Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
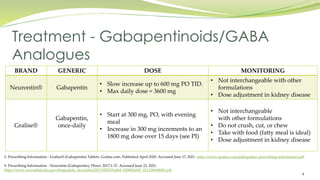
Abstract Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related adverse events (GRAEs). The recommended maximal daily dose of gabapentin is 1,500 mg in people with grade 3 chronic kidney disease (CKD), 700 mg in those with grade 4 CKD, 300 mg in those with grade 5 CKD, and 100 to 300 Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. In hemodialysis (HD) patients, the prevalence of chronic pain can be up to 92%. 1 A survey of HD patients found 55% reported a severe pain episode in the previous 24 hours. 2 Furthermore, ~75% of HD patients report inadequate pain management. 2 Despite these shocking statistics there is no universally accepted guideline for the treatment of pain in HD patients. Nevertheless, poorly managed In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range of doses The exact renal dosing for gabapentin is not specified in the provided studies, but it is recommended to use gabapentin judiciously in patients with decreased kidney function and to consider dosage adjustments based on the patient's creatinine clearance (CrCl) 4, 5. Gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in patients with CKD primarily to treat neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome and given the high prevalence of diabetes in this population, the proportion who receive these drugs is very high. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the The recommended maximal daily dose of gabapentin is 1,500 mg in people with grade 3 chronic kidney disease (CKD), 700 mg in those with grade 4 CKD, 300 mg in those with grade 5 CKD, and 100 to 300 Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance.24In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (with-out dialysis),30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. It is essential that a patient's renal function is taken into account when prescribing and reviewing medication. Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Renal function estimations and dose recommendations for dabigatran, gabapentin and valaciclovir: a data simulation study focused on the elderly Physicians should be familiar with commonly used medications that require dosage adjustments. Resources are available to assist in dosing decisions for patients with chronic kidney disease. Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance.24In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (with-out dialysis),30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis Gabapentin is a medication used to manage nerve pain (e.g., postherpetic neuralgia), restless leg syndrome, and seizures. Available as gabapentin capsules or extended-release tablets, it calms overactive nerves. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Find medical information for gabapentin on epocrates online, including its dosing, contraindications, drug interactions, and pill pictures. The starting dose (600 mg) is the therapeutic dose 1 No titration is required. Patients should take once daily at about 5 PM 1 Horizant ® 600 mg contains ~313 mg of gabapentin No tapering is required during discontinuation Tablets should be swallowed whole and should not be cut, crushed, or chewed. Tablets should be taken with food Patients with renal impairment: Doses of Horizant ® must be
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |