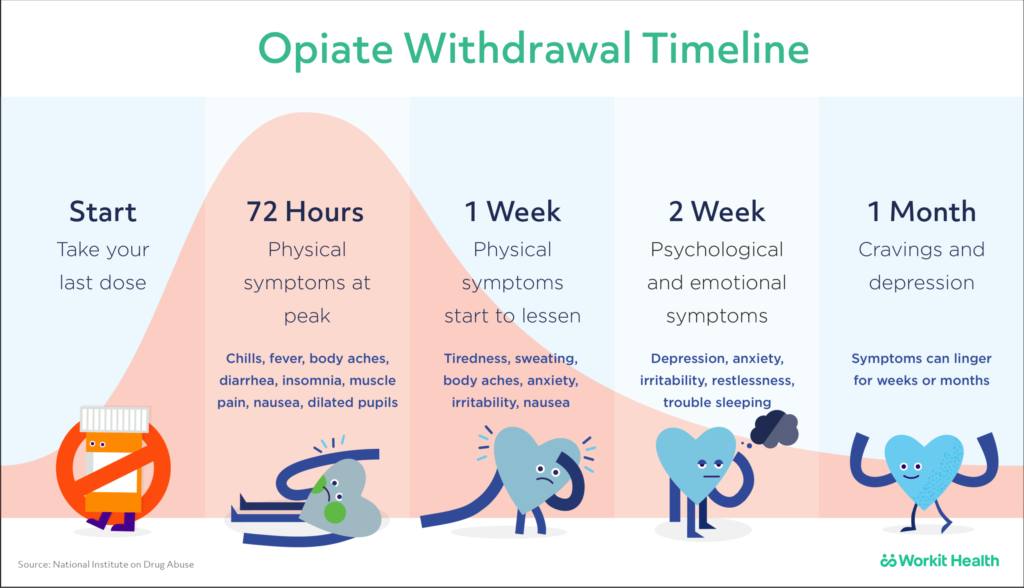
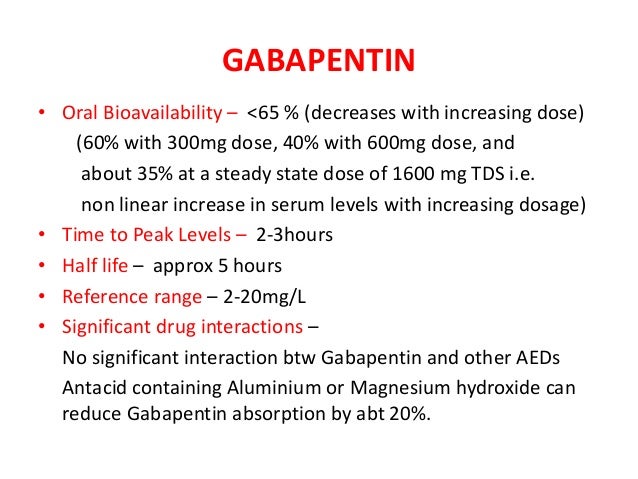
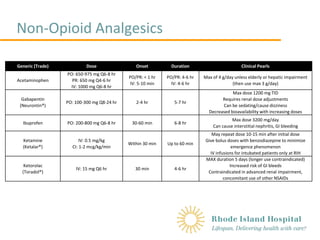
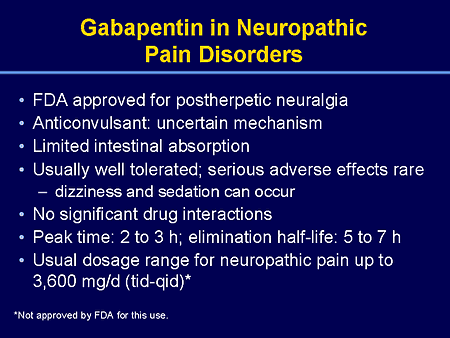
Gabapentin is likely detectable in your system for the following time frames: Urine: 1 to 2 days after last use Saliva: Up to 36 hours after last use Plasma: Gabapentin is largely excreted via the renal system and does not largely bind to plasma proteins; since the elimination half-life is about 7 hours, that means it could take up to 35 hours for the body to completely clear this drug The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2,400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3,600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. Administer gabapentin three times a Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Gabapentin Tablets, USP - (gab-ah-PEN-tin) Read the Medication Guide before you start taking gabapentin tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. The peak plasma concentration for gabapentin is 2 to 4 hours. The time to peak plasma concentration for gabapentin enacarbil is 5 hours for subjects in a fasting state and 7.3 hours for under-fed conditions. Objective: Gabapentin immediate release (GBP-IR), gabapentin gastric retentive (GBP-GR), and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil extended release formulation (GEn) have been approved for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in adults. This is the first pharmacokinetic (PK) comparison of all three formulations using FDA-recommended doses for PHN. Gabapentin gastroretentive tablets: In healthy individuals, time to peak plasma concentrations is prolonged (about 4–6 hours longer), peak plasma concentrations are higher, and systemic exposure is lower relative to immediate-release formulations. Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a prodrug of gabapentin that has been designed to overcome the limitations of gabapentin, such as poor absorption and a short duration of action. Point of Care - Clinical decision support for Gabapentin. Treatment and management. Indications, Mechanism of Action, Administration, Adverse Effects, Contraindications, Monitoring, Toxicity, Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Pharmacodynamics Mechanisms of action Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated Gabapentin's duration in the body depends on several factors, including dosage, individual metabolism, and liver and kidney function. Generally, peak blood levels occur within 2-3 hours after oral administration, with a half-life of about 5-7 hours. This means that about half of the drug is eliminated from the body every 5-7 hours. Quick onset of action times found within this table may account for the drug’s absorption in the oral liquid form. Onset of action can also differ due to the Absorption and distribution Pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed as compared to gabapentin. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. The duration over which you’ve been taking gabapentin may affect how long it stays in your system before elimination. Duration of administration is thought to influence: dosing, physiology, and accumulation of the drug in a person’s system. Hemodialysis: In a study in anuric subjects (n=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about 132 hours; dialysis 3 times a week (4 hours duration) lowered the apparent half-life of gabapentin by about 60%, from 132 hours to 51 hours. Another reason gabapentin takes time to work is that the dose is usually started low and gradually increased over time to reach an effective dose. For example, when used to relieve nerve pain, the initial dose may be started at 300 mg and increased by 300 mg daily over several days, gradually reaching up to 600 mg three times per day. Learn how long gabapentin stays in your system, its half-life, detection times, and factors influencing its elimination. Neurontin (gabapentin) has a short half life of 5 to 7 hours and a short duration of action of 6 to 8 hours.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |